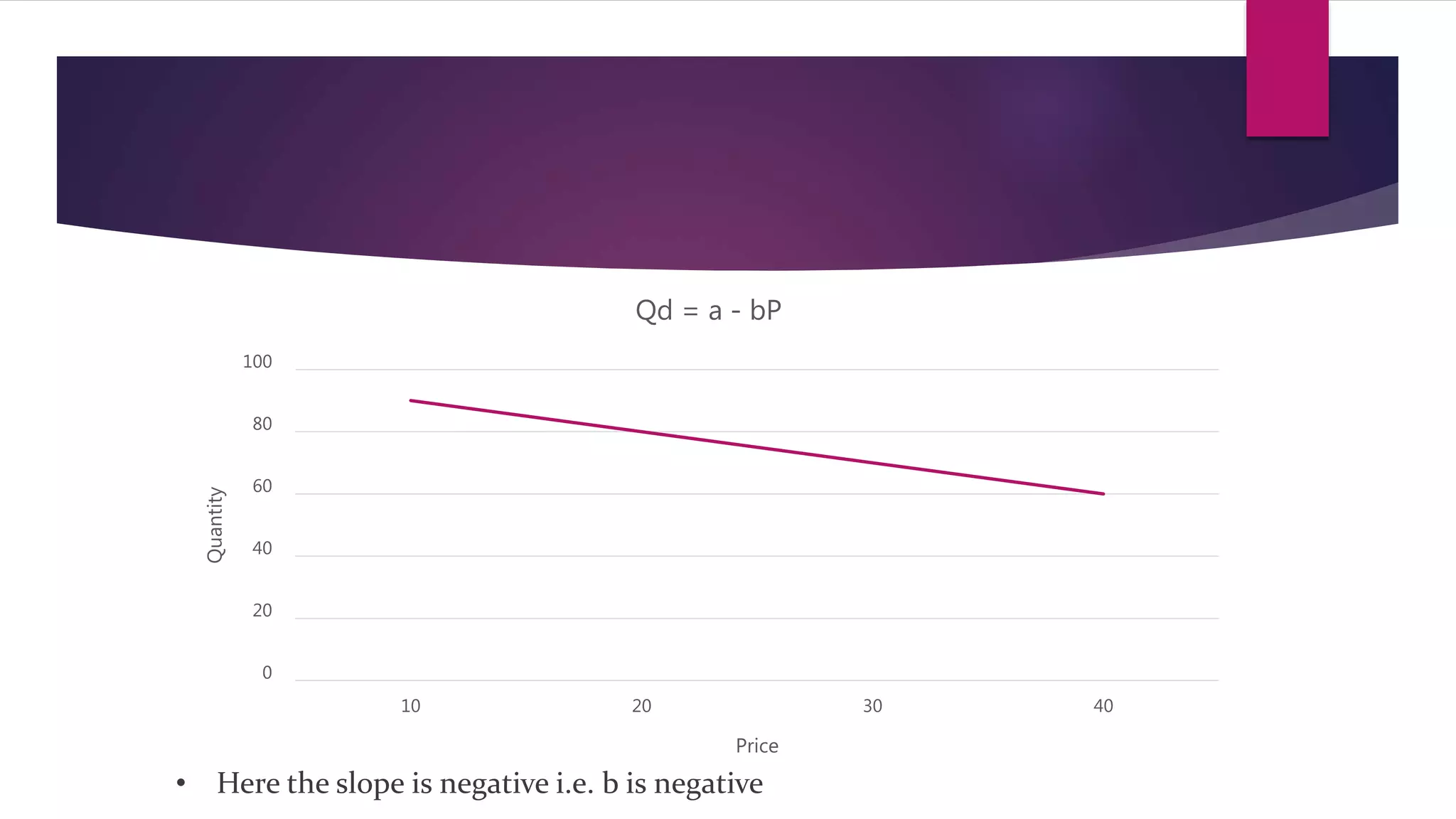
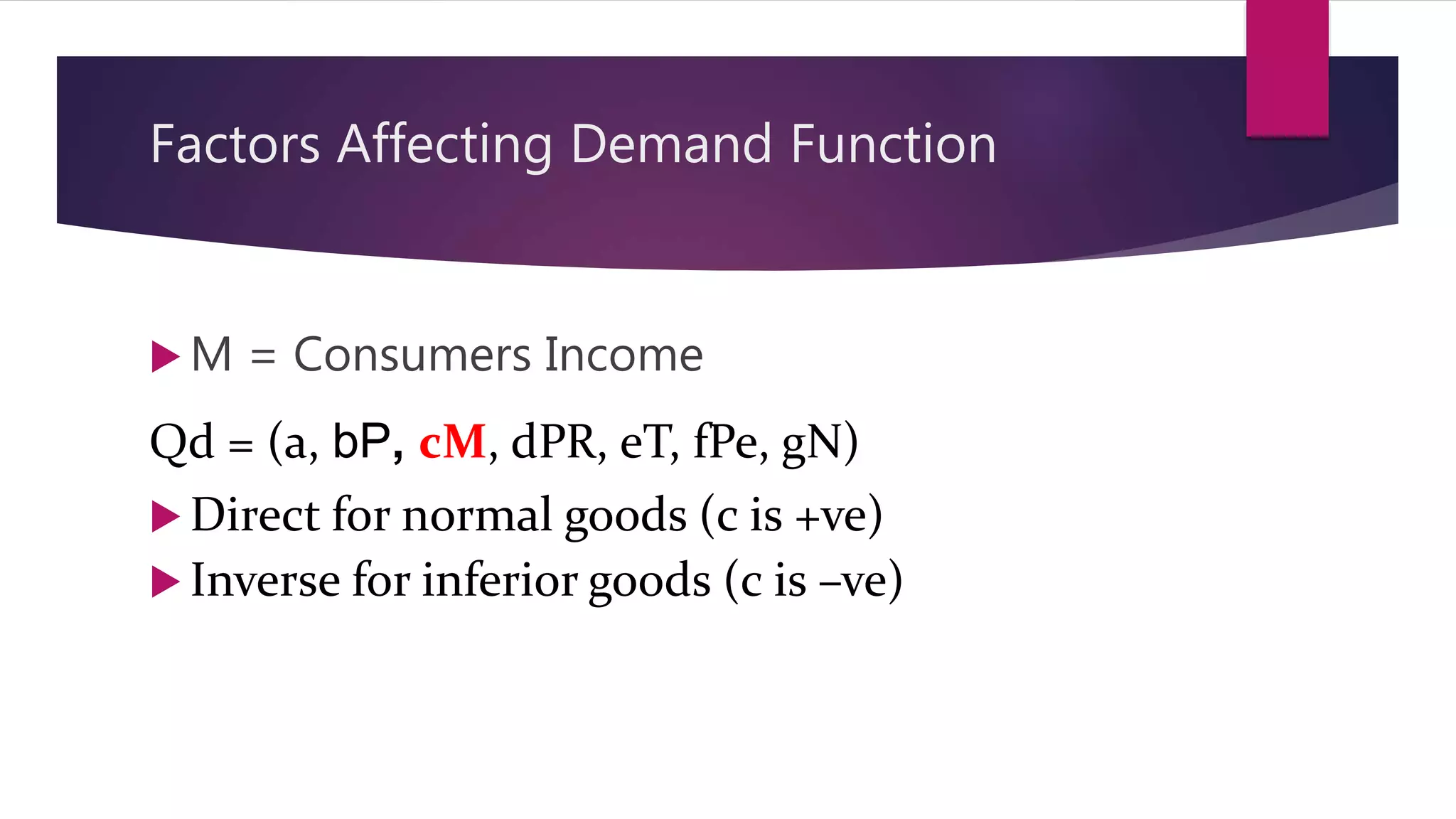
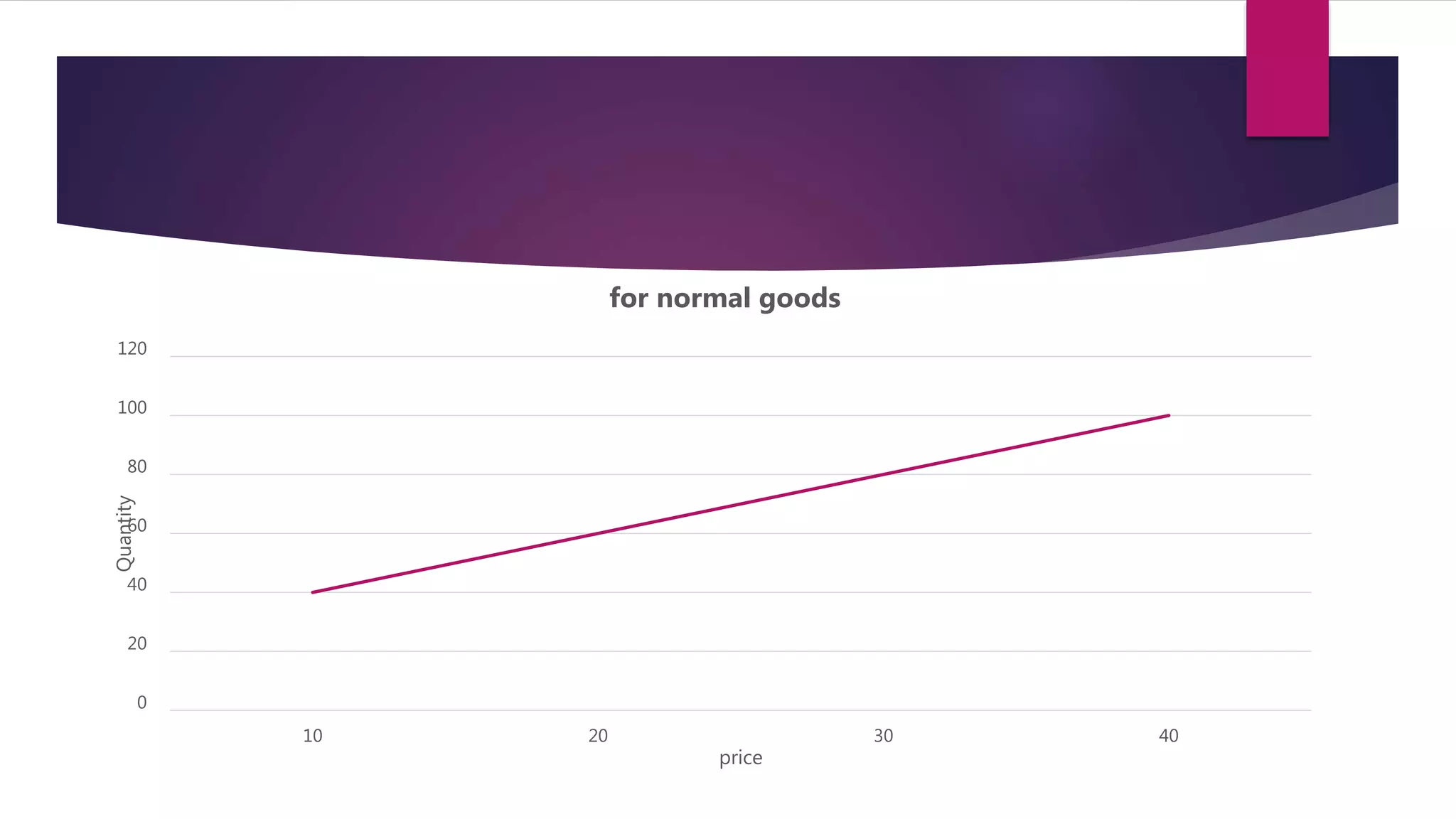
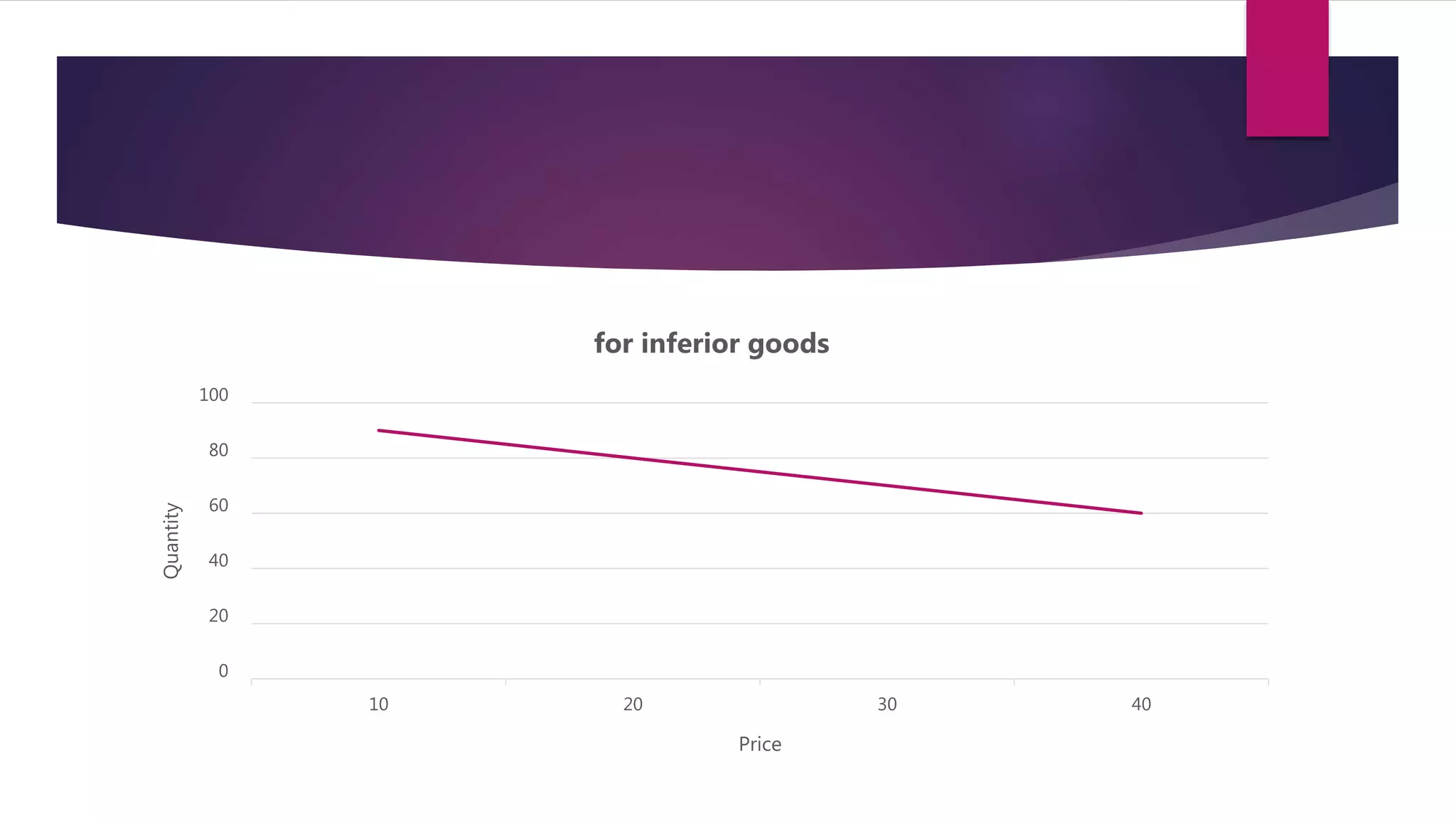
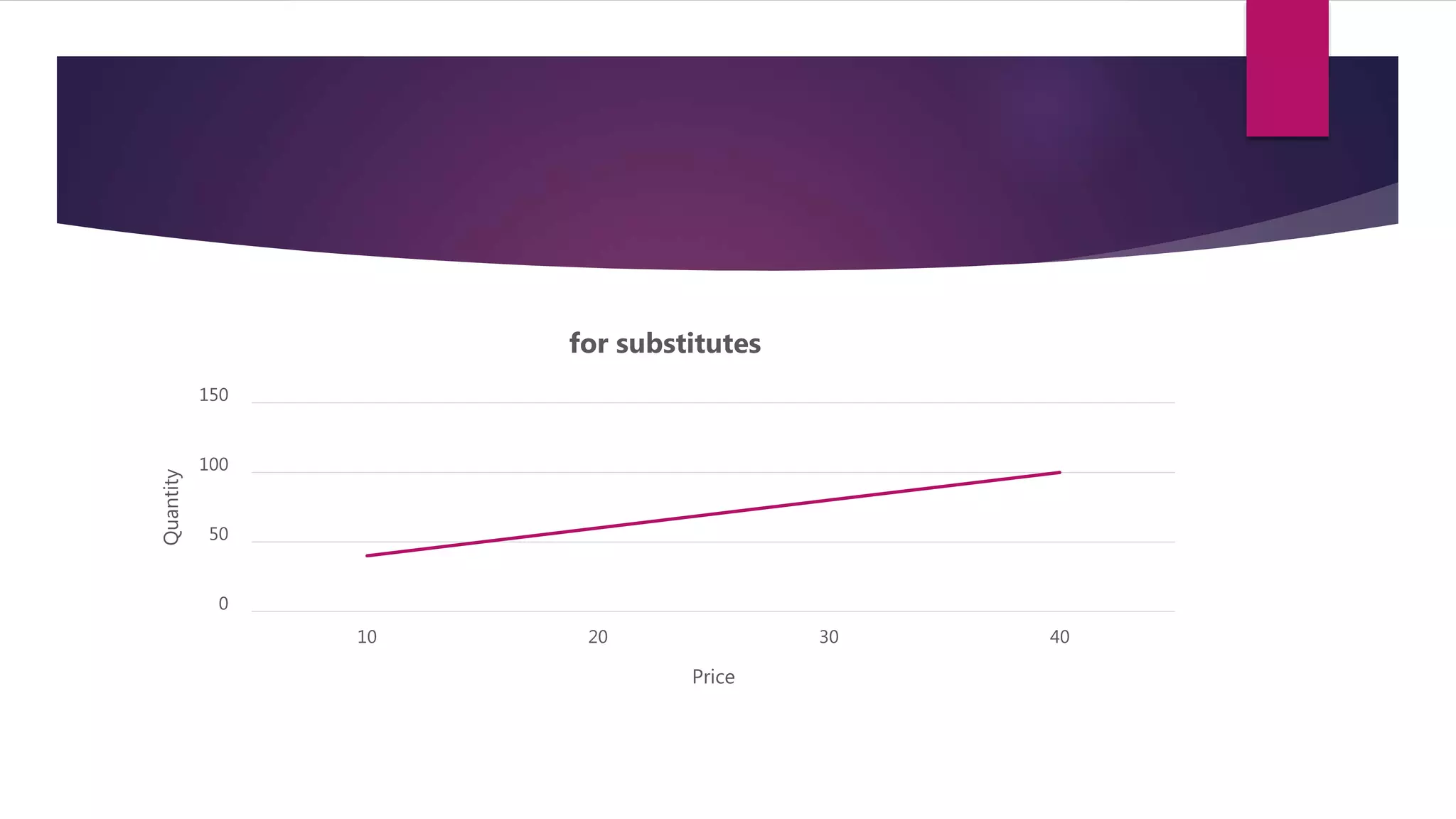
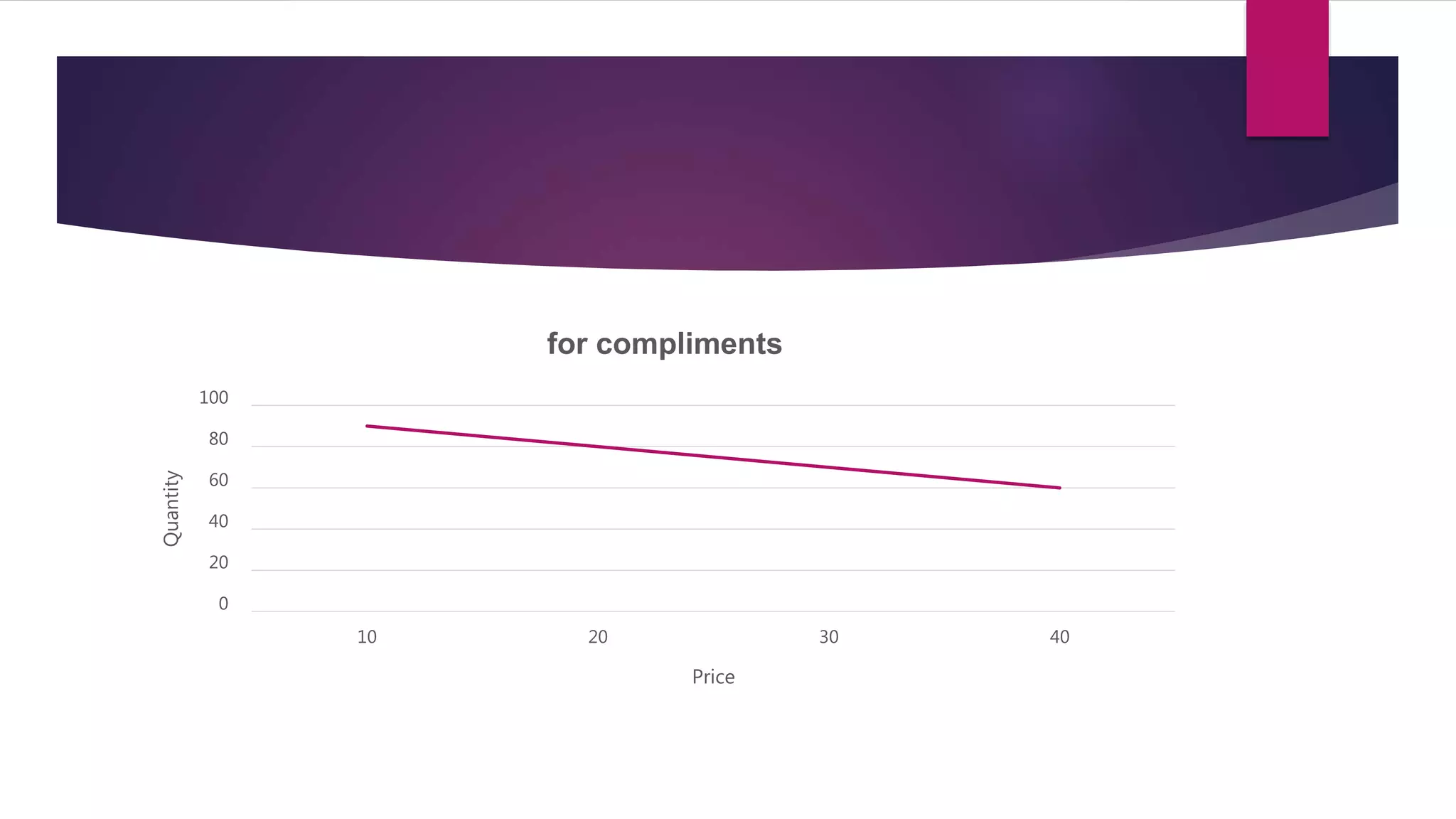
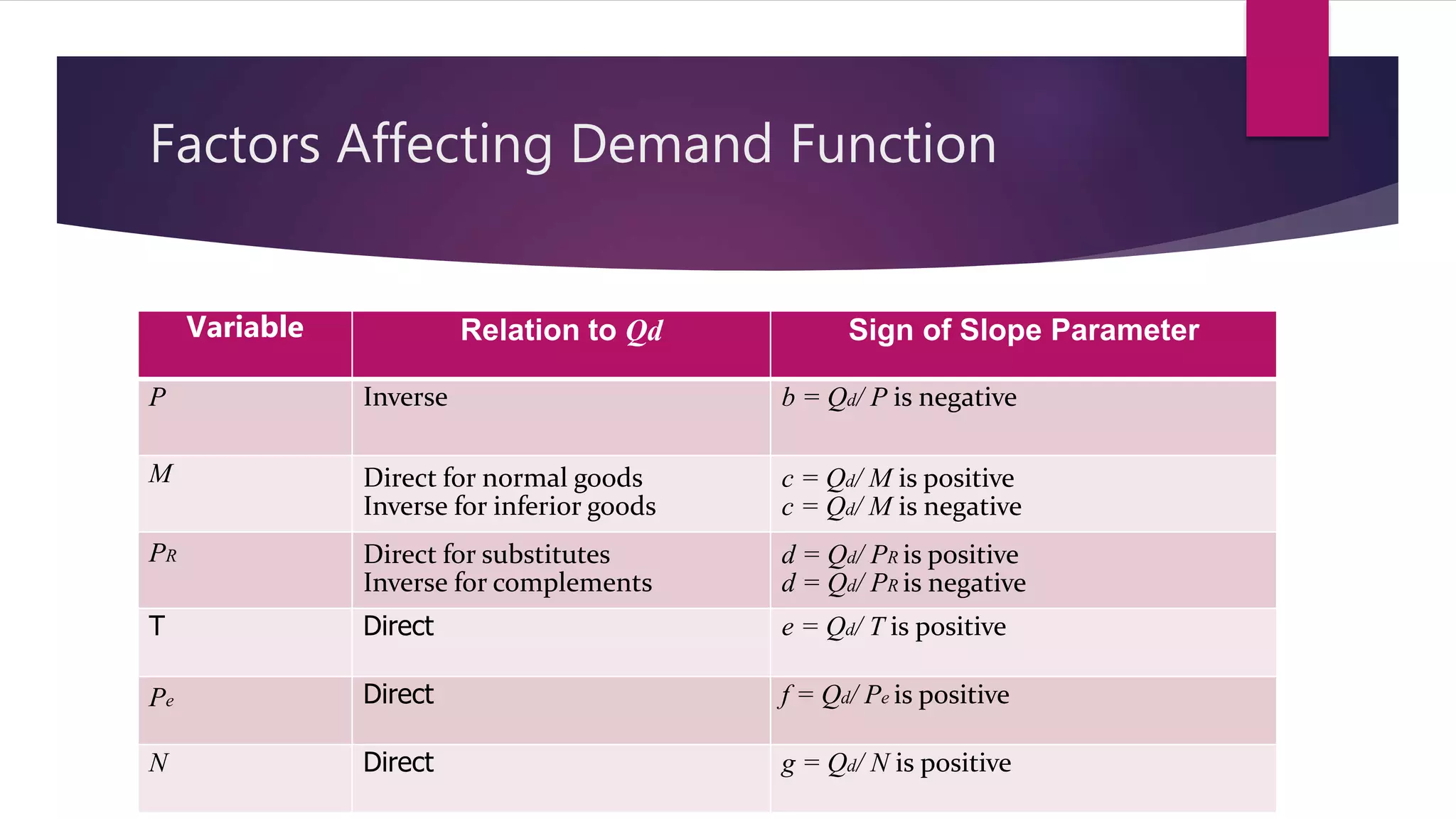
Demand is defined as a consumer's desire and willingness to pay for a good or service. Demand depends on factors like price, income, tastes, and the prices of related goods. A demand function expresses the quantitative relationship between quantity demanded of a good and the various factors that influence demand. It shows the inverse relationship between price and quantity demanded - as price increases, quantity demanded decreases. The demand function can take the general form of Qd = a - bP, where a is the intercept, b is the slope, Qd is quantity demanded, and P is price. Factors like income, prices of substitutes and complements, tastes, expected future prices, and number of consumers impact the demand function and quantity demanded