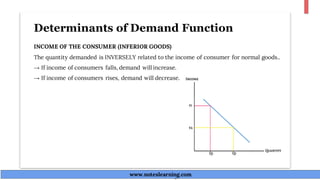
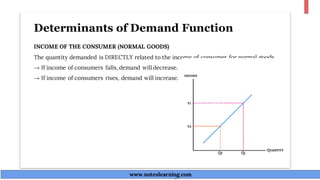
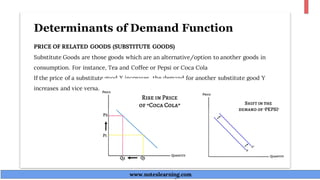
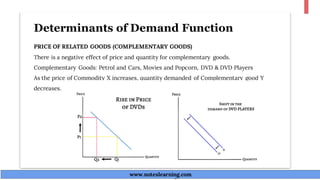
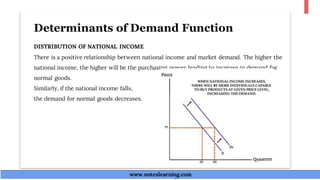
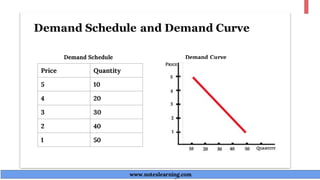
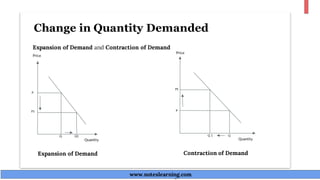
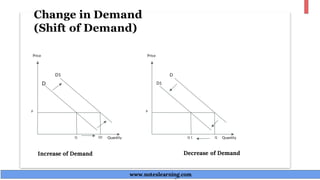
The document discusses demand theory and the demand function. It defines demand as the willingness and ability of consumers to purchase a good at a given price. A demand function shows the relationship between quantity demanded and its determinants like price, income, tastes, and expectations. The key determinants of demand that are outlined include price of the good, income, prices of substitutes and complements, tastes, expectations, population, income distribution, and government policy. The document also explains the law of demand, assumptions of the law of demand, exceptions to the law, demand schedules, demand curves, and why demand curves slope downward.