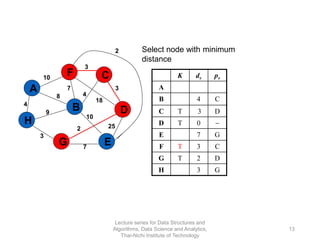
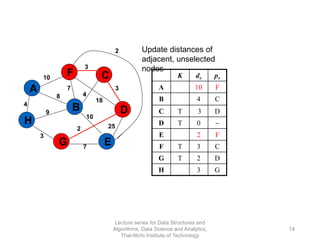
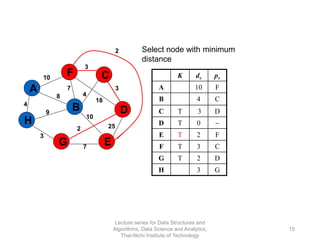
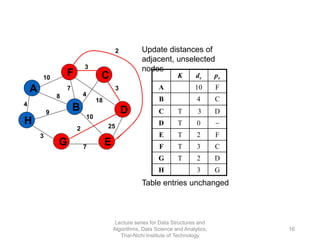
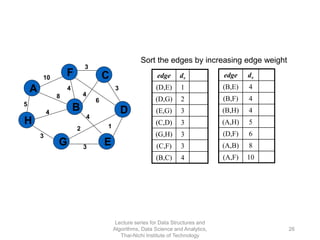
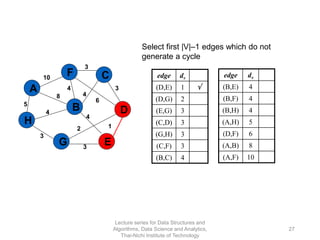
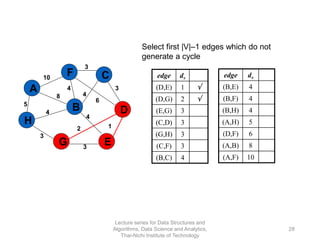
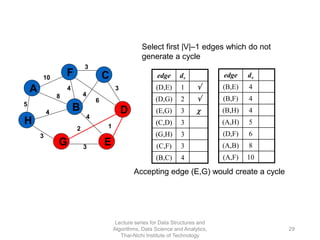
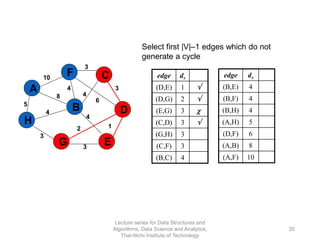
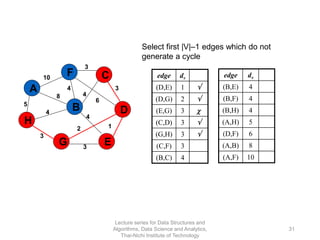
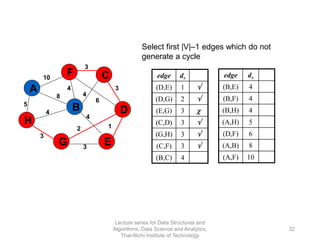
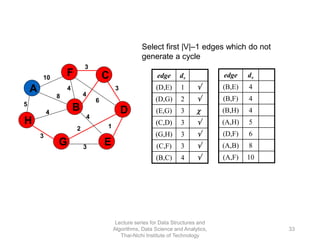
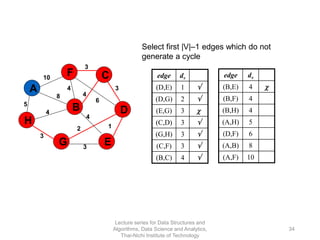
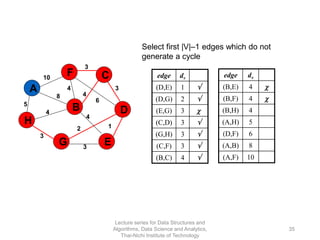
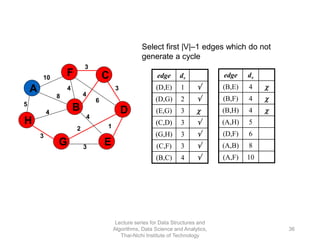
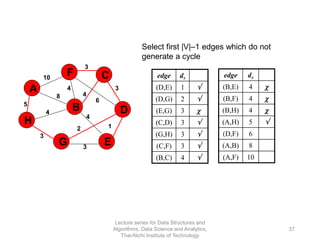
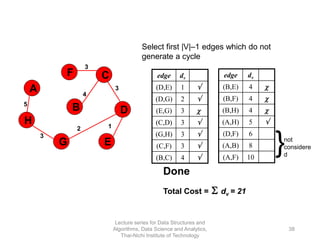
The document discusses minimum spanning trees and provides examples of Prim's and Kruskal's algorithms. It includes:
- A definition of minimum spanning tree as a subgraph that spans all nodes with minimum total edge weight.
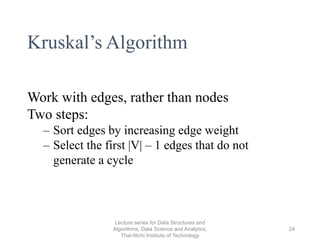
- Characteristics of Prim's and Kruskal's algorithms such as working with undirected, weighted/unweighted graphs and producing optimal solutions greedily.
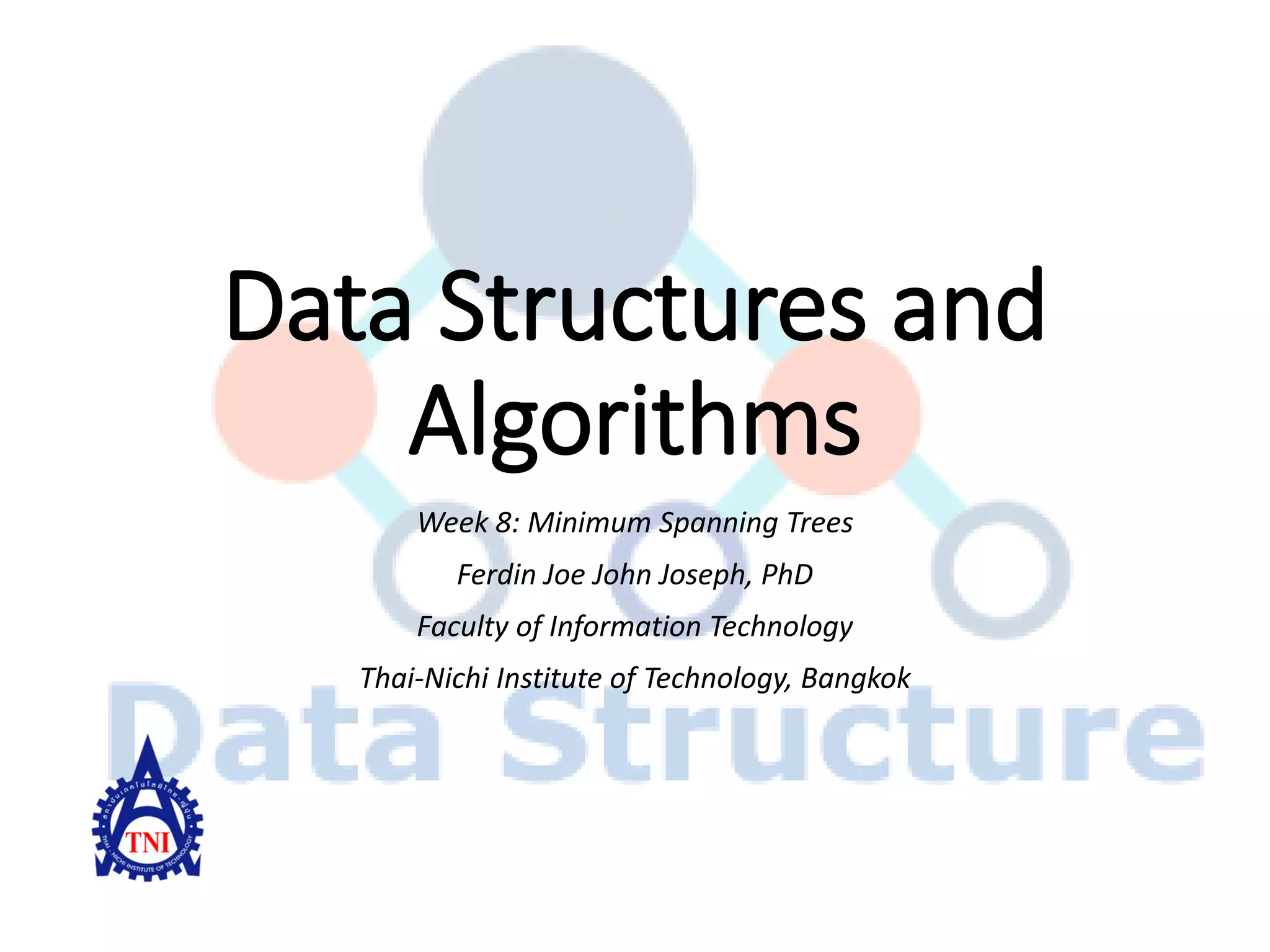
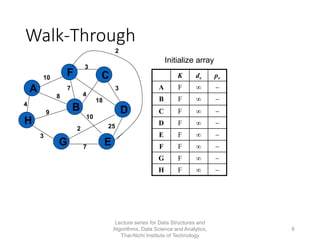
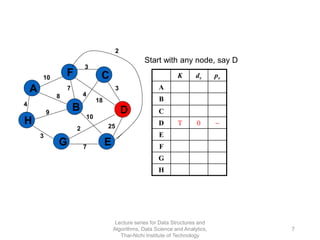
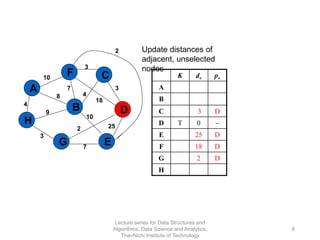
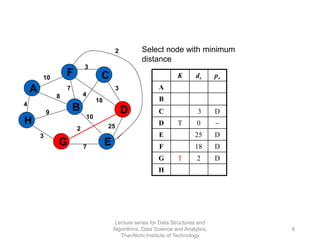
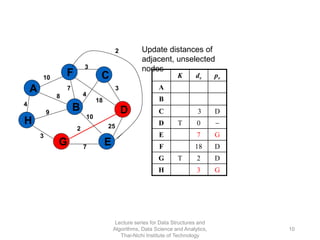
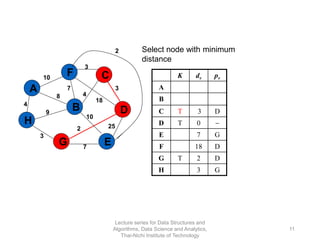
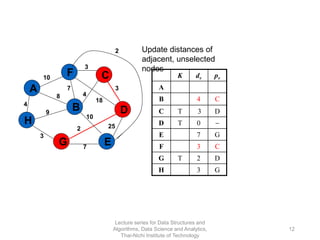
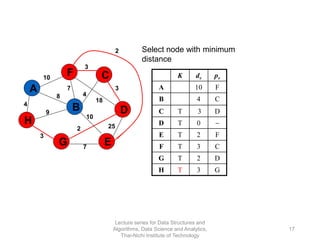
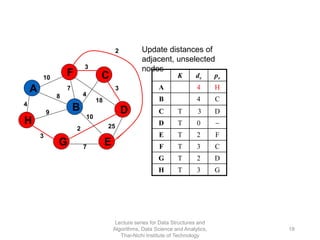
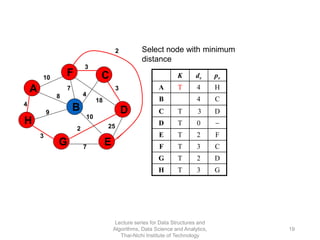
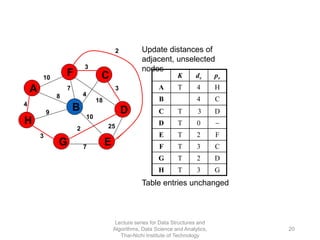
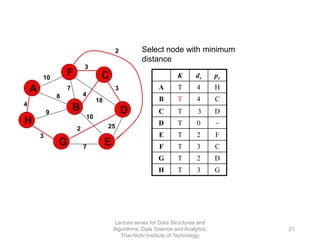
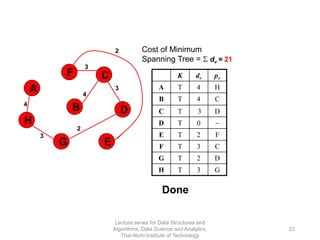
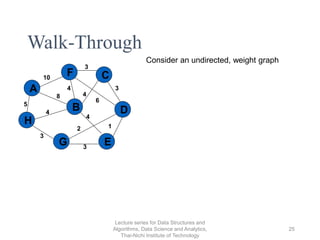
- A walk-through example of Prim's algorithm on a graph and calculating the minimum spanning tree cost.