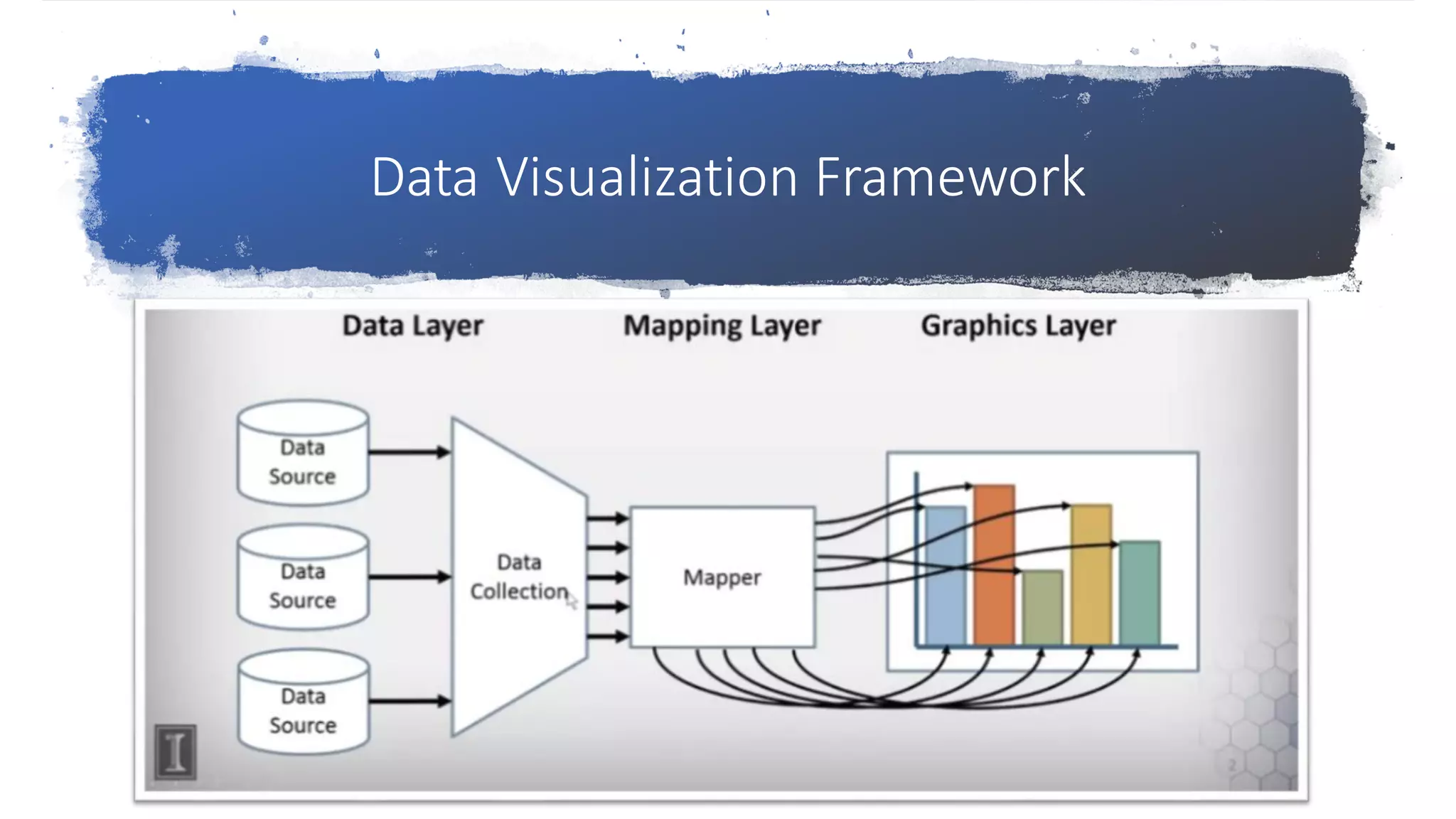
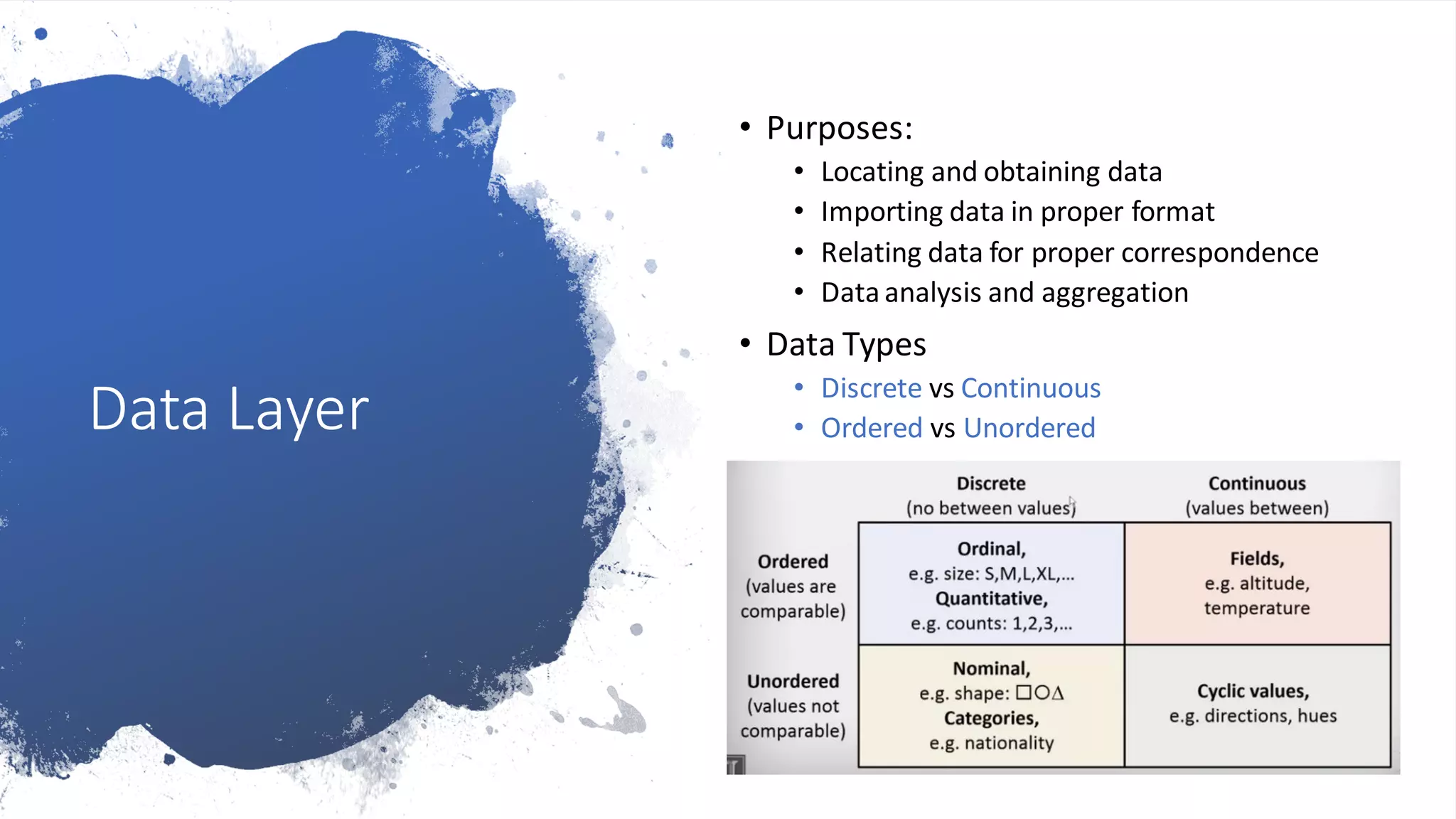
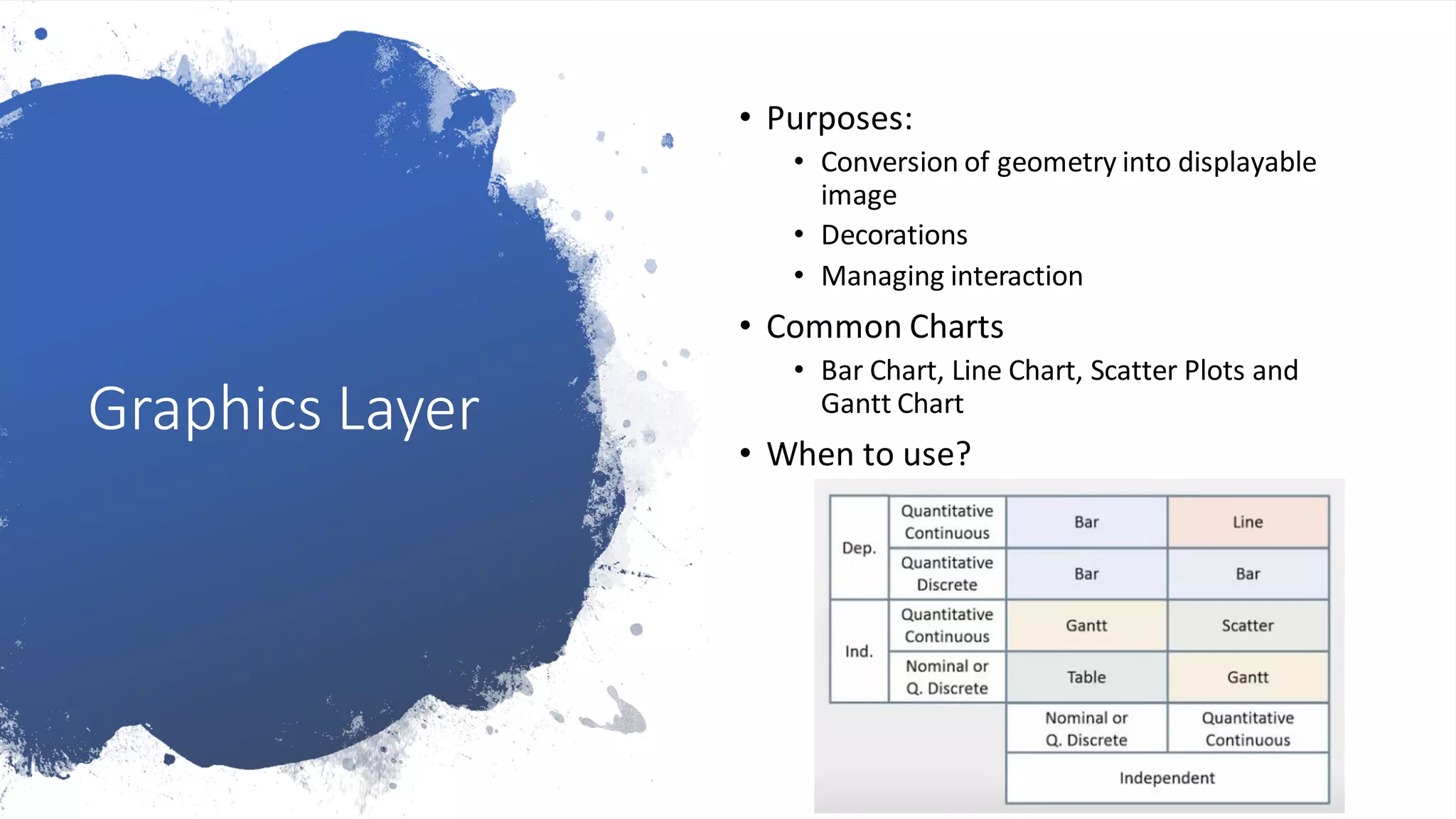
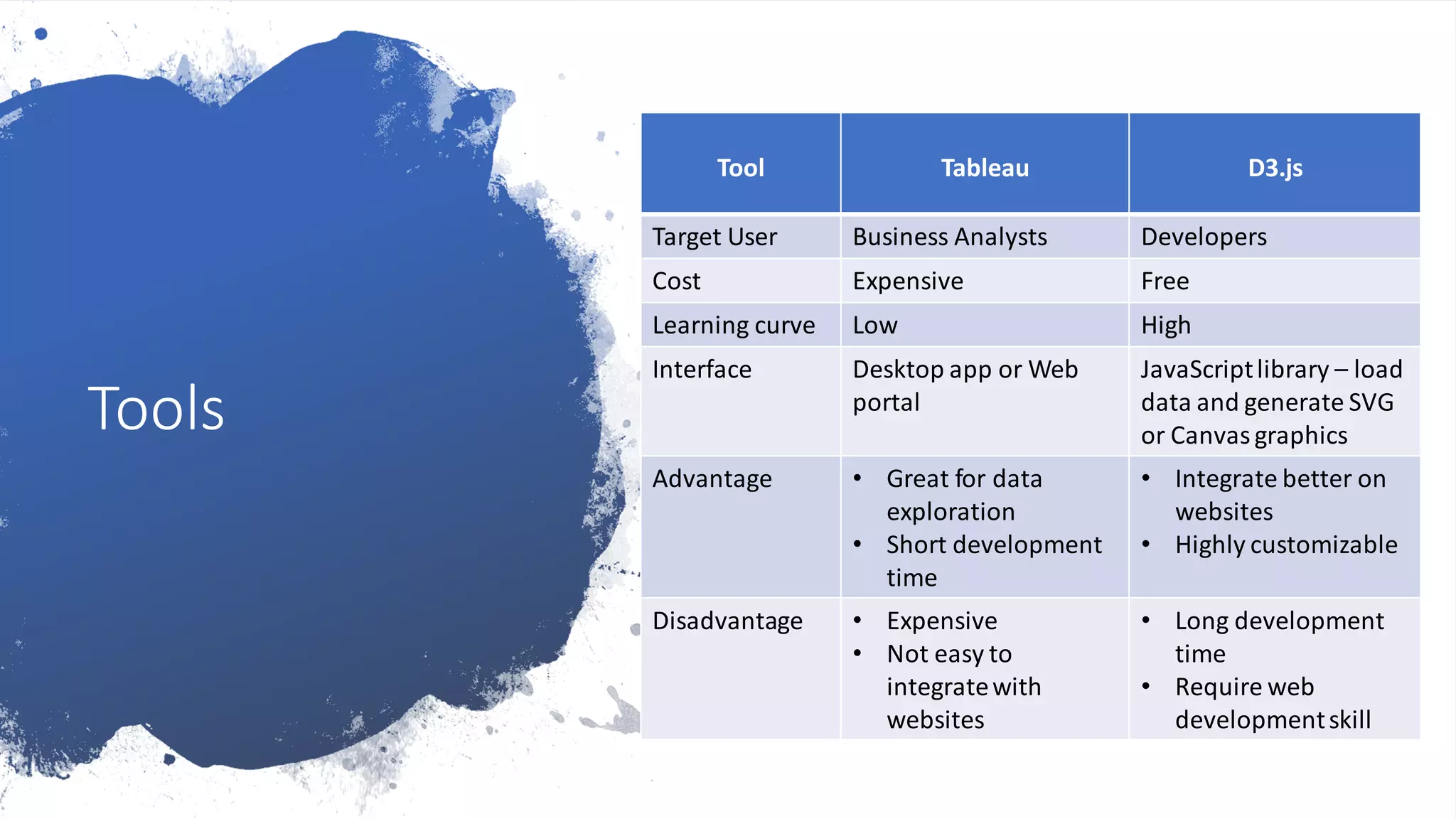
The document presents an overview of data visualization, explaining its importance in analyzing large data sets through graphical representations like charts and maps. It outlines a data visualization framework consisting of data, mapping, and graphics layers, and discusses three styles of data visualization: interactive, presentation, and storytelling. Additionally, it compares two popular tools, Tableau and D3.js, highlighting their target users, costs, and advantages and disadvantages.