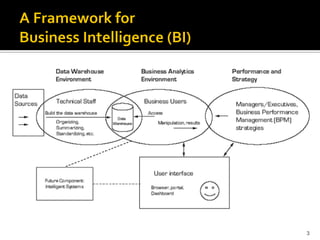
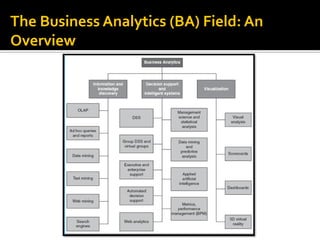
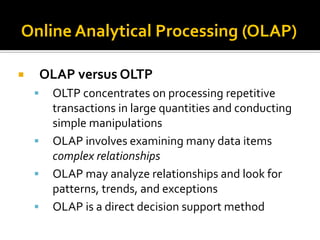
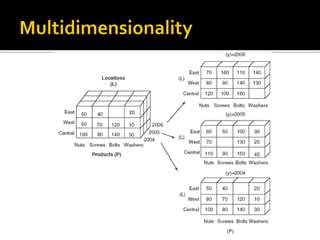
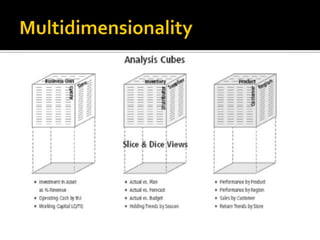
BI's architecture includes a data warehouse, business analytics, and performance and strategy components. Business analytics involves applying models directly to business data using management support systems and decision support. Online analytical processing (OLAP) creates new business information through calculations on existing data using graphical tools that provide multidimensional views of data and allow for simple analysis. OLAP differs from OLTP in examining complex relationships across many data items.