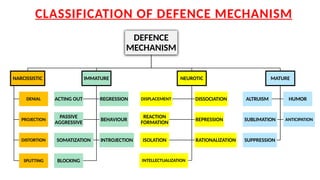
This document discusses Freud's psychoanalytic theory of defense mechanisms, defining them as unconscious strategies employed by the ego to protect against anxiety from unacceptable impulses. It classifies various defense mechanisms into categories based on their maturity, such as pathological, immature, neurotic, and mature defenses, providing examples for each. The conclusion highlights that while these mechanisms can reduce anxiety, their effectiveness and consequences depend on their context and usage.