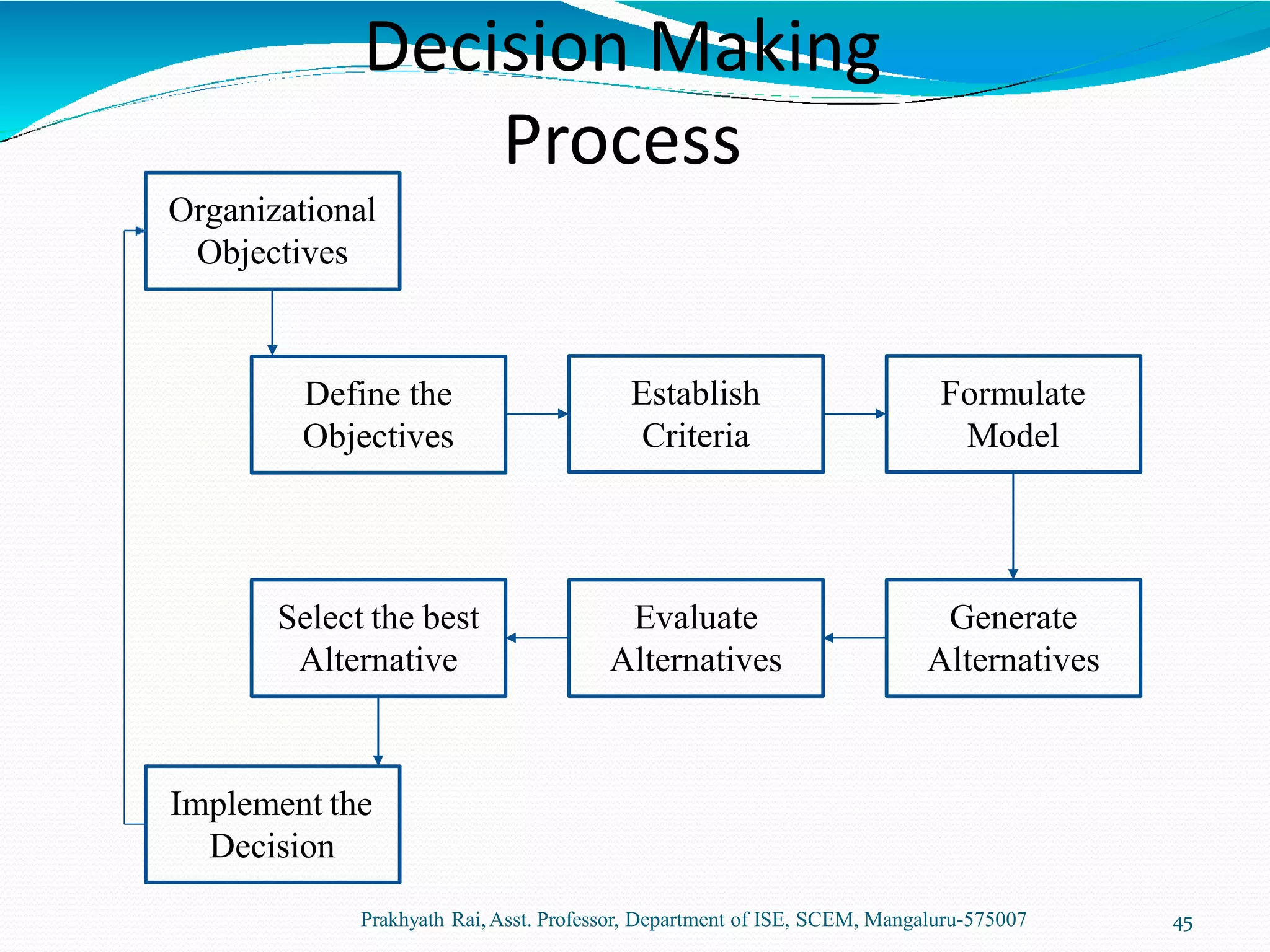
This document discusses decision making in organizations. It describes decision making as the cognitive process of selecting a course of action from alternatives. It then lists some key characteristics of decision making, such as being goal-oriented, analytical, and situational. The document outlines the typical decision making process, which involves defining objectives, establishing criteria, generating and evaluating alternatives, selecting the best alternative, and implementing and monitoring the decision. Finally, it discusses some quantitative techniques used in decision making, selecting techniques based on the level of certainty in the variables.