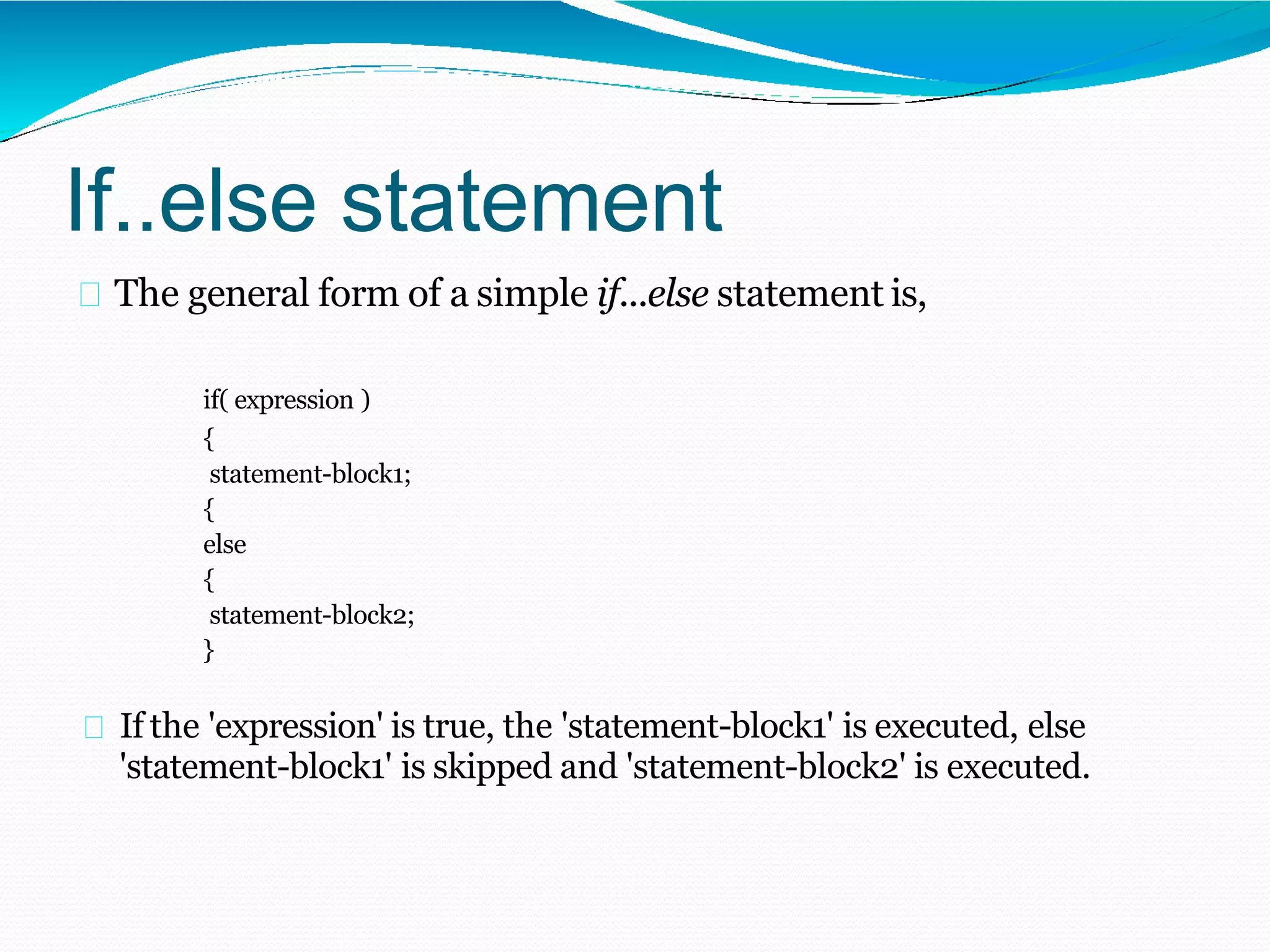
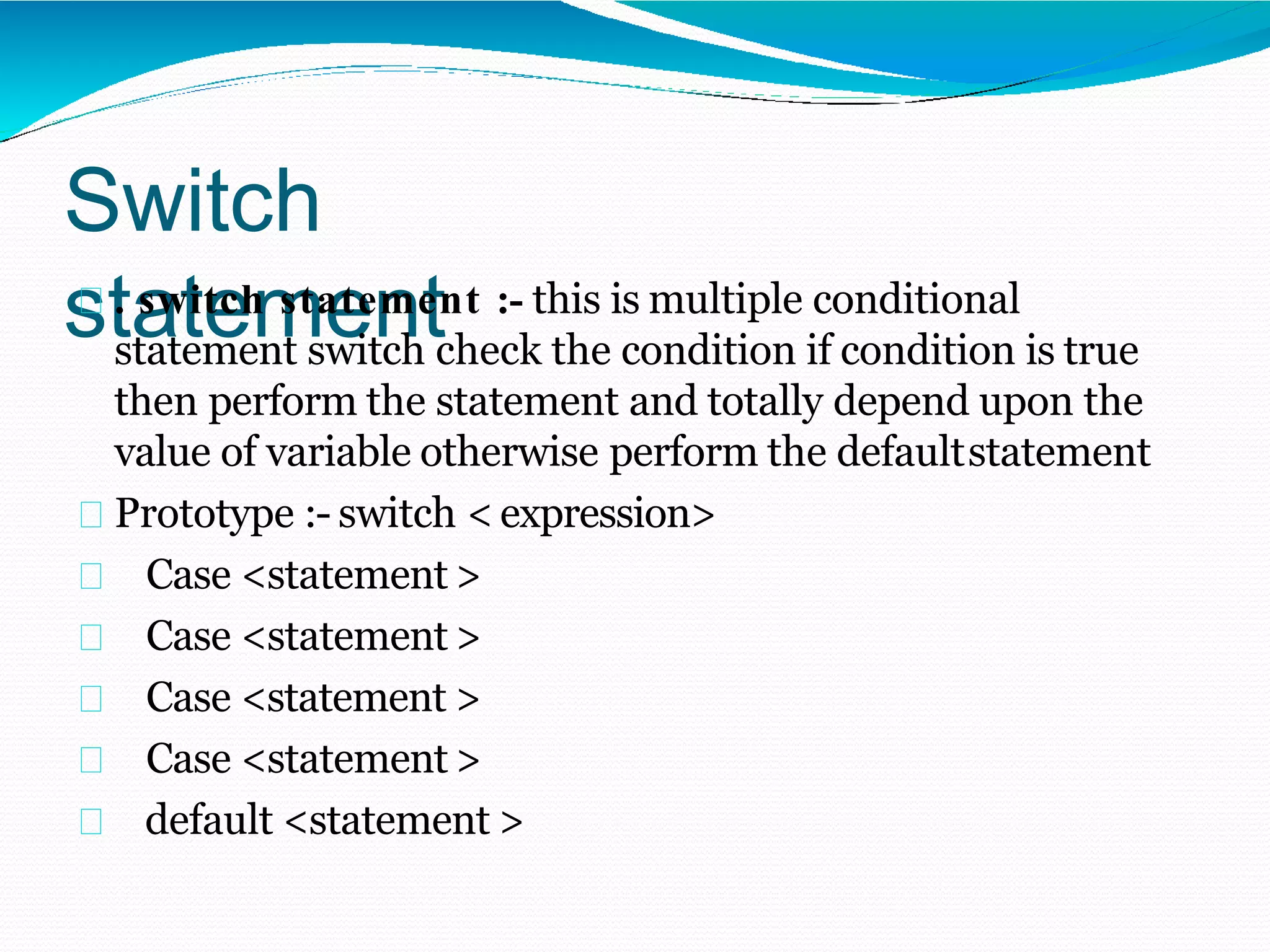
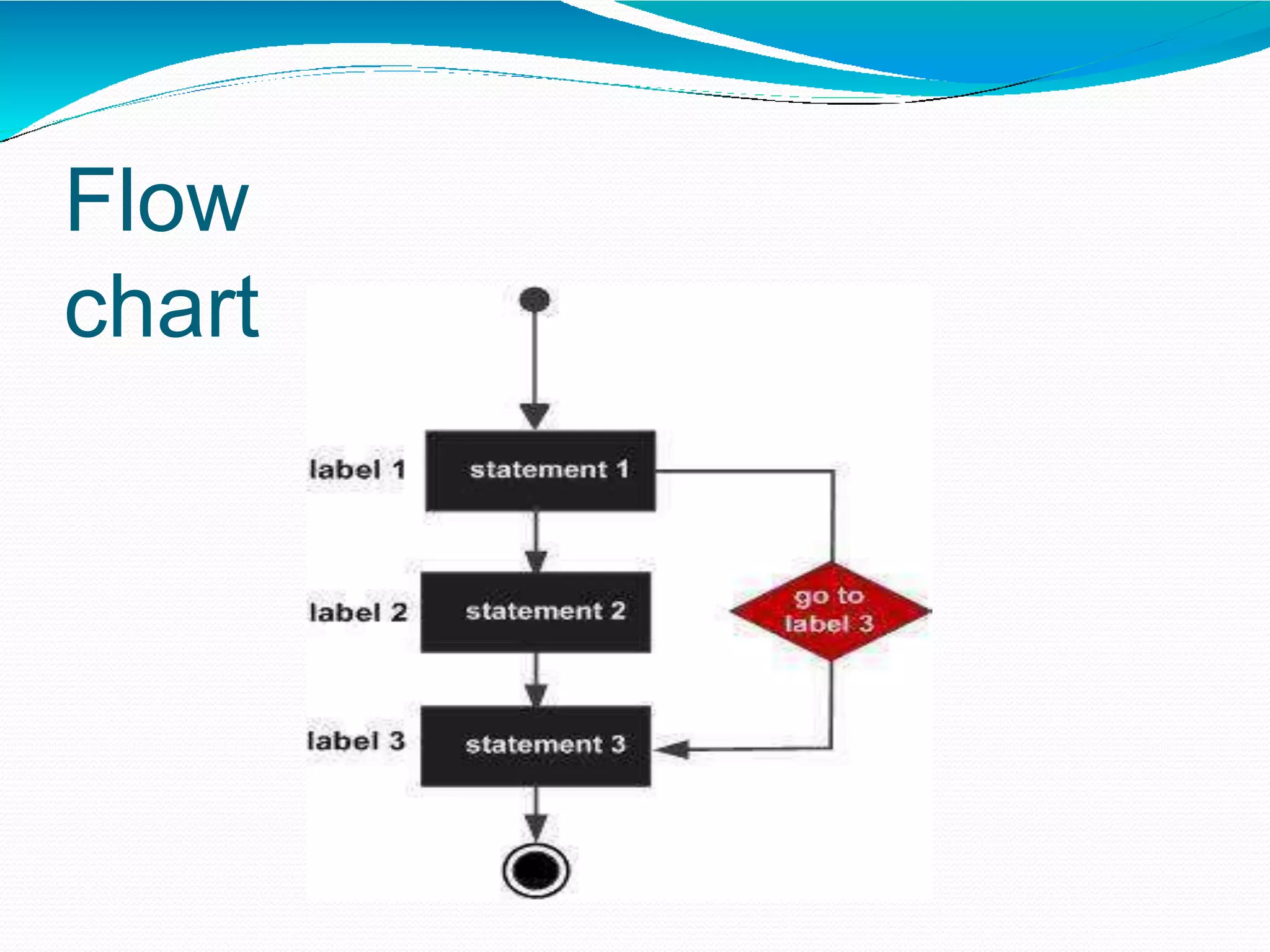
The document discusses different types of decision making statements in C++ including if, if-else, nested if-else, switch, and goto statements. It provides the syntax and examples of using each statement type to control program flow based on certain conditions. Algorithm is defined as a step-by-step procedure to solve a problem before writing an actual program, and flowcharts use symbols like flow lines, terminals, and inputs/outputs to visually represent the logic of a program.