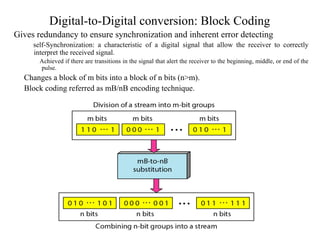
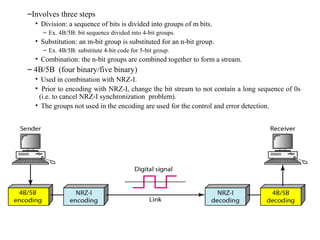
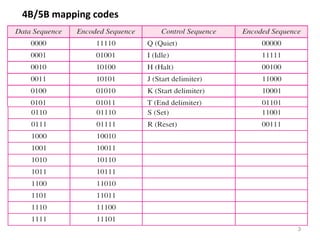
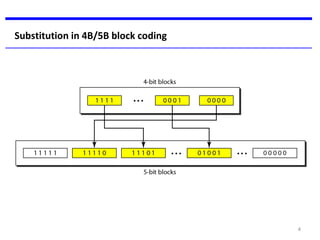
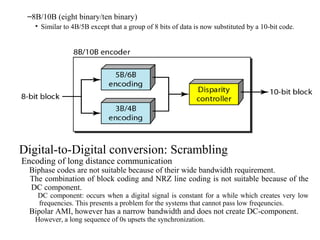
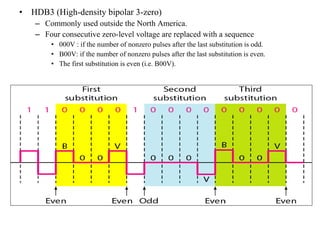
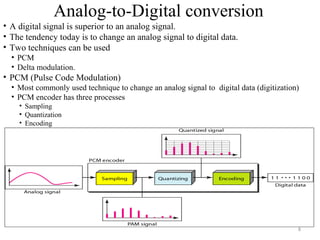
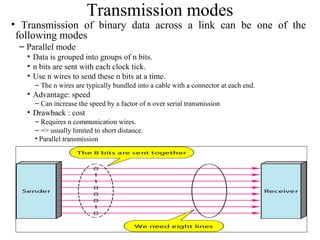
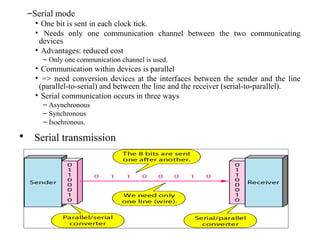
Block coding involves dividing a bit stream into blocks, substituting code blocks for data blocks, and combining the code blocks. It provides error detection and ensures synchronization. 4B/5B and 8B/10B block codes map 4- and 8-bit groups to 5- and 10-bit codes. Scrambling techniques like B8ZS and HDB3 modify AMI encoding to prevent long runs of zeros from disrupting synchronization. PCM converts analog signals to digital using sampling, quantization, and encoding. It samples the signal, assigns amplitude levels, and encodes each sample as a code word. Transmission can be parallel, sending multiple bits simultaneously over multiple wires, or serial, sending one bit at a time over

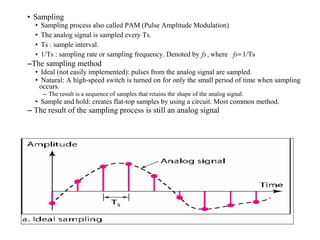
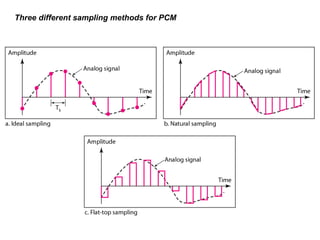
![– Sampling rate
• Nyquist theorem: to reproduce the original analog signal the sampling rate
should be at least equal to twice the highest frequency of the original signal.
– Example
• Telephone companies digitize voice assuming a maximum frequency of
4000Hz.
– The sampling rate is therefore 8000 samples per second.
•What sampling rate is needed for a signal with a bandwidth of 10000Hz
[1000,11000]Hz?
– The sampling rate must be twice the highest frequency of the signal
– Sampling rate = 2*11000 = 22000 samples/second.
• A complex low-pass signal has a bandwidth of 200KHz. What is the minimum
sampling rate for this signal?
– The bandwidth of a low-pass signal is between 0 and f (f is the maximum frequency).
– So f=200KHz and the sampling is done at : 2*200KHz=400000 samples/s.
•Quantization
– Steps of quantization
1. Assume the original analog signal has instantaneous amplitudes between Vmin and Vmax.
2. Divide the range into L zones each of high ∆
• Formula : ∆= Vmax–Vmin / L
1. Assign quantized values of 0 to L-1 to the midpoint of each zone.
2. Approximate the value of the sample amplitude to the quantized values.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dc4-t1-180423125401/85/Dc4-t1-11-320.jpg)
![– Quantization levels
• The choice of L, the number of levels, depend on the range of the amplitudes of the
analog signal and the accuracy to recover the signal.
– If the amplitude fluctuates between two levels => L=2.
– With audio digitizing => L=256.
–Quantization errors
• The input values to the quantizer are the real values.
• The output values are the approximate values and are chosen in the middle of the zone.
• The difference between the real values and the approximate values is the quantization
error.
– Example
• Assume a sample signal with the sample amplitudes in [-20,20]V. Nine samples are
shown using ideal sampling.
• Quantization levels with L=8 => ∆=5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dc4-t1-180423125401/85/Dc4-t1-12-320.jpg)
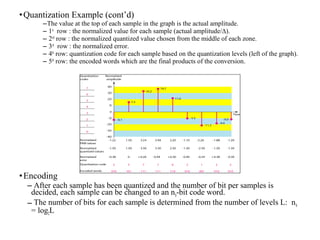
![–Previous example
• nb = log2L = 3bits. A quantization code of 2 is encode as 010.
–Bit rate = sampling rate * number of bits per sample => Bit rate = fs* nb
– Example
• What is the bit rate to digitize the human voice assuming 8 bits per sample.
–Frequencies of the human voice [0,4000]Hz. Sampling rate = 4000*2 = 8000 samples/s Bit rate = 8000*8
= 64000 bps = 64 Kbps.
•Signal recovery
– Requires a PCM decoder.
– The decoder converts the code words into a pulse that holds the amplitude until the next
pulse.
– The resultant staircase signal is passed through a low-pass filter to smooth it into an
analog signal.
• The filter has the same cutoff frequency as the original signal at the sender.
– If the signal has been sampled >= the Nyquist sampling rate and if there is enough
quantization levels => the original signal will be recreated.
– The minimum and maximum values of the original signal can be achieved by using
amplification.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dc4-t1-180423125401/85/Dc4-t1-14-320.jpg)

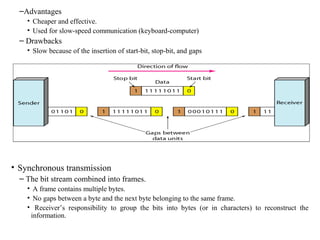
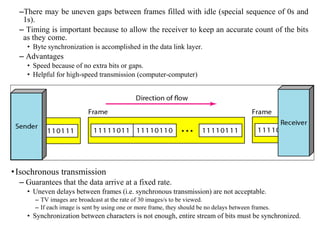

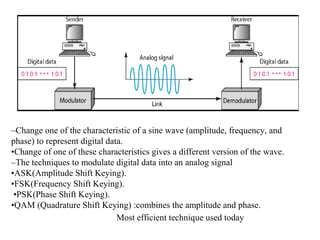

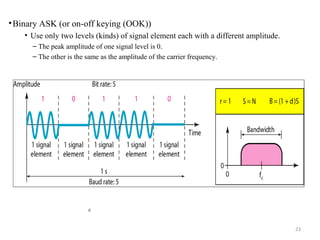
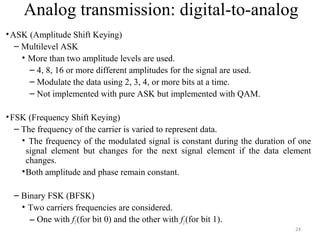
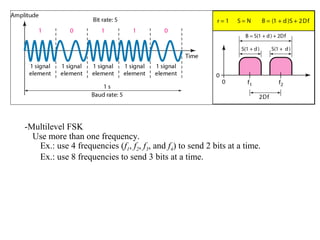
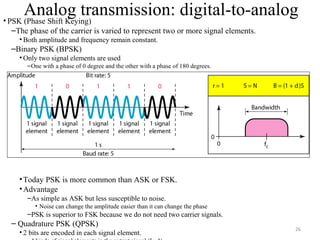
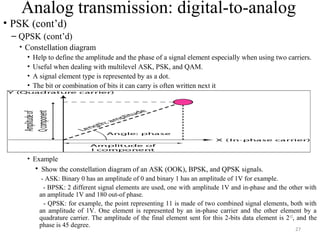
![30
Analog transmission: analog-to-analog• AM (cont’d)
– Standard bandwidth allocation for AM radio
• The bandwidth of an audio signal (speech and music) is usually 5 KHz.
• An AM station bandwidth should be 10KHz.
• Federal Communication Commission (FCC)
– AM stations are allowed frequencies in [530, 1700]KHz
– Each AM station is assigned 10KHz.
– To avoid interference: each station carrier frequency must be separated from those on either sides by at least
10KHz.
• FM
–The frequency of the carrier signal is modulated to follow the voltage level (amplitude) of the
modulated signal.
• The peak amplitude and the phase of the carrier signal remain constant.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dc4-t1-180423125401/85/Dc4-t1-30-320.jpg)
![31
Analog transmission: analog-to-analog• FM (cont’d)
–Standard Bandwidth Allocation for FM Radio
• Bandwidth of an audio signal broadcast in stereo is 15KHz.
• FCC allows 200KHZ for each station.
• FM stations allowed carrier frequencies in [88, 108]MHz.
• Stations separated by 200KHz.
• To avoid more interfering, alternate bandwidth allocation may be used.
• PM
– The phase of the carrier signal is modulated to follow the changing amplitude of the modulated signal.
• The peak amplitude and the frequency of the carrier signal remain constant.
• Proved mathematically: PM is the same as FM.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dc4-t1-180423125401/85/Dc4-t1-31-320.jpg)