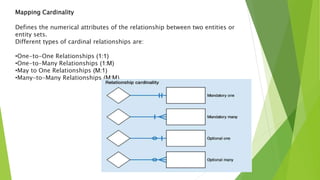
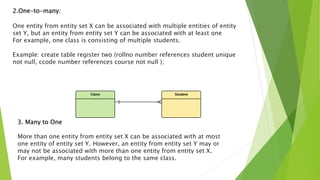
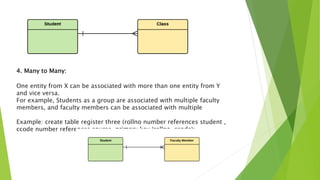
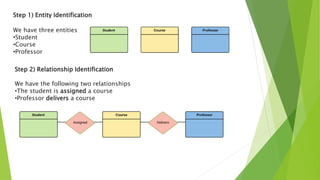
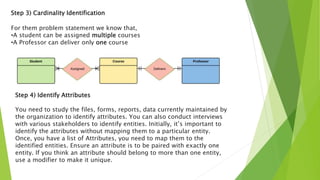
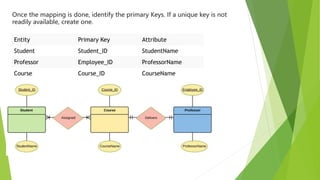
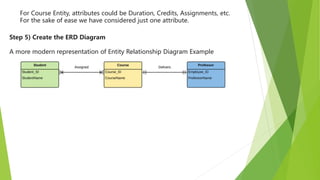
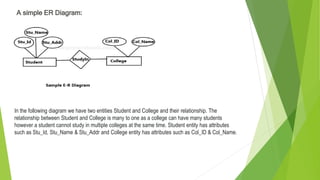
This document discusses entity relationship diagrams and how to create them. It defines the different types of cardinal relationships as one-to-one, one-to-many, many-to-one, and many-to-many. It provides examples of each type of relationship. The document then outlines the steps to create an ER diagram, including identifying entities, relationships, cardinality, and attributes. It provides an example of an ER diagram for a university with students, courses, and professors.