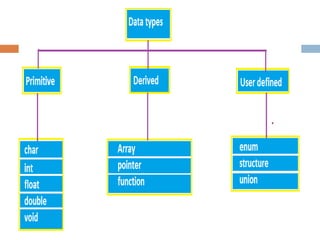
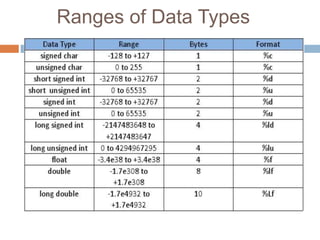
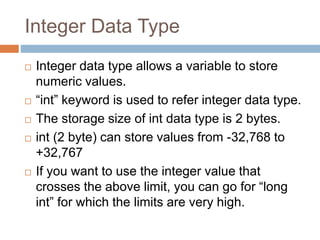
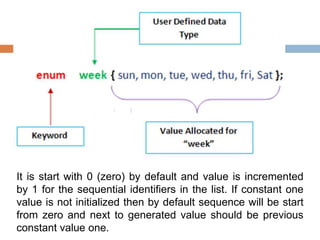
Data types define the type of data that variables can store in a C program. There are three main types of data types: primitive, derived, and user-defined. Primitive types include integer, character, float, and double, which store numeric or character values of different ranges and sizes. Derived types are based on primitive types, while user-defined types like enums allow the user to define their own custom data types as a series of integer constants.