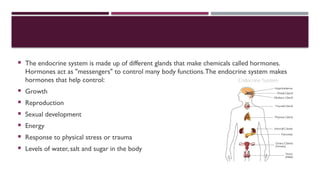
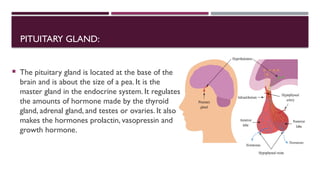
The document outlines the endocrine system, emphasizing the functions and types of glands, specifically distinguishing between endocrine and exocrine glands. It details various hormones produced by glands such as the pituitary, thyroid, adrenal, ovaries, and testes, and discusses their roles in regulating body functions including growth, metabolism, and reproduction. Additionally, it highlights conditions related to hormone imbalances and the impact of hormones on physical and mental health.








![SECRETION FROM ANTERIOR PITUITARY GLAND:
1- Growth hormone
Are essential for the growth and development of bones, muscle and other organs. It enhances protein synthesis decrease the use
of glucose and promotes fat destruction
Growth hormone [Hyper secretion of it during
childhood causes Gigantism, hypersecretion during
adulthood causes Acromegaly, and hyposecretion
causes Dwarfism].
2-Adrenocorticotropin(ACTH):
Essential for the growth and development of the adrenal cortex
ACTH [Hypersecretion causes Cushing’s
disease, while hyposecretion is rare].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/endocrinesytem-241103095645-06ece183/85/Endocrine-system-anatomy-presentation-ps-11-320.jpg)
![SECRETION OFTHE THYROID GLAND:
3-Thyroid-Stimulating Hormones: •
(TSH) are essential for the growth and development of the thyroid gland •
[Hypersecretion causes Grave’s disease, and
hypo secretion causes cretinism in children and
myxedema in adults].
4- Follicle stimulating Hormone: •
(FSH) are gonadotropic hormone. It stimulates the growth ,ovarian follicles in the female and the
production of sperm in male •[Hypersecretion causes no known
effects, while hyposecretion can cause failure of sexual maturation]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/endocrinesytem-241103095645-06ece183/85/Endocrine-system-anatomy-presentation-ps-12-320.jpg)
![ 5- Luteinizing Hormone:
(LH) is a gonadotropic hormone stimulating the development of corpus luteim the female
ovarian follicles and the production of testosterone in male[Disorders are similar to
those for FSH
6- Prolactin:
(PRL) stimulates the development and growth of the mammary glands and milk production during
pregnancy[Hypersecretion can disrupt
normal menstrual cycles in female and causes impotence in male;
and hyposecretion causes poor milk production in female].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/endocrinesytem-241103095645-06ece183/85/Endocrine-system-anatomy-presentation-ps-13-320.jpg)
![ 7- Melanocyte stimulating Hormones:
(MSH) regulates skin pigmentation and promotes the deposit of melanin in the skin
after exposure t0 sunlight[Hypersecretion causes abnormally dark skin pigment, and
hyposecretion causes abnormally light skin pigment]..](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/endocrinesytem-241103095645-06ece183/85/Endocrine-system-anatomy-presentation-ps-14-320.jpg)
![SECRETION FROM THE POSTERIOR LOB OF PITUITARY GLAND:
1- Oxytocin:
stimulates the uterus to contract during labor( delivery).A synthetic version of the
hormone used to induce labor is called Pitocin . It also stimulates mammary glands to
release milk. [Disorders are
rare and have no known effects, except in some
hyposecretion cases, weak labor contraction is
reported].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/endocrinesytem-241103095645-06ece183/85/Endocrine-system-anatomy-presentation-ps-15-320.jpg)
![ 2-Antiduretic Hormone:
(ADH) stimulates the reabsorption of water by renal tubes. Hyposcreation of the
hormone can result in diabetes insipidus[Hypersecretion
has no know effects, and hyposecretion causes
frequent urination called diabetes insipidus].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/endocrinesytem-241103095645-06ece183/85/Endocrine-system-anatomy-presentation-ps-16-320.jpg)


![SECRETION OF THE THYROID GLAND:
1- Calcitonin:
influence bone and calcium metabolism maintain a homeostasis of calcium in blood plasma. [Both
hyposecretion and
hypersecretion would affect normal balances of calcium and phosphate
2-Thyroxine and triiodothyronine:
essential to BMR - basal metabolic rate ,influence physical,mental development of
growth[Hyposecretion causes hypothyroidism, similar to
cretinism and myxedema, and hypersecretion causes hyperthyroidism
that results in a goiter or in Graves’ disease].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/endocrinesytem-241103095645-06ece183/85/Endocrine-system-anatomy-presentation-ps-19-320.jpg)
![SECRETIONS OF PARATHYROID GLAND:
The two pairs of parathyroid gland are located on
dorsal side of the thyroid gland.They secrete
parathyroid(PTH) which play a role in the
metabolism of phosphorus.Too little result in
cramping.Too much results in osteoporosis or
kidney stones. [Hyposecretion causes tetany, and
hypersecretion causes osteitis fibrosa cystica].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/endocrinesytem-241103095645-06ece183/85/Endocrine-system-anatomy-presentation-ps-20-320.jpg)
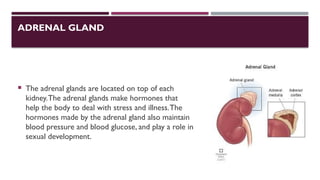
![SECRETIONS FROMTHE ADRENAL CORTEX:
1- Cortisol:
regulates carbohydrates, protein and fat metabolism has an anti-inflammatory effect
help the body cope during times of stress
2- Corticosterone:
Like cortisol it is steroid influences potassium and sodium
metabolism[Hyposecretion causes Addison’s disease ,
and hypersecretion causes Cushing’s syndrome].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/endocrinesytem-241103095645-06ece183/85/Endocrine-system-anatomy-presentation-ps-22-320.jpg)
![ 3- Aldosterone: •
Essential in regulating electrolyte and water balance by promoting sodium
and chloride retention and potassium excretion. Hyposecretion causes
Addison’s disease , and hypersecretion causes Cushing’s syndrome].
4- Androgens: •
Several hormones including testosterone they promote the development of secondary
sex characteristics in the male. [Hyposecretion causes congenital adrenal hyperplasia, and
hypersecretion causes gynecomastia in male](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/endocrinesytem-241103095645-06ece183/85/Endocrine-system-anatomy-presentation-ps-23-320.jpg)

![ 3- Norepinephrine:
Like epinephrine it release when the body is under stress.It creates the underlying
influences in the fight or flight response. [No known effects are due to hyposecretion
of these, but hypersecretion can caused hypertension, increased blood glucose level ,
and high heart rate].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/endocrinesytem-241103095645-06ece183/85/Endocrine-system-anatomy-presentation-ps-25-320.jpg)
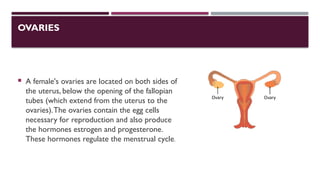
![SECRETION OFTHE OVARIES:
The ovaries produce several estrogen hormones and progesterone.These hormones
prepare the uterus for pregnancy promote the development of mammary glands.play
a role in sex drive and develop secondary sex characteristics in female. Estrogen is
essential for the growth and development of female sex organs. Both hyposecretion
and hypersecretion will have broad effects in female reproduction].Progesterone
Disorders are similar to estrogen](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/endocrinesytem-241103095645-06ece183/85/Endocrine-system-anatomy-presentation-ps-27-320.jpg)

![SECRETIONS OFTHETESTES:
The testes produce the male sex hormones called testosterone. It is essential for
normal growth and development of the male sex organs. • Testosterone is
responsible for the erection of the penis. Both hyposecretion and hypersecretion and
will have broad effects in male reproduction].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/endocrinesytem-241103095645-06ece183/85/Endocrine-system-anatomy-presentation-ps-29-320.jpg)

