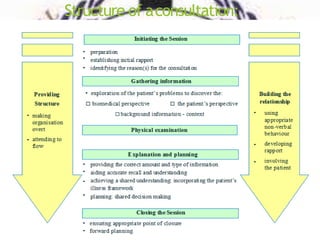
Medical deontology outlines ethical standards for doctors in their treatment of patients. Effective doctor-patient communication is essential, with principles including mutual respect, shared goals, transparency, and continuous learning. Summaries should be concise and highlight the most important points.