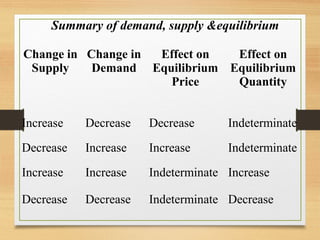
This document summarizes key concepts of demand and supply, including:
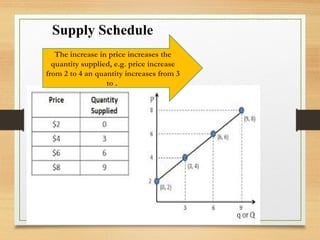
- Demand is the quantity of a good consumers will purchase at a given price, governed by the law of demand. Supply is the quantity produced at a given price, governed by the law of supply.
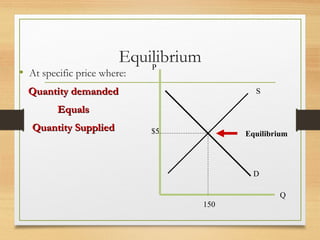
- Equilibrium occurs when quantity demanded equals quantity supplied at the equilibrium price.
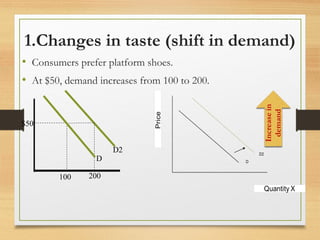
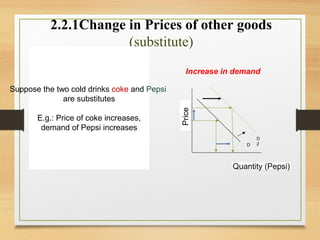
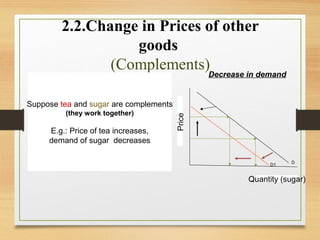
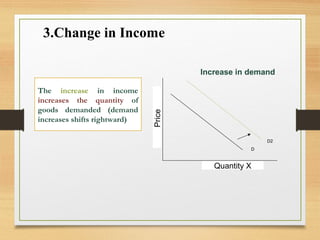
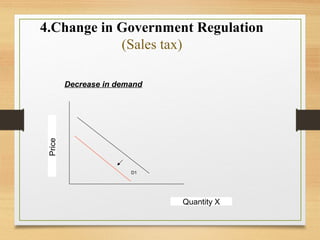
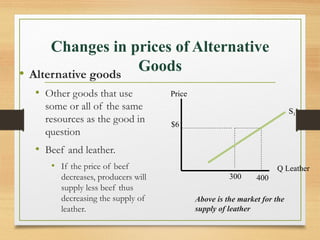
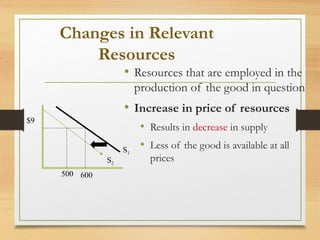
- Factors like income, tastes, prices of substitutes/complements can shift the demand curve. Factors like technology, input prices, and number of producers can shift the supply curve.
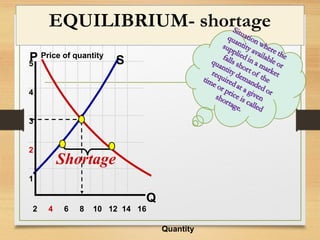
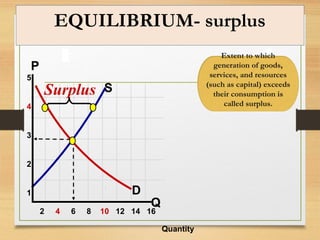
- When price is above equilibrium, a surplus occurs. When price is below equilibrium, a shortage occurs bringing prices back to equilibrium.




![Demand Schedule
Point Price [Rs per unit]
Quantity demanded of X
[kg. per month]
a
b
c
d
e
f
0.50
1.00
2.00
2.50
1.50
7.0
3.
52.5
3.00
5.0
1.0
1.5
1 2 3
0.50
1.00
2.00
Quantity of X
PriceofX
3.00
2.50
654 7
Demand Curve
a
b
c
e
d
f
1.50
Demand schedule](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/demandandsupply-180823131110/85/Demand-and-supply-5-320.jpg)