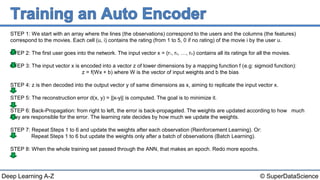
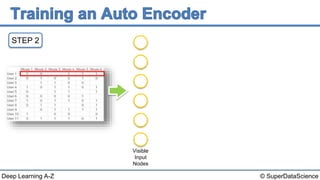
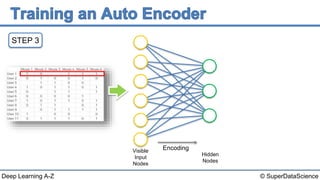
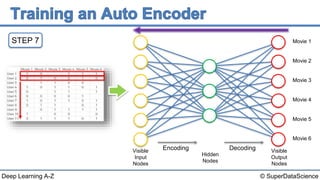
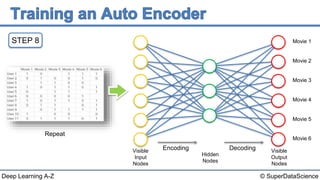
The document describes the steps to build an autoencoder using deep learning. It starts with a matrix of user ratings for movies as input data. It then walks through 8 steps: 1) preparing the input data, 2) feeding an individual user's ratings into the network as input, 3) encoding the input into a lower dimensional representation, 4) decoding the encoded representation back into ratings, 5) calculating the reconstruction error, 6) backpropagating the error to update weights, 7) repeating for each user or batch of users, and 8) repeating the process over multiple epochs until completion.