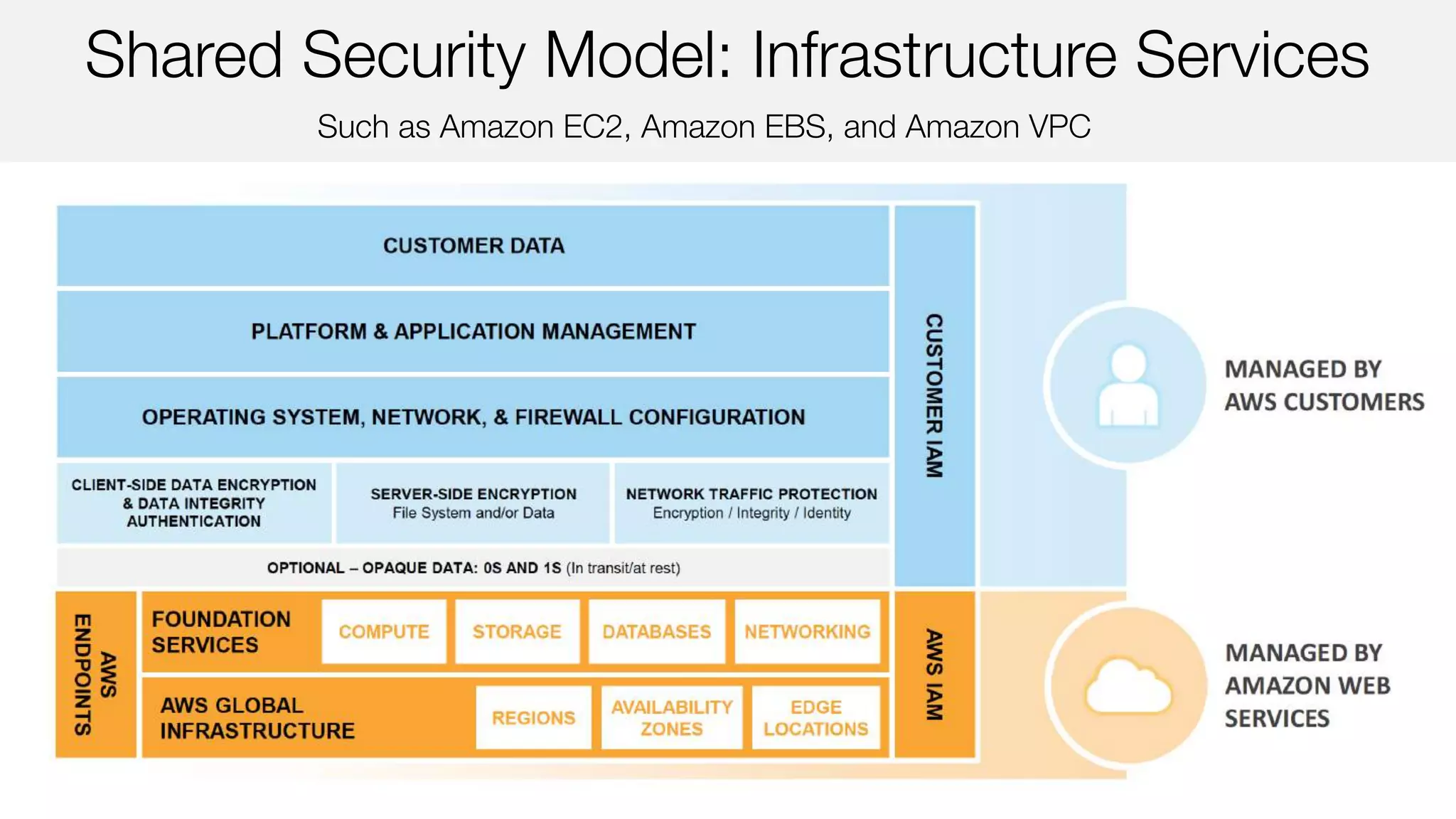
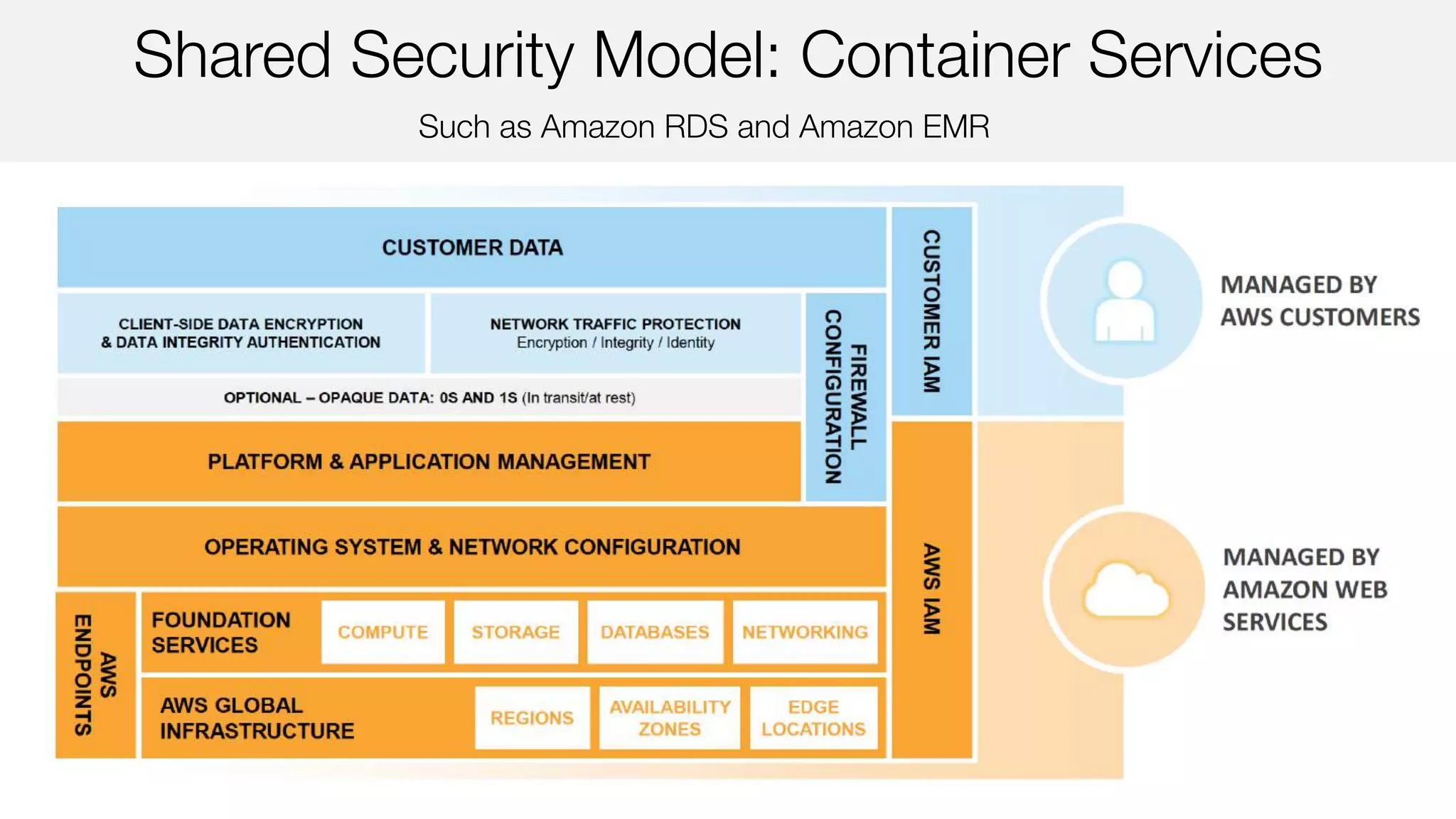
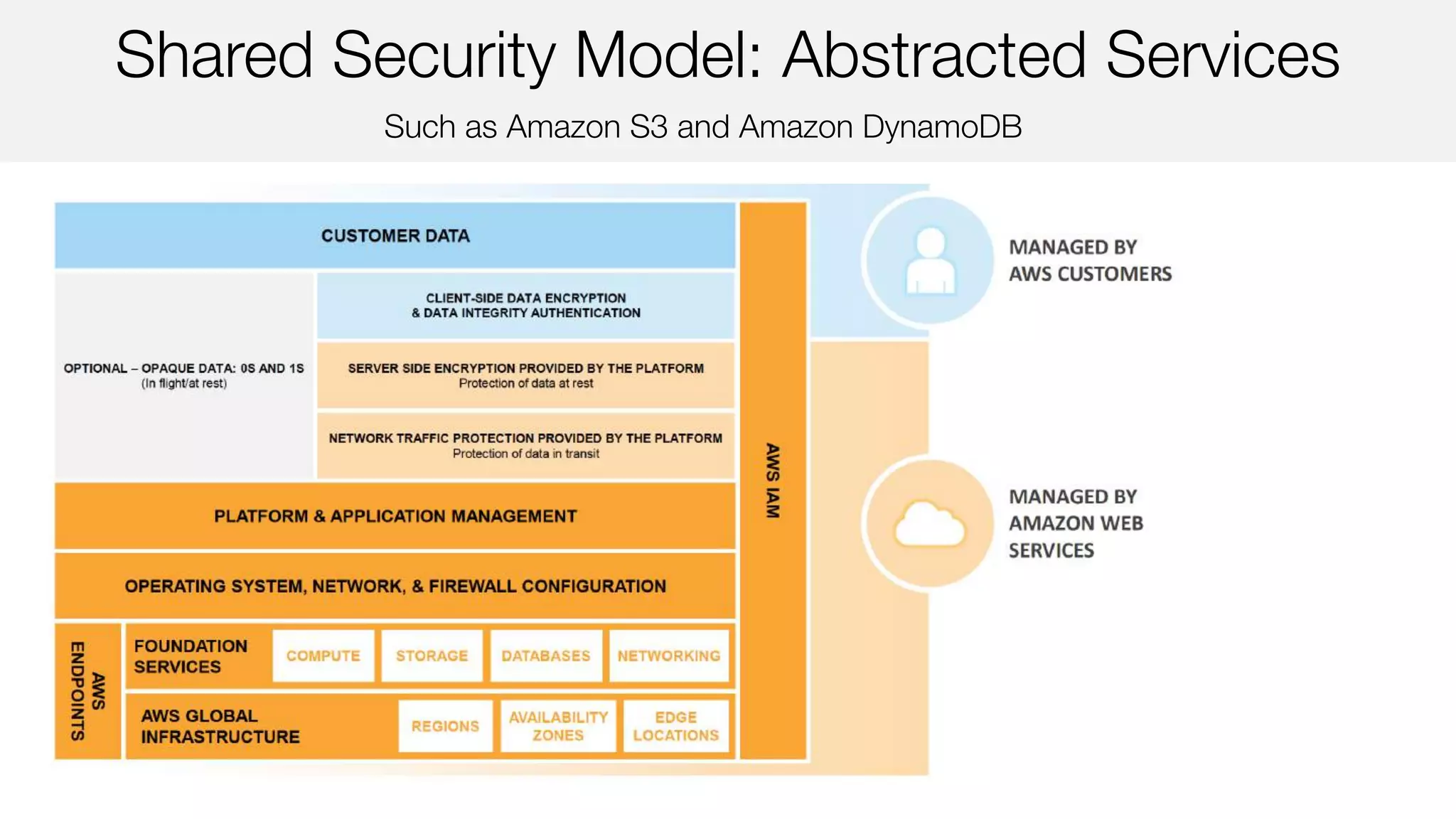
The document outlines AWS security best practices, detailing the shared responsibility model where AWS handles physical and infrastructure security while customers manage application and data security. It provides guidance on implementing a secure cloud environment through identity and access management, data encryption, and compliance with various certifications like ISO 27001 and PCI DSS. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of monitoring, logging, and incident response to enhance security posture in AWS deployments.




























![Secure Your Data
At rest & in transit
Resource Access Authorisation
Users or IAM Roles can only access resources after authentication
Fine-grained resources policies can restrict users or permit users to access only
the resources that you specify
{
"Effect": "Allow”,
"Action": ["s3:GetObject”,"s3:PutObject”],
"Resource": ["arn:aws:s3:::myBucket/amazon/snakegame/${cognito-identity.amazonaws.com:sub}"]
}
7](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/securitybestpractices-170212170636/75/Security-Best-Practices-AWS-AWSome-Day-Management-Track-34-2048.jpg)