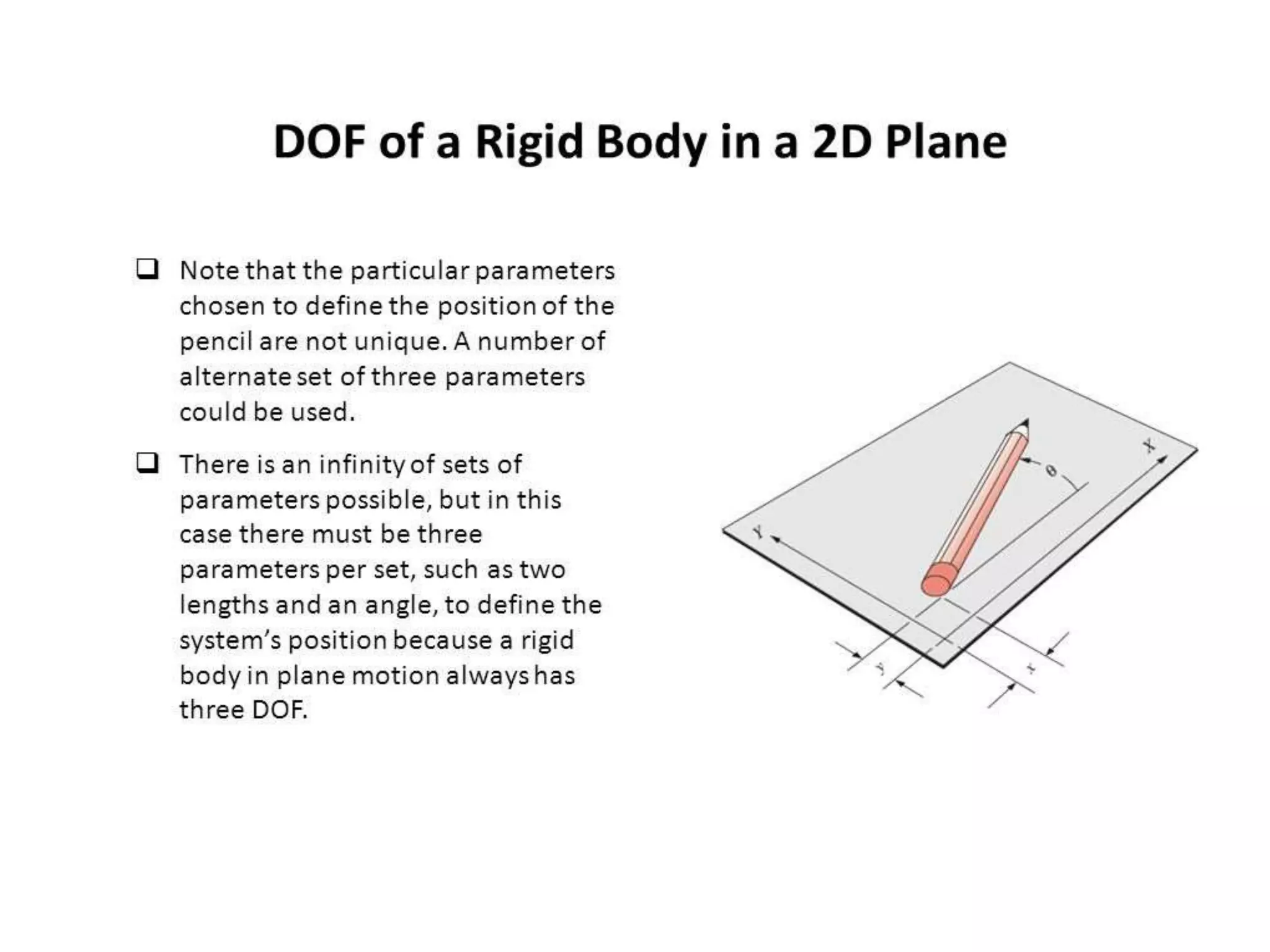
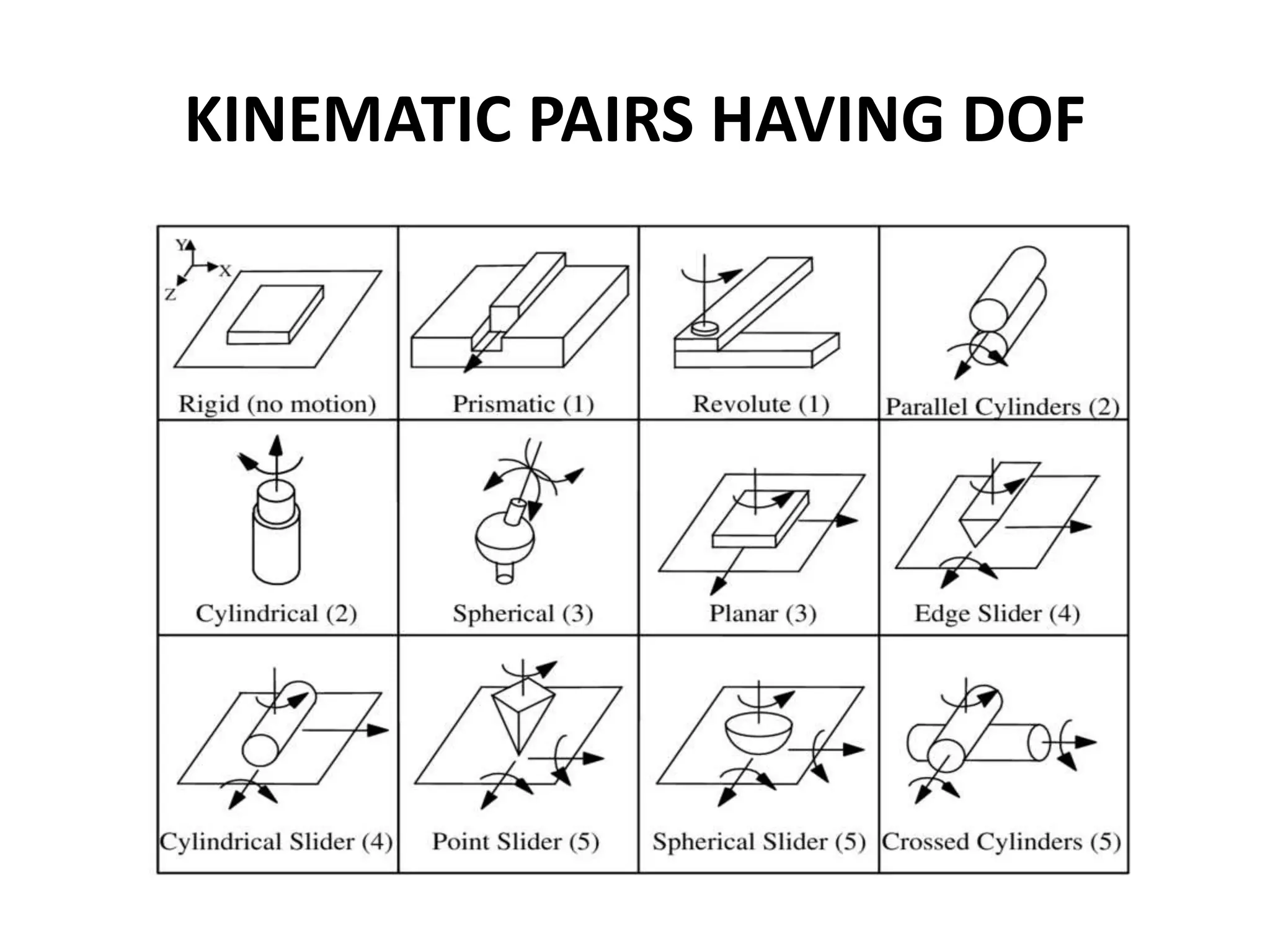
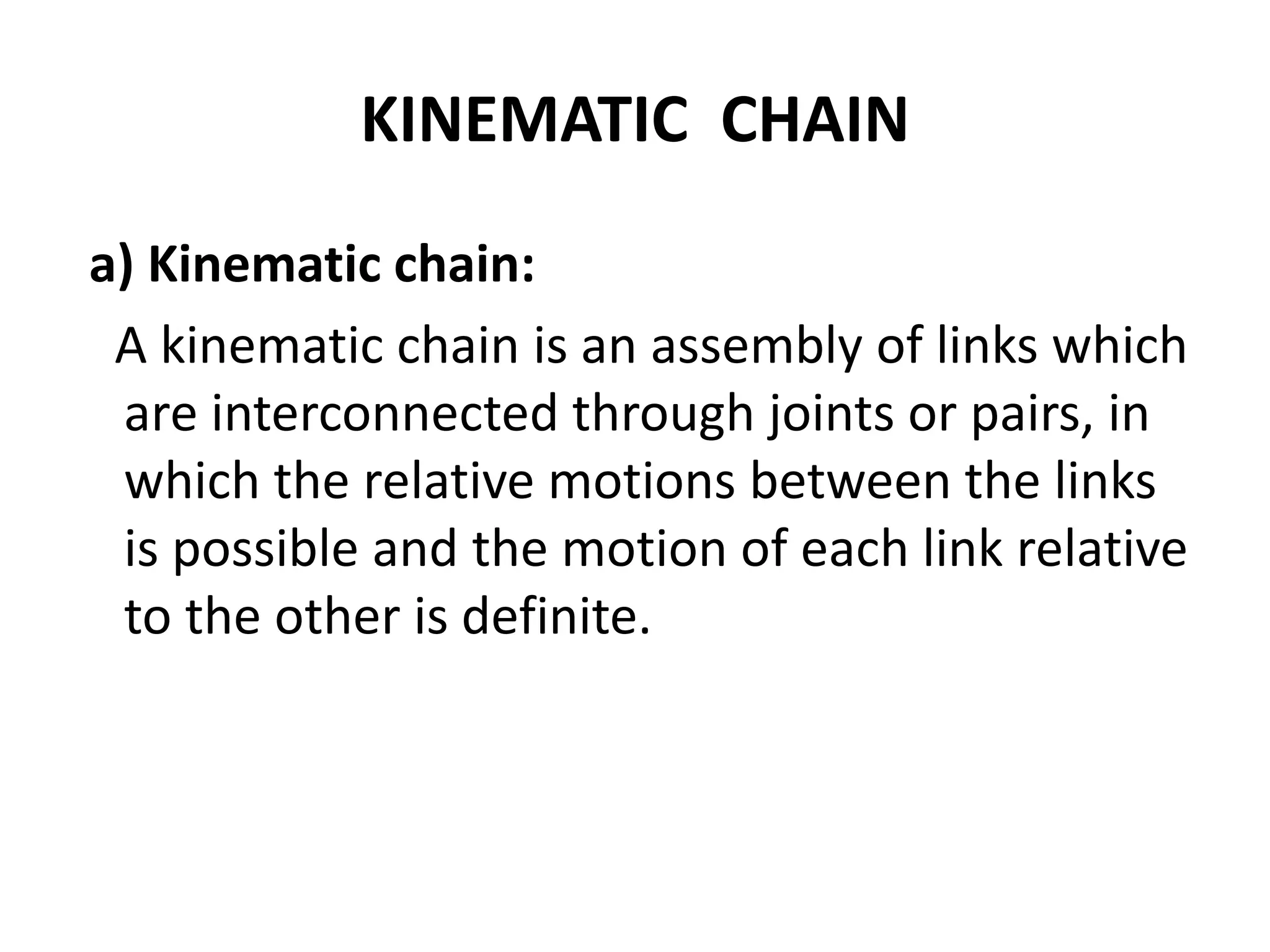
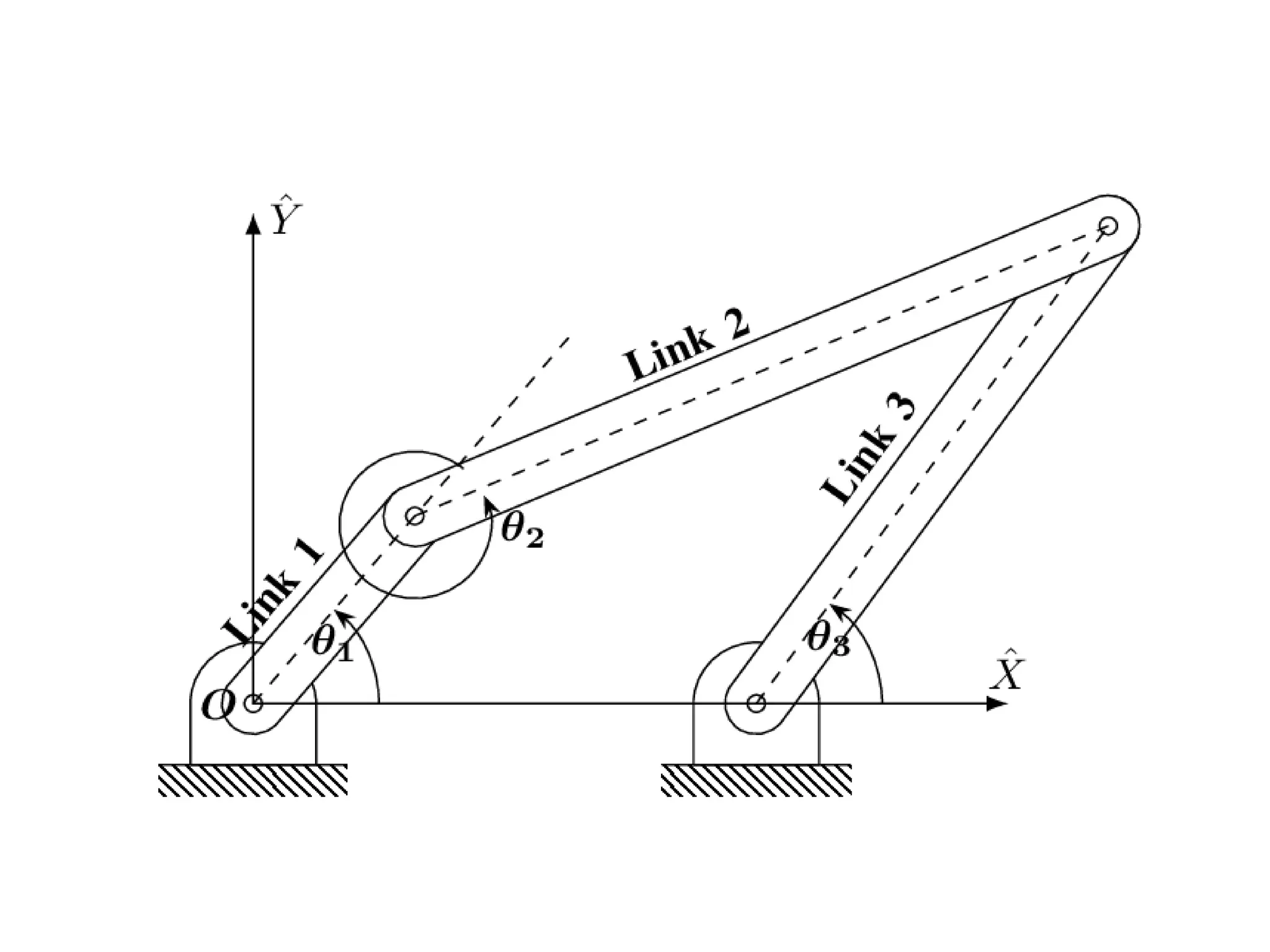
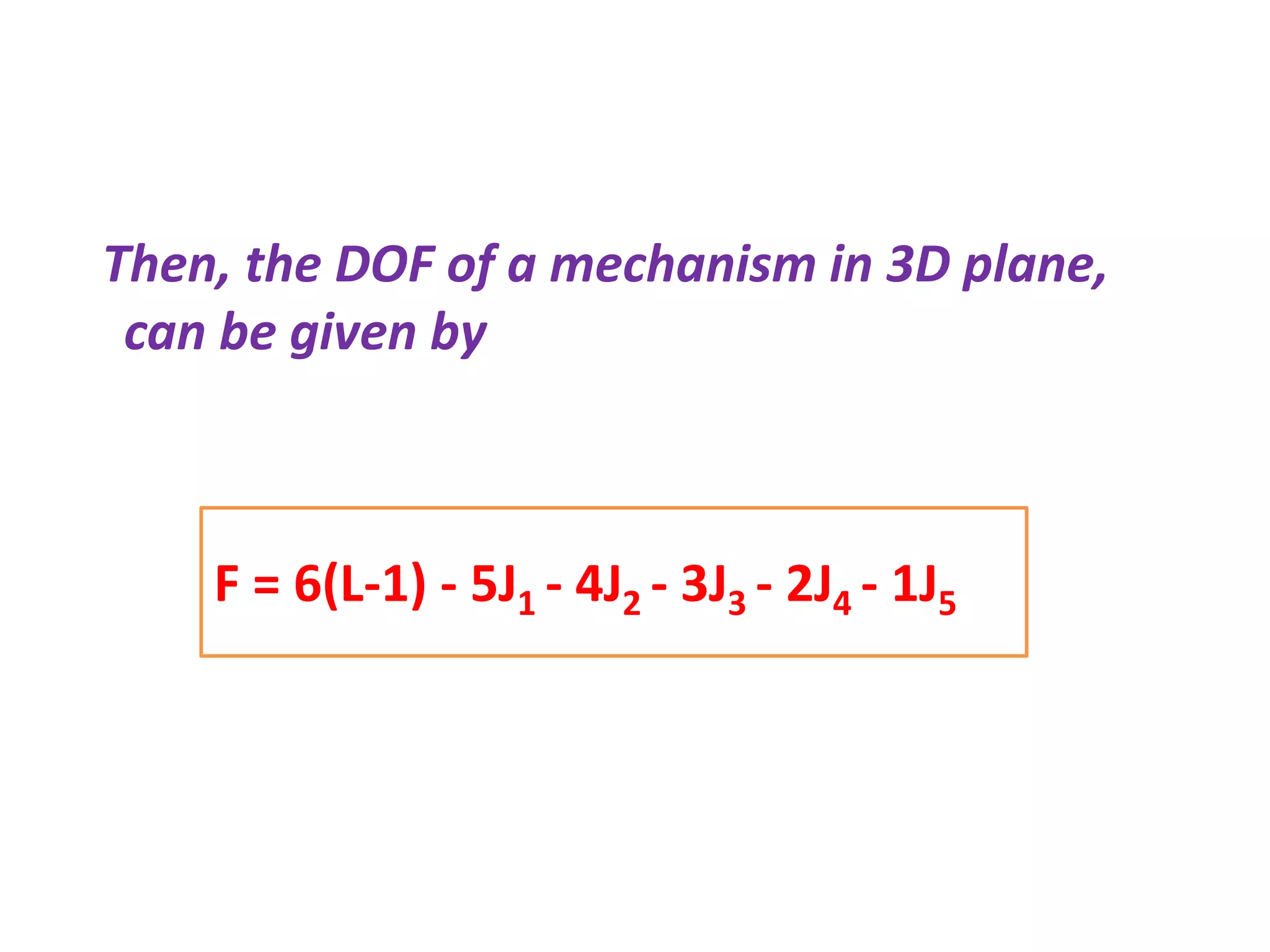
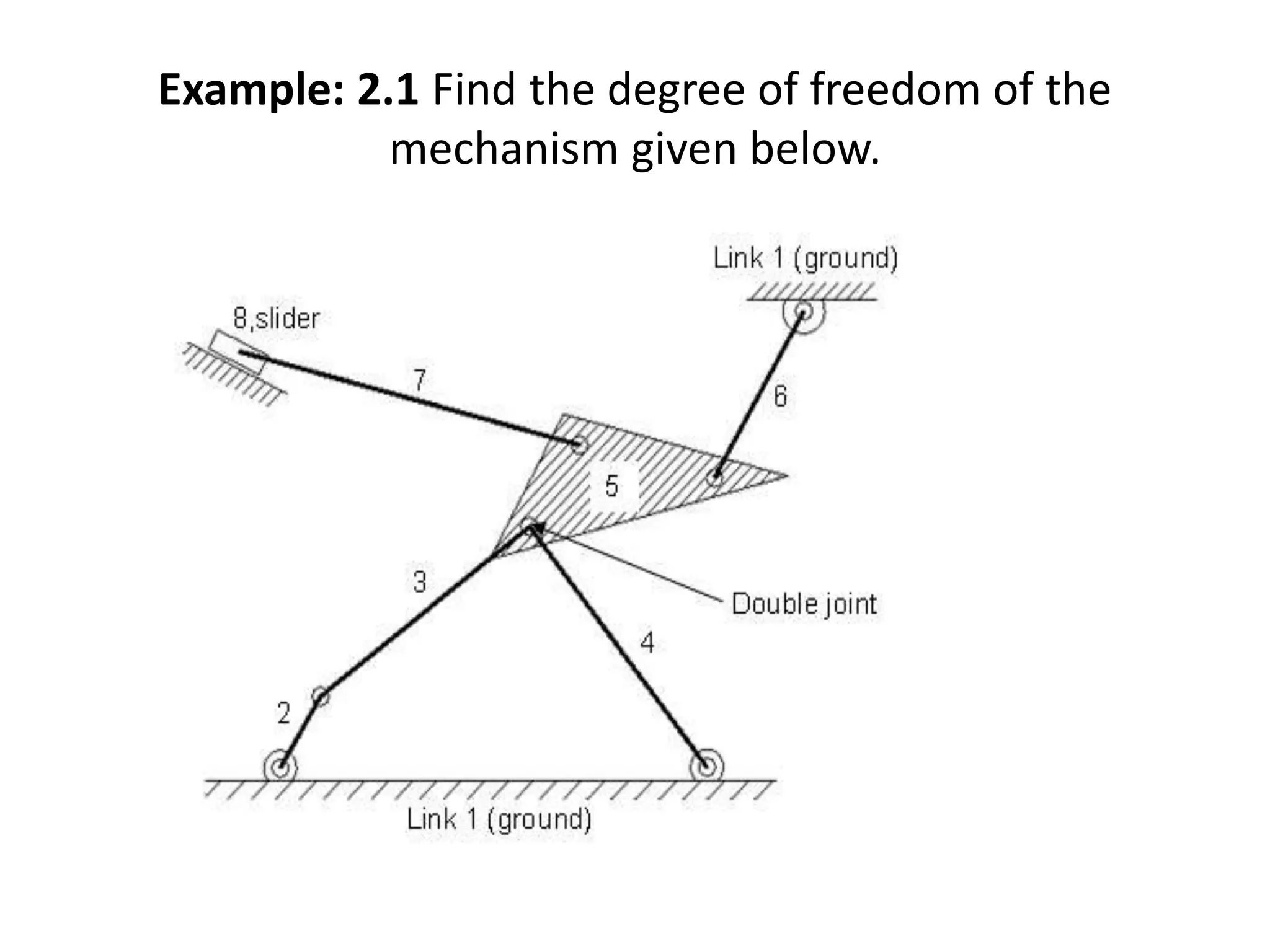
The document discusses degrees of freedom (DOF) of rigid bodies and kinematic mechanisms. It states that a rigid body in 3D space has 6 DOF, while in a 2D plane it has 3 DOF consisting of translations along two axes and a rotation. For mechanisms, DOF is calculated using formulas that account for the number of links, joints, and their types. DOF indicates the number of independent motions a mechanism can perform, with higher values indicating less constraint. Formulas to calculate DOF in 2D and 3D are provided along with examples worked out.