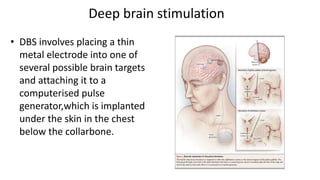
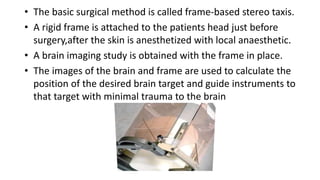
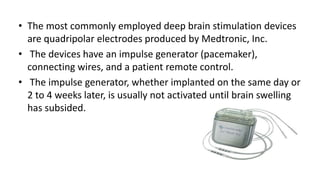
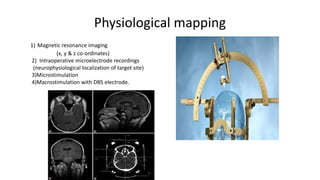
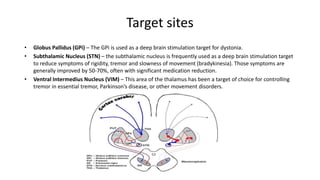
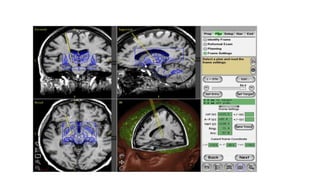
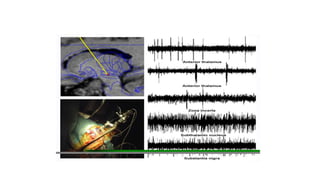
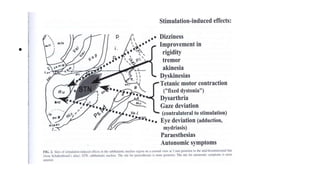
Parkinson's disease (PD) is a degenerative disorder affecting the central nervous system, characterized by motor symptoms such as shaking, rigidity, and slowness, with treatments ranging from medications like levodopa to surgery, including deep brain stimulation (DBS). DBS involves implanting an electrode to deliver electrical impulses to specific brain areas, effectively reducing symptoms, especially tremors. Ongoing advancements in neuroscience and technology aim to enhance DBS techniques and explore new therapeutic avenues for managing PD.