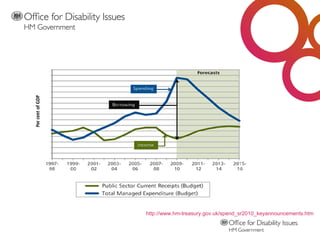
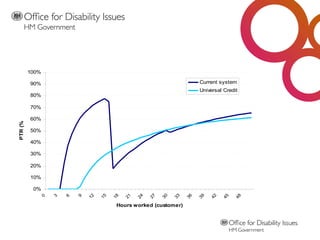
The document outlines the UK government's roadmap to disability equality, emphasizing the need for equal access to education, employment, and services for disabled individuals. It discusses the current political context, the legal framework established by the Equality Act 2010, and various welfare reforms aimed at improving support for disabled people. The text highlights the importance of co-production and changing societal attitudes towards disability while providing resources and links for further information.