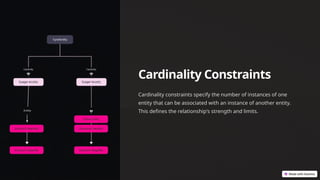
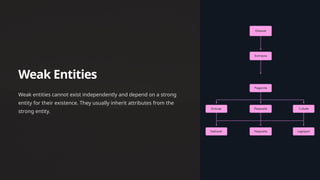
An ER diagram visually represents data and relationships within a database, serving as a blueprint for database schema design. It consists of entities, attributes, and cardinality constraints, aiding in understanding data relationships and improving database design. ER diagrams facilitate clear communication among stakeholders and reduce development time by streamlining the design process.