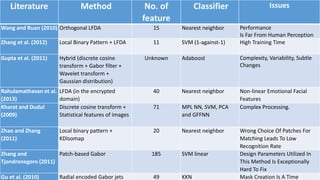
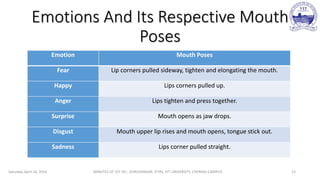
The document discusses facial emotion recognition including the challenges, approaches, and applications. It summarizes the key phases of facial emotion recognition: face acquisition, feature point extraction and tracking, and facial expression classification. Common techniques are discussed for each phase, including Haar cascade classifiers for face detection, active appearance models for feature tracking, and support vector machines or neural networks for classification. Overall challenges include dealing with variability in imaging conditions and achieving optimal preprocessing, feature extraction, and classification for successful recognition performance. The student's aim is to choose optimized feature points, transform them to mathematical models for better classification, and train machine learning models to improve recognition.
















![References
[1] P. Ekman, W.V. Friesen, “Constants across cultures in the face and emotion”, J.Personality Social Psychol. 17 (2),124–129, 1971.
[2] Paul Viola, Michael J. Jones, “Robust Real-Time Face Detection”, International Journal of Computer Vision 57(2), 137–154, 2004.
[3] P. Ekman and W. Friesen. “The Facial Action Coding System: A Technique for the Measurement of Facial Movement”, Consulting Psychologists Press, San Francisco, 1978.
[4] Kotsia.I, Pitas.I, “Facial Expression Recognition in Image Sequences using Geometric Deformation Features and Support Vector Machines”, IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, pages(s): 172 - 187 ,
Jan. 2007.
[5] T.F. Cootes, G. Edwards, C. Taylor, “Comparing active shape models with active appearance models”, in: Proceedings of British Machine Vision Conference, BMVA Press, pp. 173–182, 1999.
[6] Ying-li Tian, Takeo Kanade, and Jeffrey F. Cohn, “Recognizing Action Units for Facial Expression Analysis”, IEEE Transactions On Pattern Analysis And Machine Intelligence, Vol. 23, No. 2, February 2001.
[7] Maurício Pamplona Segundo, Luciano Silva, Olga Regina Pereira Bellon, “Automatic Face Segmentation and Facial Landmark Detection in Range Images”, IEEE Transactions On Systems, Man, And
Cybernetics—Part B: Cybernetics, Vol. 40, No. 5, October 2010.
[8] Irene Kotsia, Ioan Buciu, Ioannis Pitas, “An analysis of facial expression recognition under partial facial image occlusion”, Image and Vision Computing 26 ,1052–1067, 2008.
[9] José M. Buenaposada, Enrique Muñoz, Luis Baumela “Efficient illumination independent appearance-based face tracking”, Image and Vision Computing Volume 27, Issue 5, Pages 560–578, April 2009.
[10]Mahdi Ilbeygi a,n, HamedShah-Hosseini, “A novel fuzzy facial expression recognition system based on facial feature extraction from color face images”, Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence
25 (2012) 130–146.
Saturday, April 16, 2016 MINUTES OF 1ST DC:- SIVASHANKAR, IFTRS, VIT UNIVERSITY, CHENNAI CAMPUS 24](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/9fef2425-d783-4095-9ee7-441484e66abd-160416050900/85/DC_1-24-320.jpg)