This document provides an overview of demand and supply concepts including:
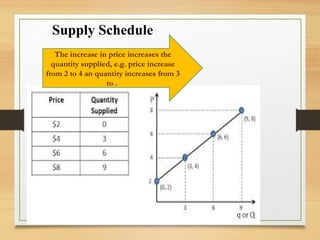
- The law of demand and supply which states that quantity demanded increases with lower prices and decreases with higher prices, while quantity supplied increases with higher prices and decreases with lower prices.
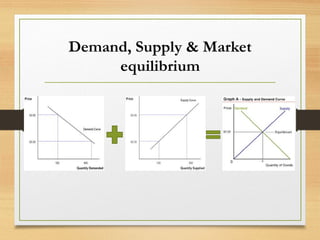
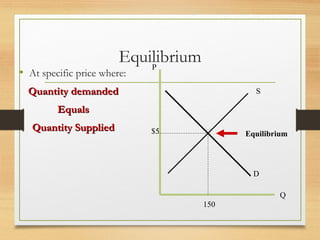
- Demand and supply schedules and curves which plot the relationship between price and quantity and intersect at the market equilibrium point.
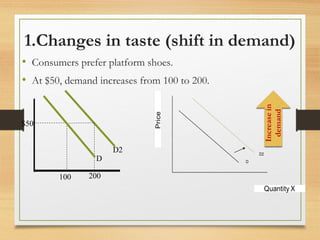
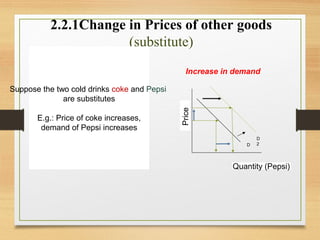
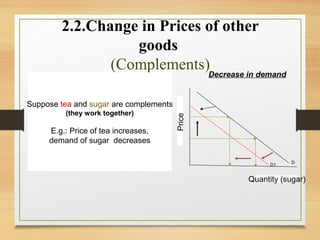
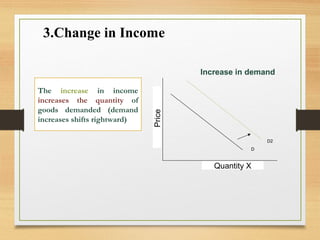
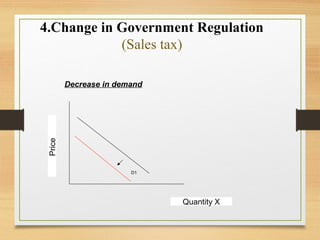
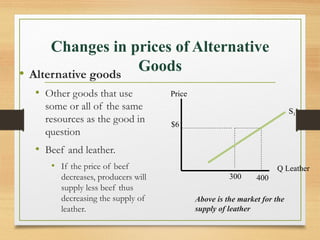
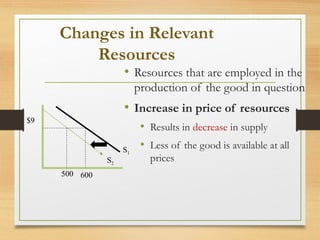
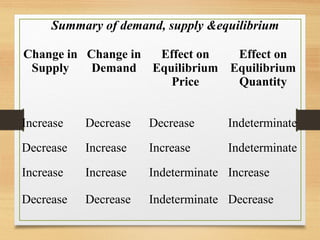
- Factors that can cause a shift in the demand or supply curves such as changes in income, tastes, prices of substitutes/complements, technology, and production costs.
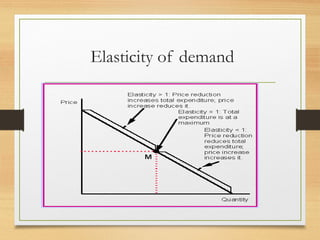
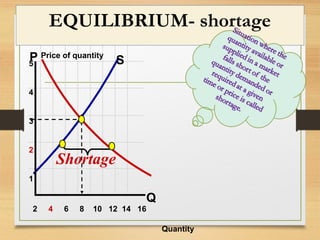
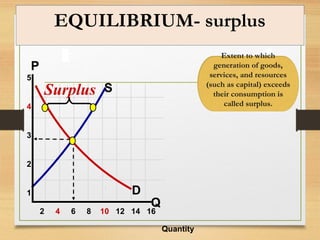
- How equilibrium shortages and surpluses occur when price is above or below the equilibrium point and how markets adjust back towards equilibrium.




![Demand schedule
Demand Schedule
Demand Curve
Price [Rs per unit]
Quantity demanded of X
[kg. per month]
a
b
c
d
e
f
0.50
1.00
1.50
2.00
2.50
3.00
7.0
5.0
3.
5
2.5
1.5
1.0
3.00
f
e
2.50
d
Price of X
Point
2.00
c
1.50
b
1.00
a
0.50
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
Quantity of X](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/complilationpowepointfinal-140306030604-phpapp02/85/Complilation-powepoint-final-5-320.jpg)