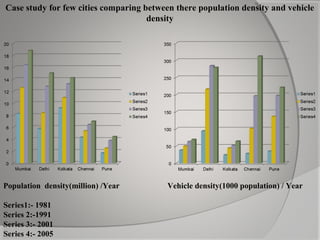
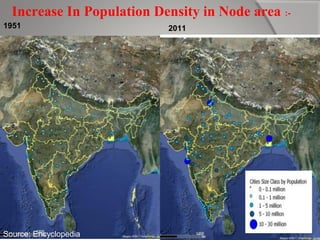
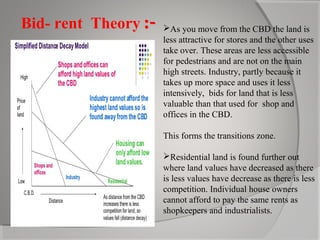
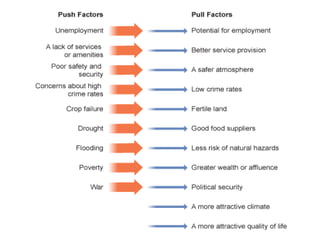
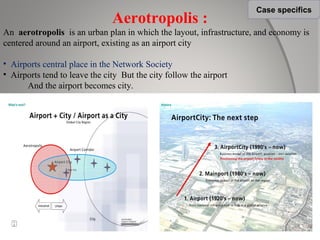
This document provides an overview of decentralization and theories of migration. It discusses concepts of decentralization including city evolution driven by factors like the motor age and globalization. It describes nodes for decentralization like recreational, educational, and technological areas. The document also summarizes push-pull factors and theories of migration. Specific examples of cultural intricacies in migration patterns in regions like the Middle East, Africa, and North Africa/Southwest Asia are provided. The concept of an aerotropolis centered around an airport is introduced with examples.