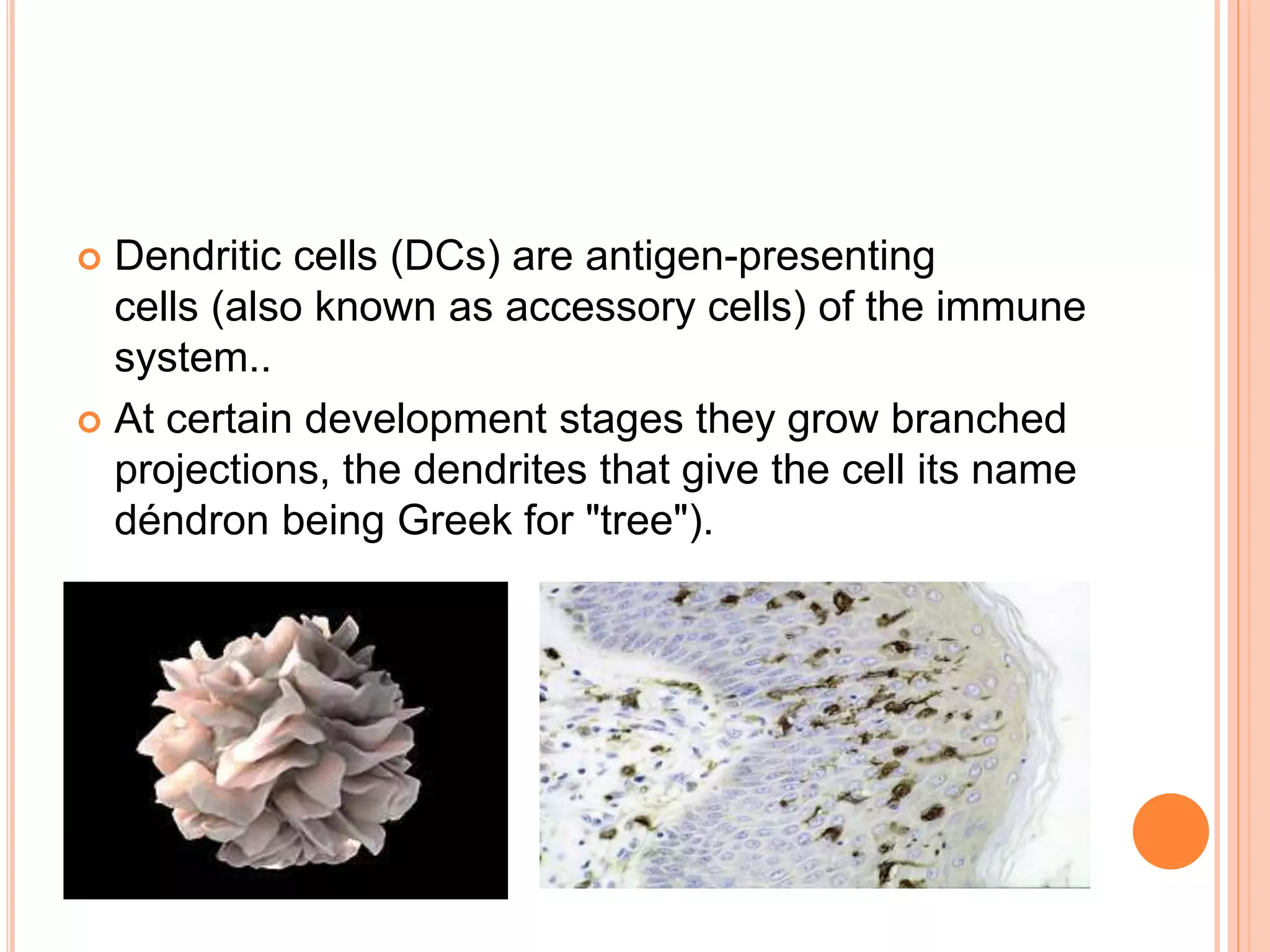
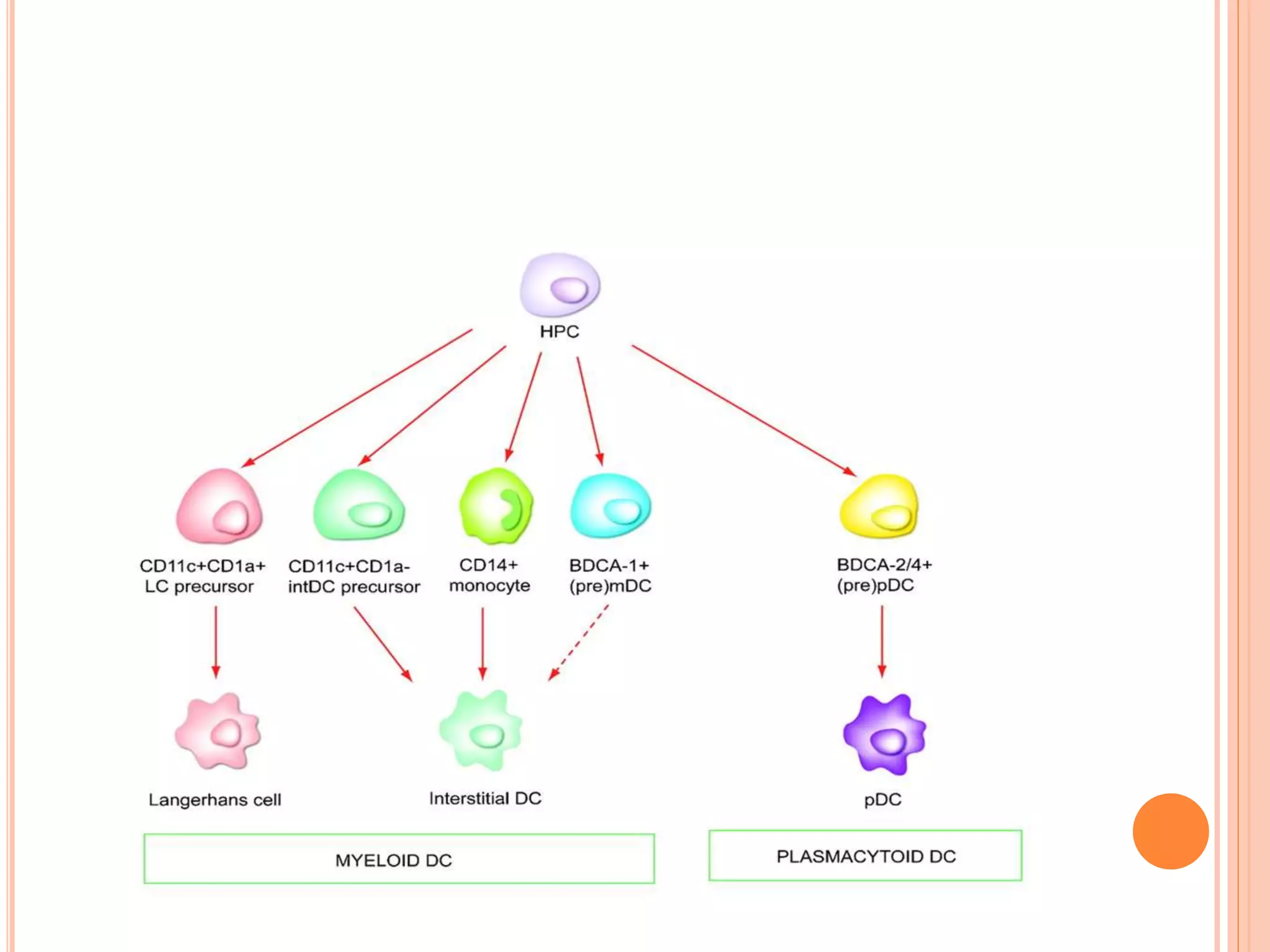
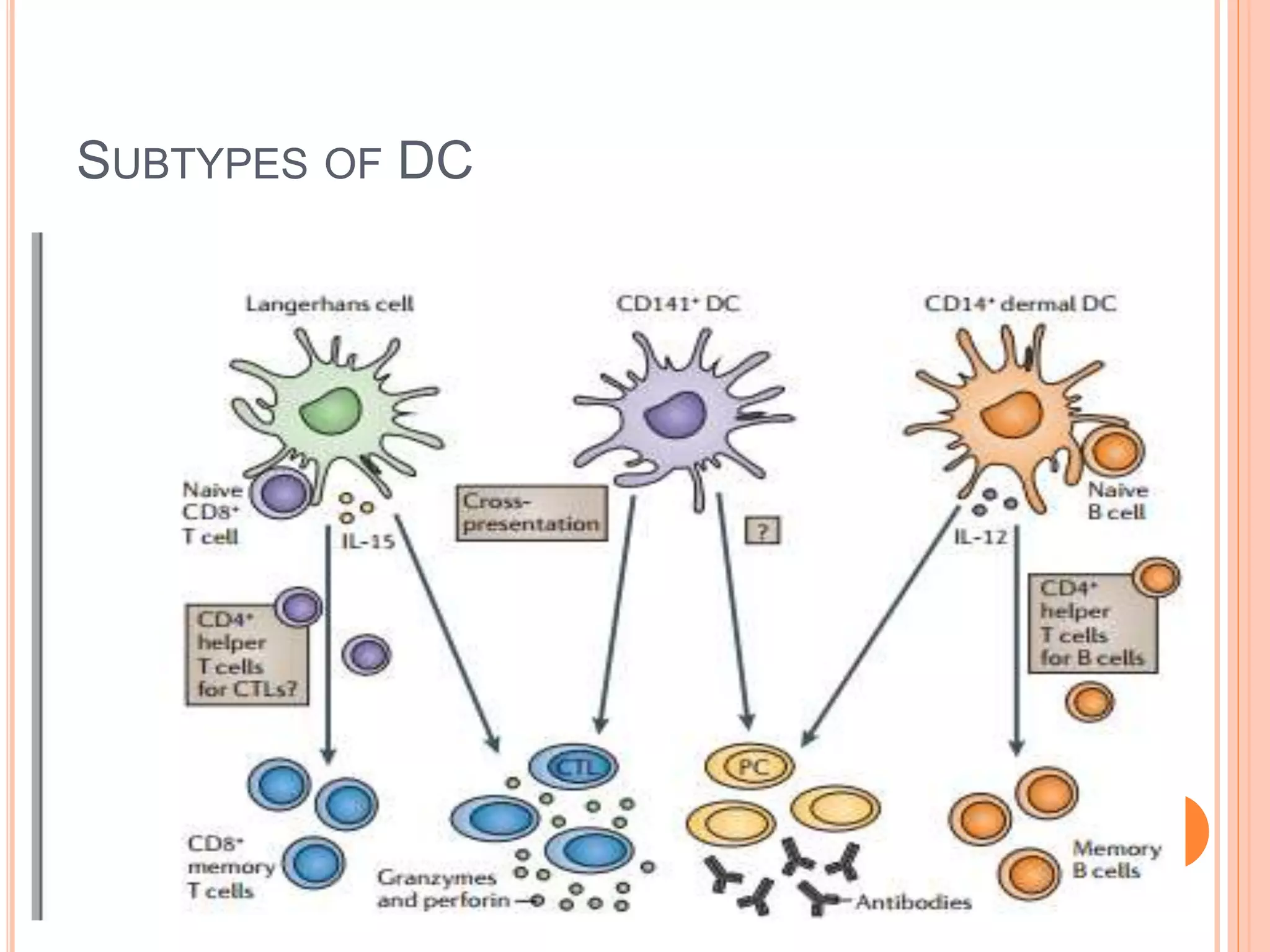
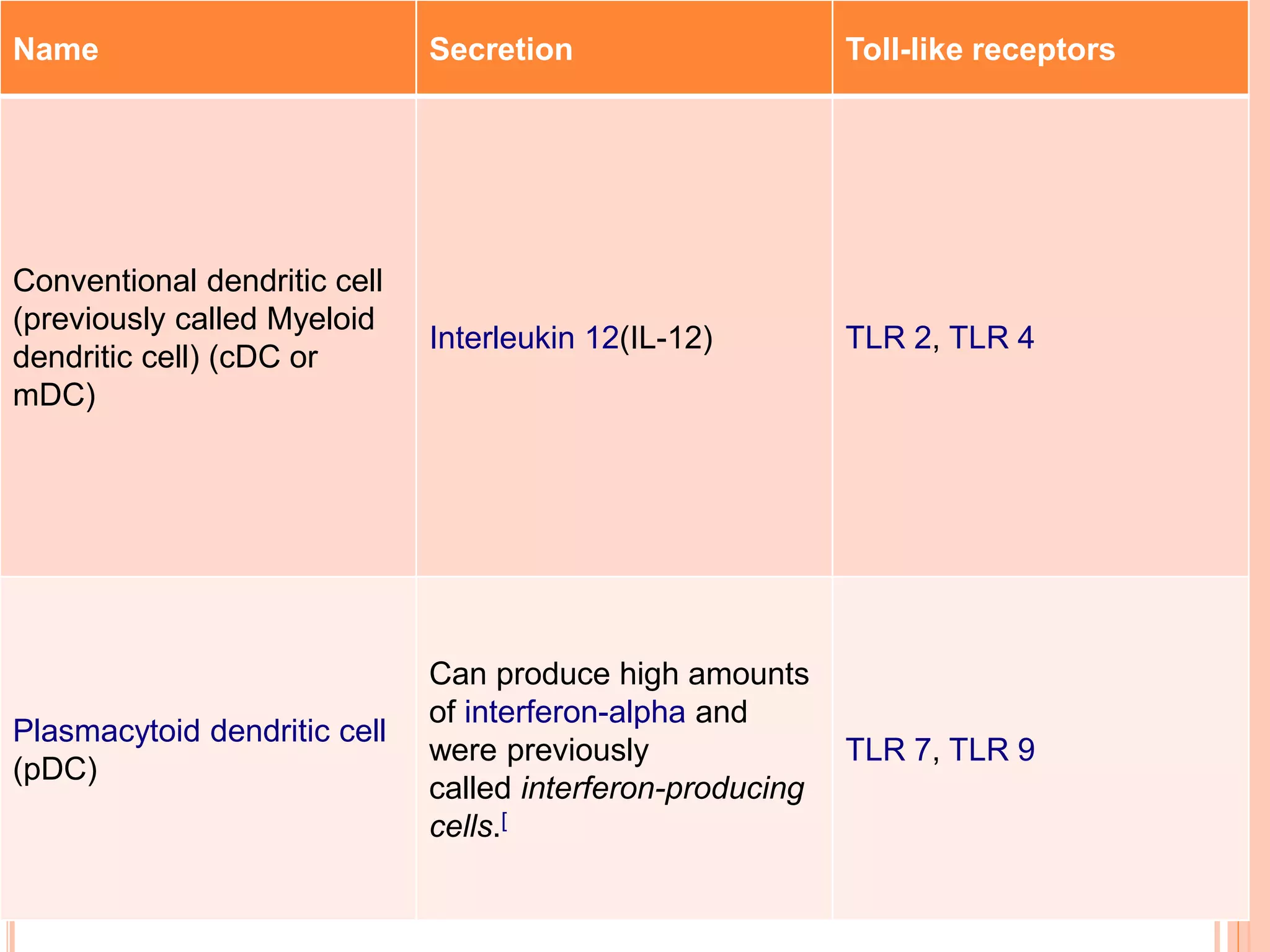
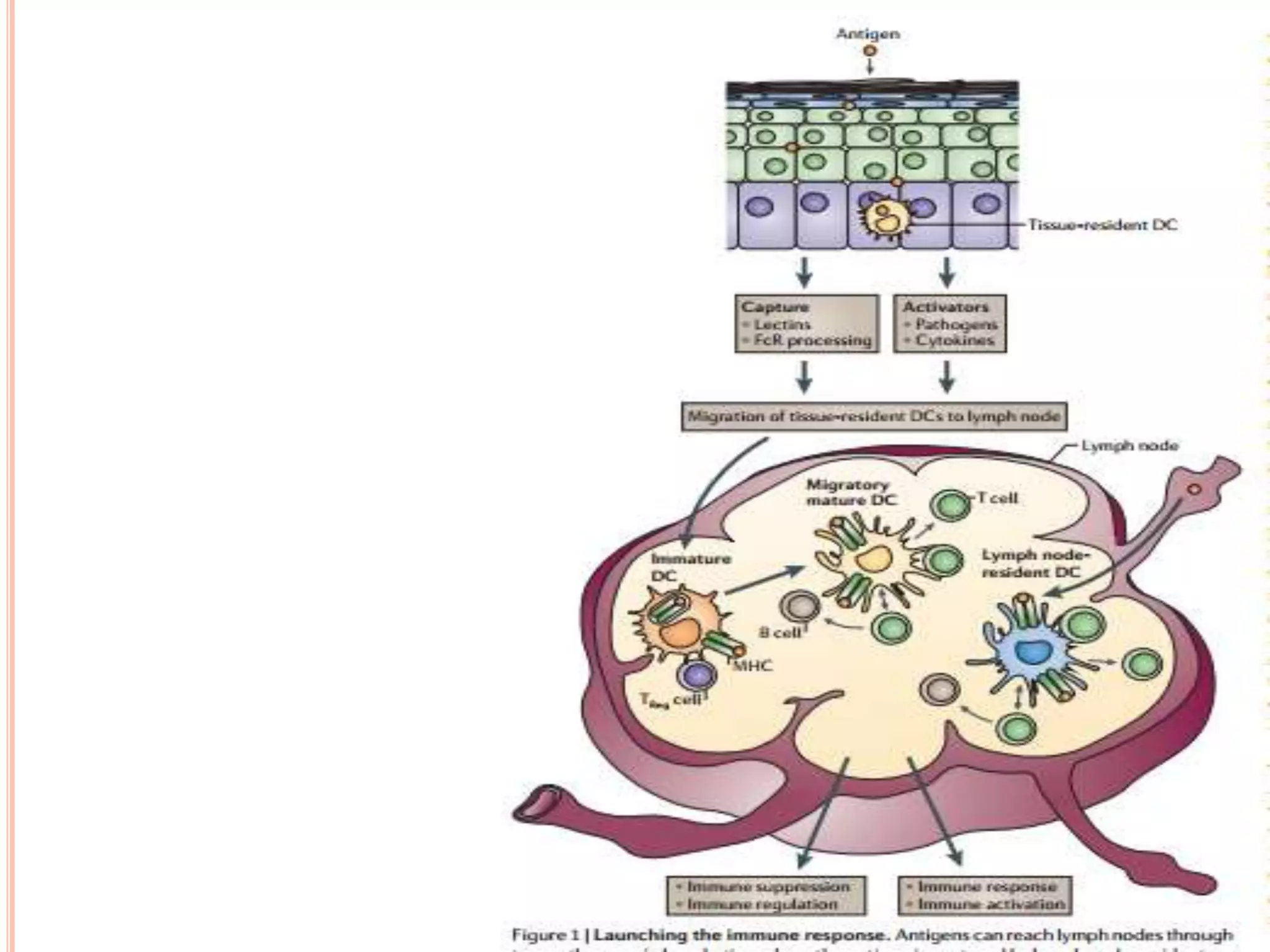
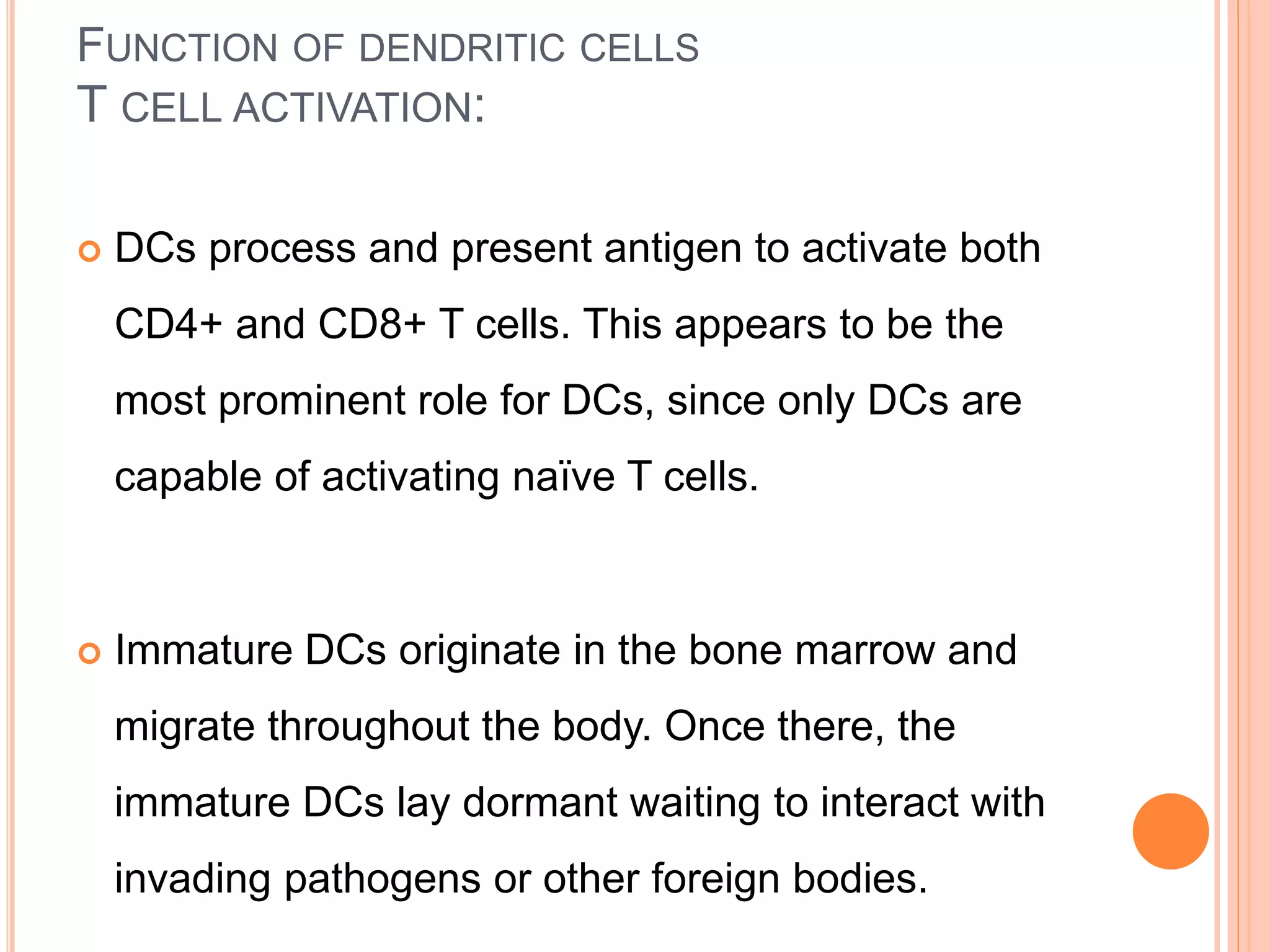
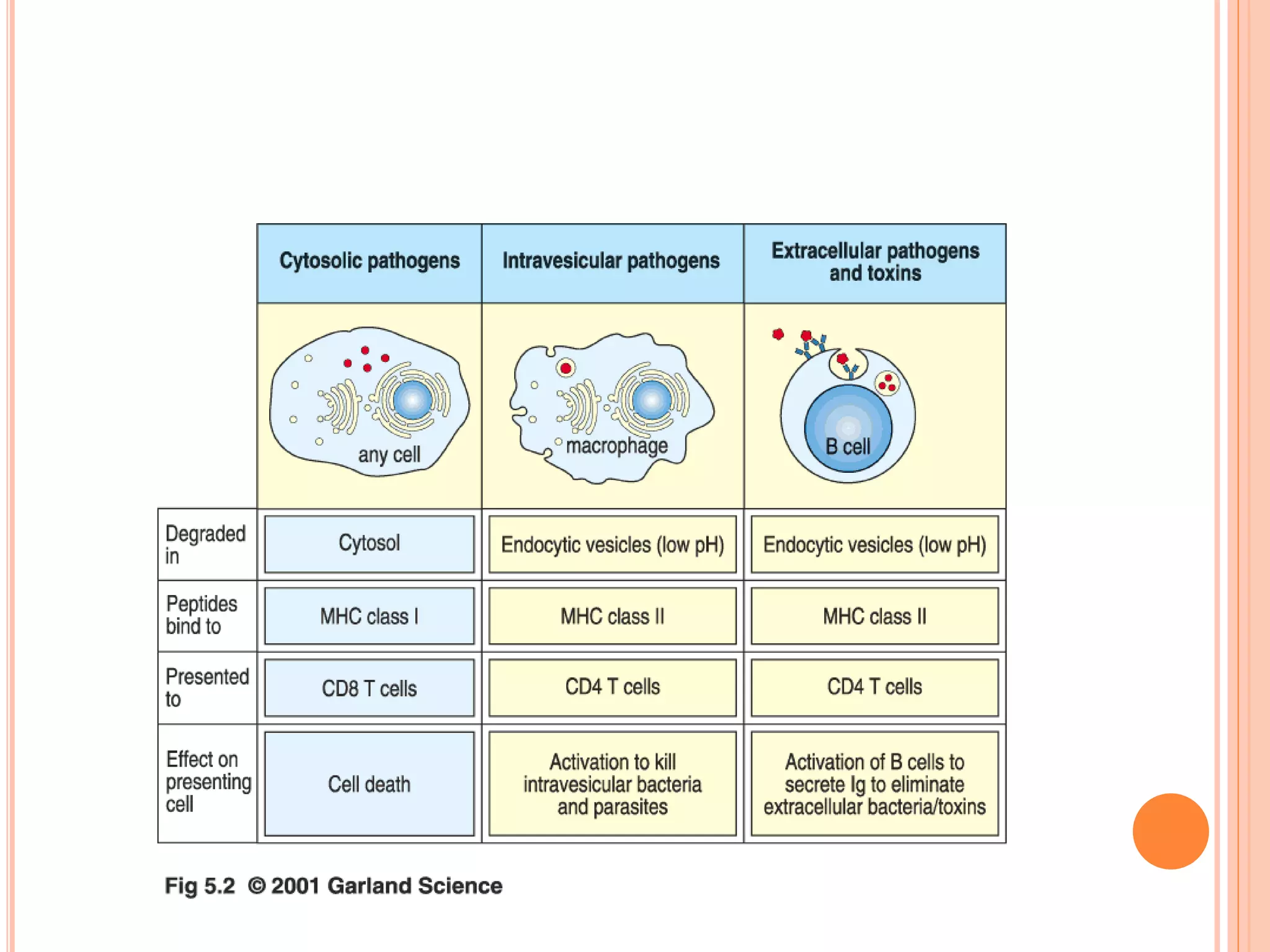
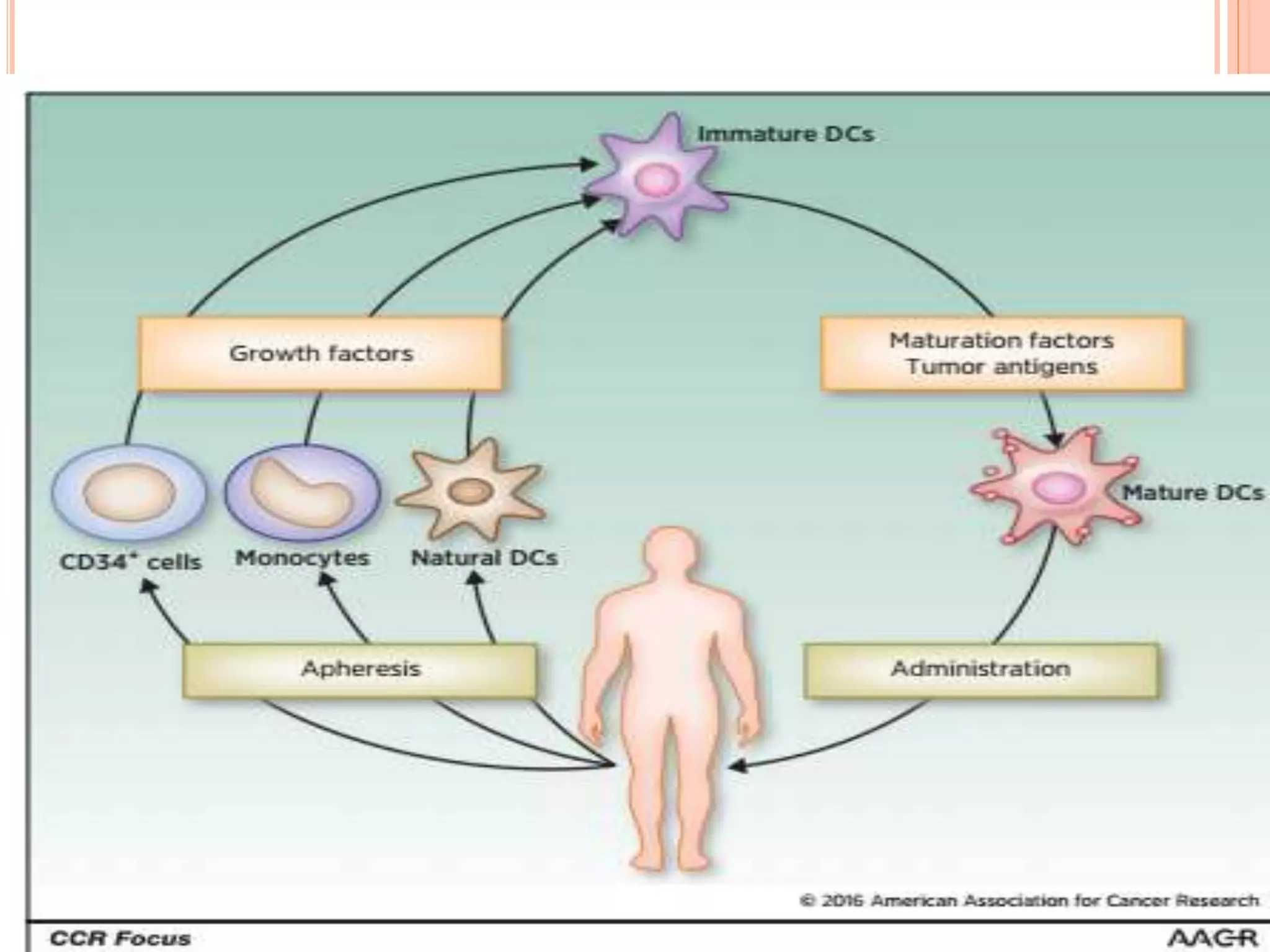
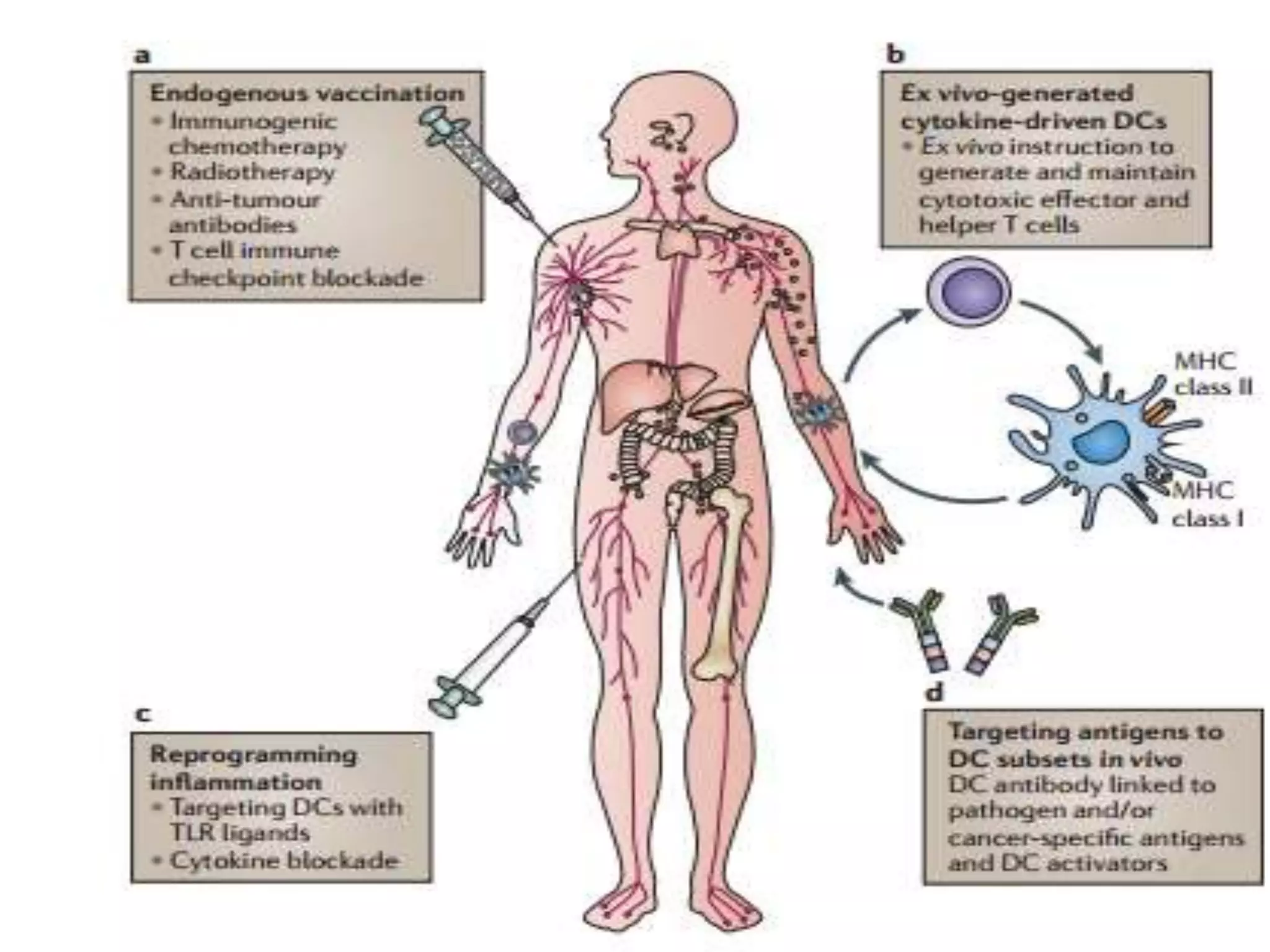
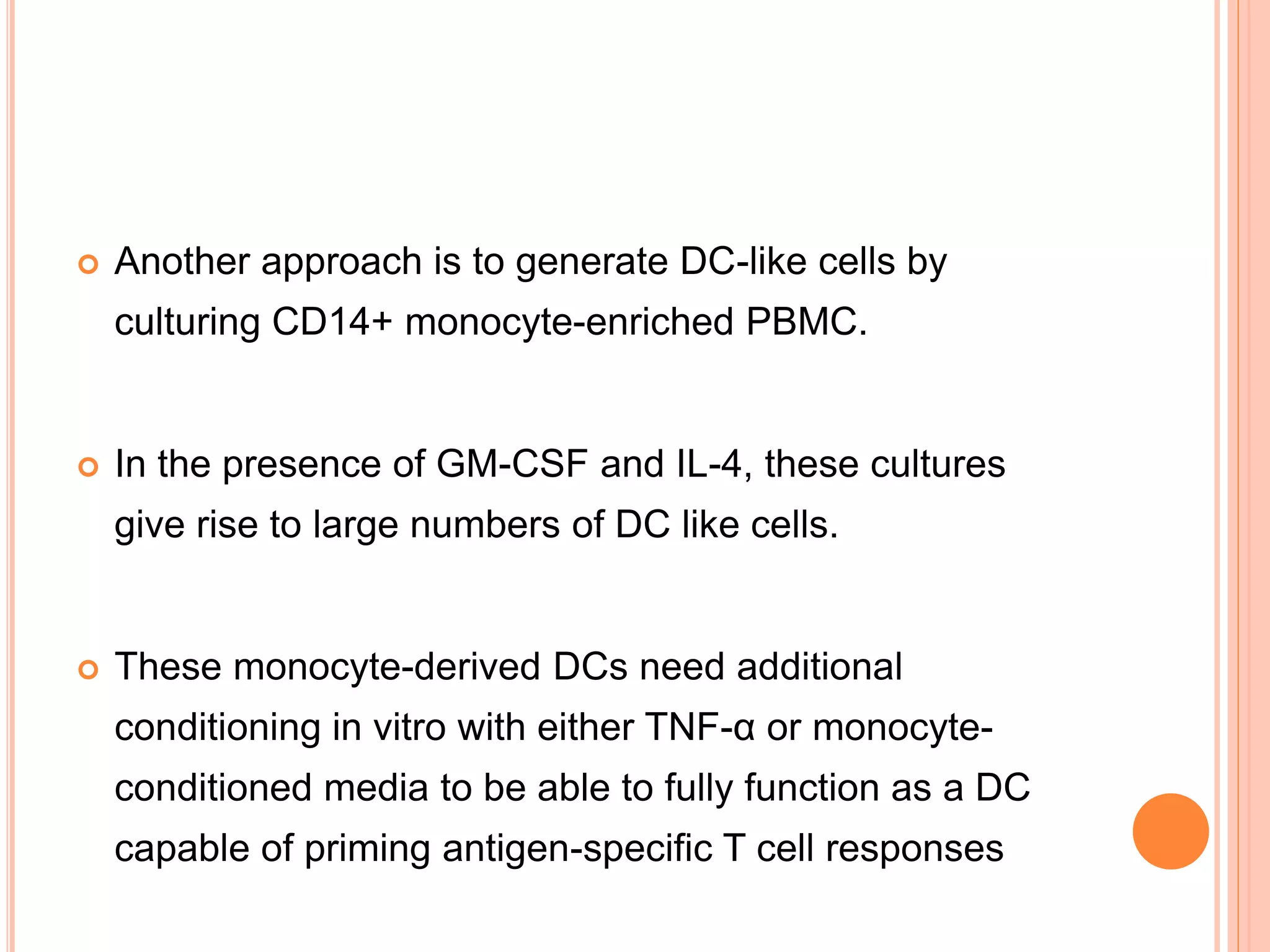
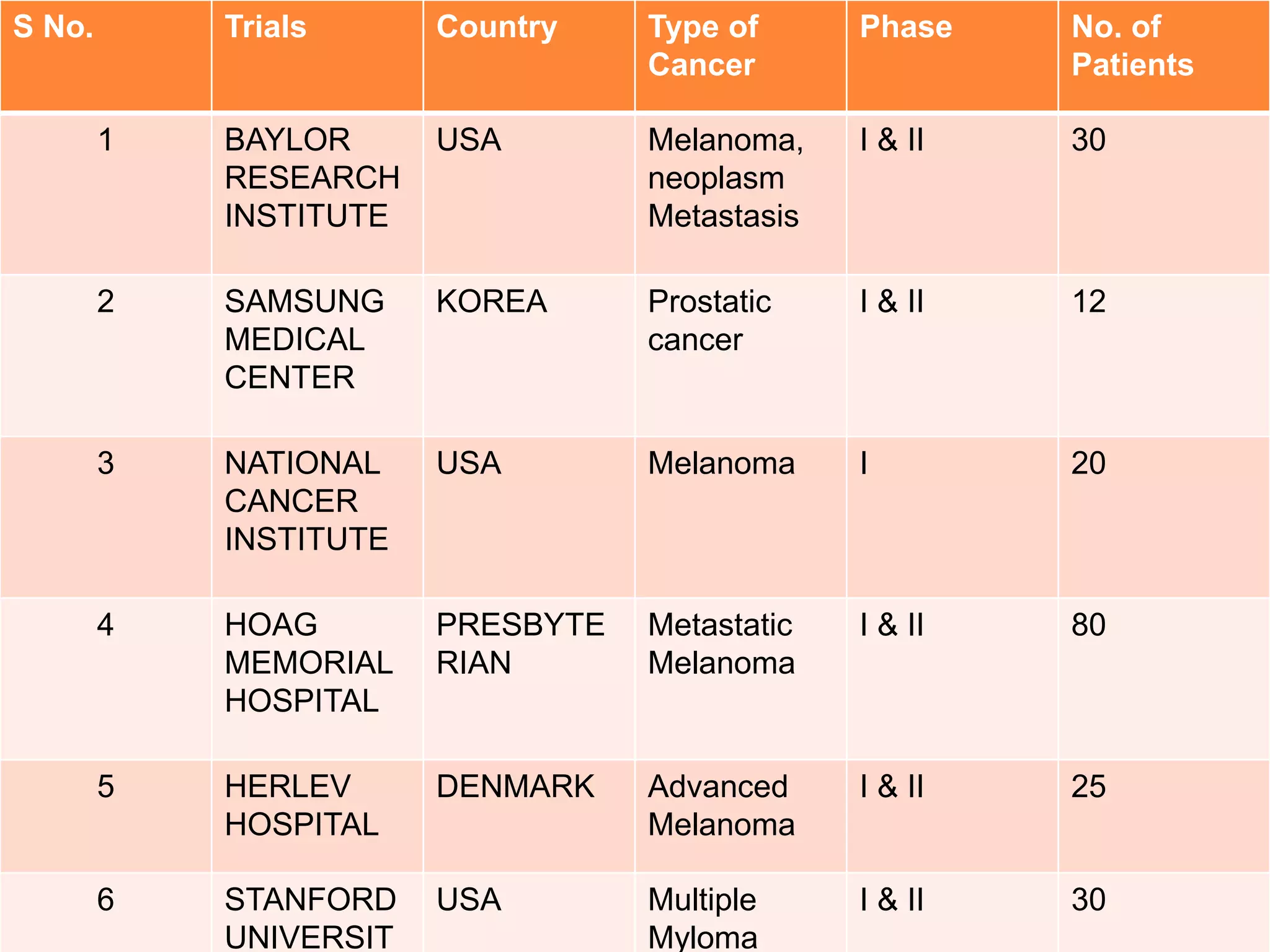
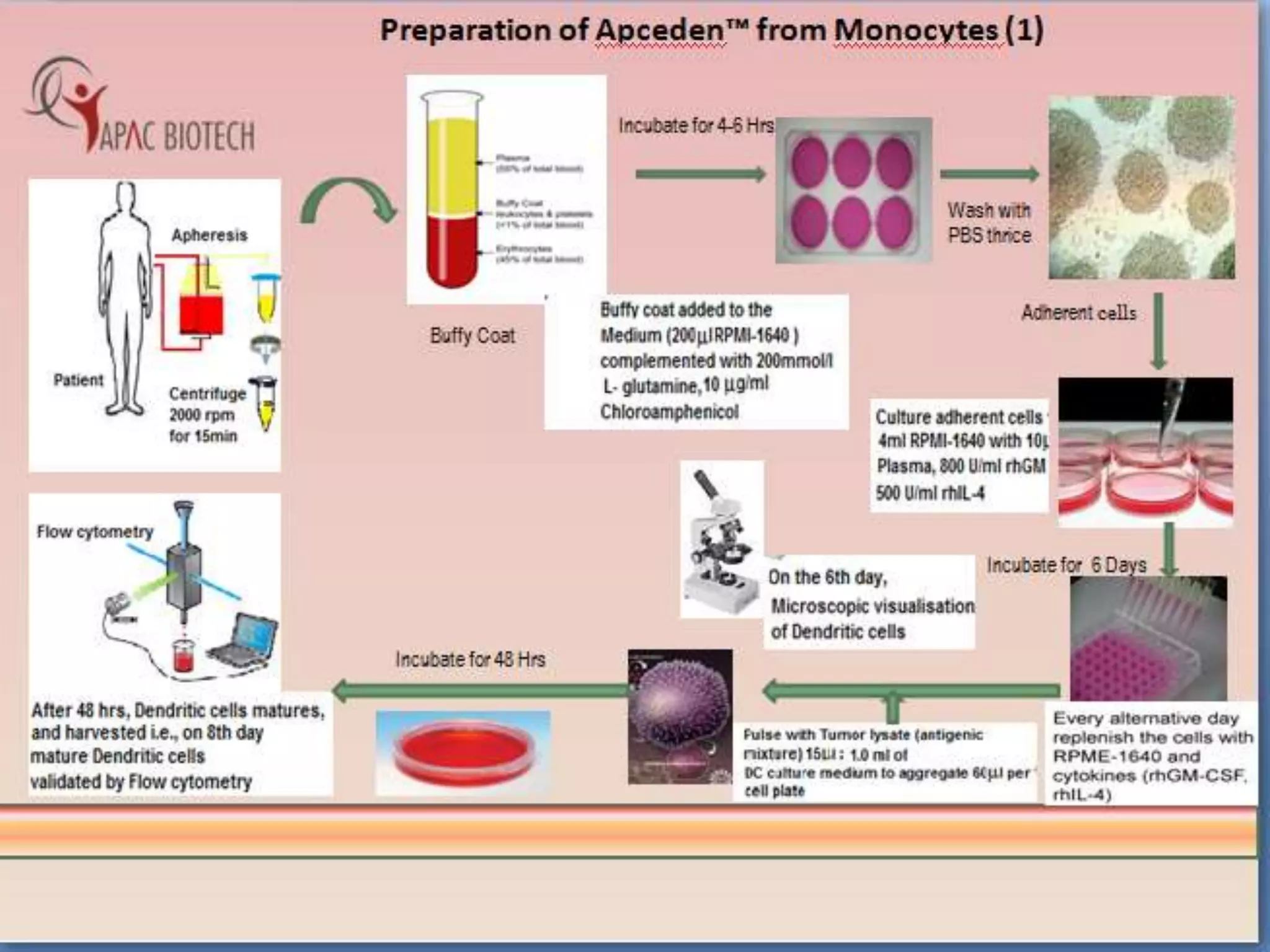
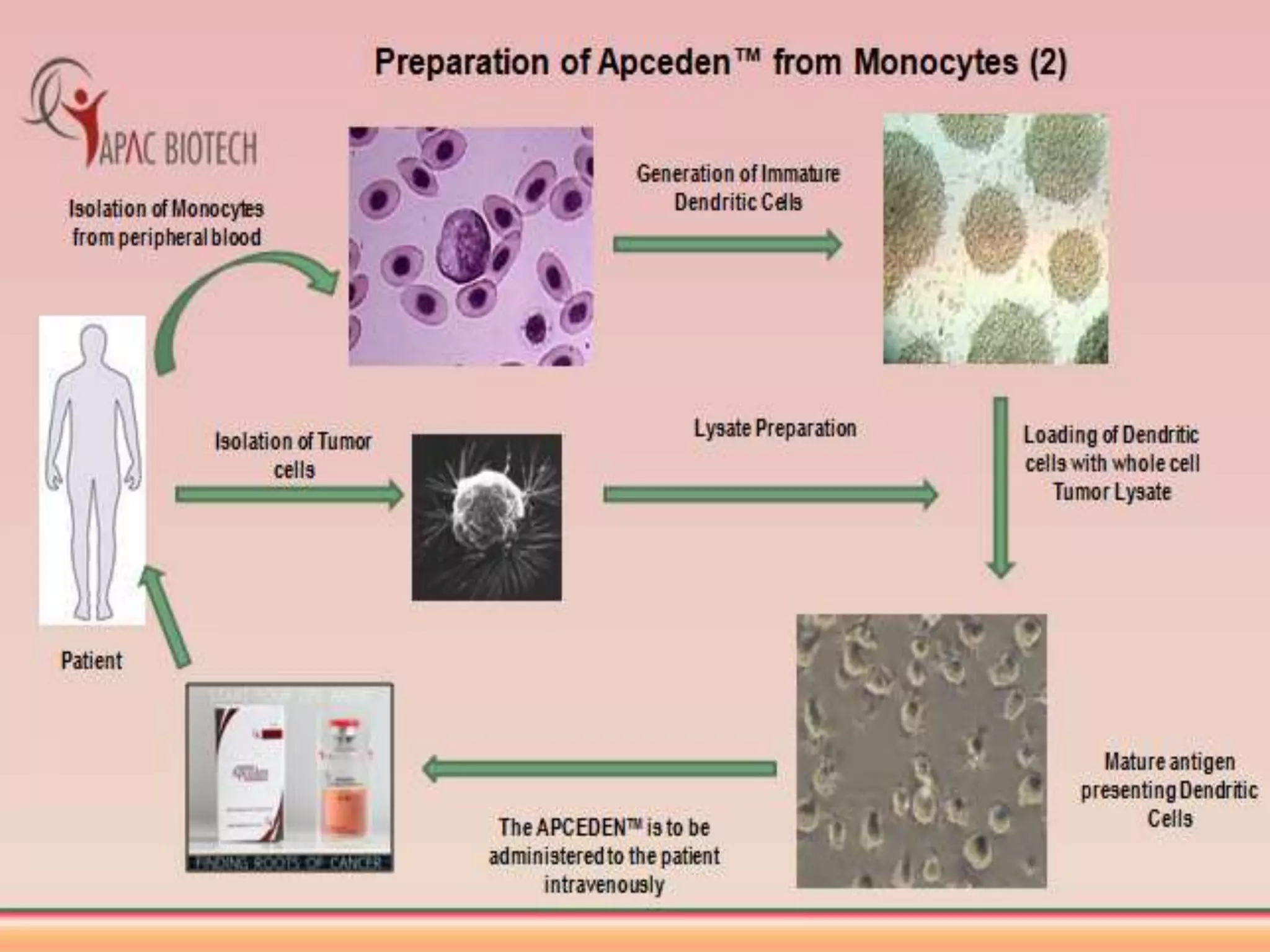
Dendritic cells were first described in the late 19th century and are antigen-presenting cells of the immune system. There are multiple types of dendritic cells that originate from both lymphoid and myeloid lineages. Dendritic cells have several key functions, including activating T cells to launch immune responses, inducing tolerance to prevent autoimmunity, and stimulating B cell responses. They capture antigens and present them to T cells via MHC molecules to activate both CD4+ and CD8+ T cells. Dendritic cells play an important role in cancer immunotherapy by targeting tumor antigens to activate anti-tumor immune responses.