Embed presentation
Downloaded 256 times













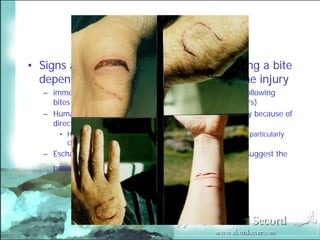





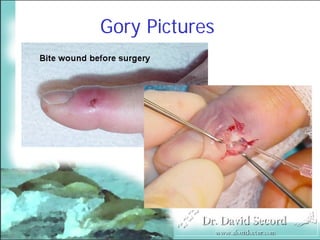
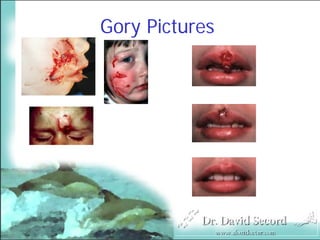










Management of Human and Animal Bite Wounds provides an overview of bite wound infections. Over 1 million animal bites occur annually in the US, with dog bites accounting for 80-90% and resulting in over a dozen deaths each year. Bite wounds can become infected by bacteria from the biting animal's mouth and skin flora. Common complications are lymphangitis, septic arthritis, and osteomyelitis. Proper management includes thorough wound cleansing, debridement if needed, antibiotics, and tetanus prophylaxis. Cultures may be taken to guide antibiotic selection.






























