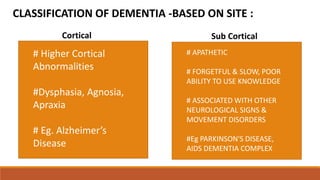
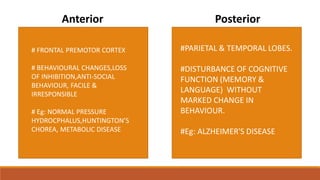
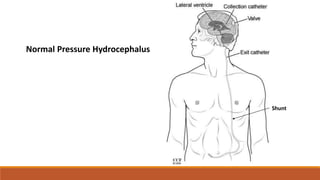
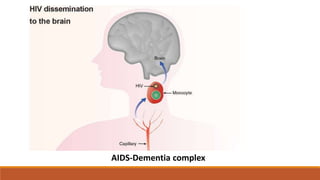
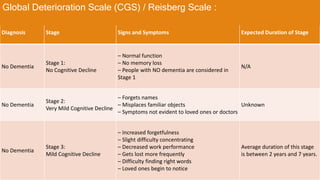
The document provides a comprehensive overview of dementia, its classification, types, symptoms, and stages of progression. It discusses major types such as Alzheimer's disease, vascular dementia, and dementia with Lewy bodies while outlining diagnostic criteria and potential management strategies. Additionally, it highlights the importance of awareness regarding the signs, symptoms, and treatments associated with dementia.