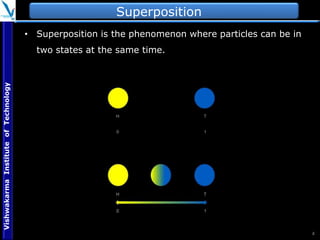
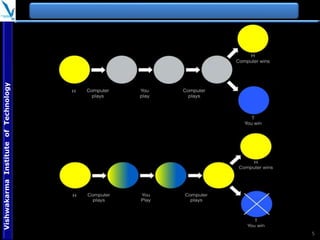
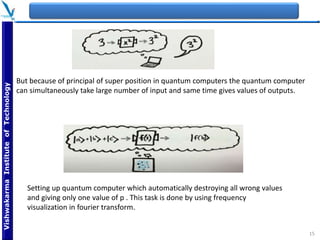
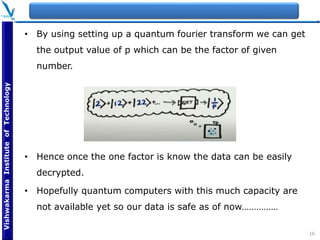
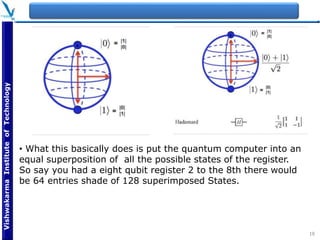
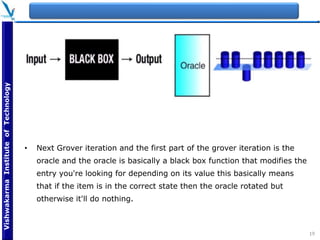
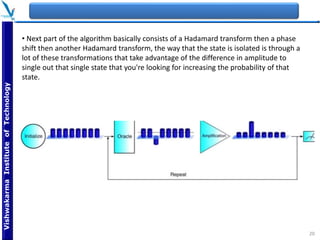
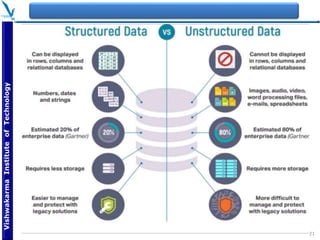
The document provides an overview of quantum computing, explaining key concepts such as superposition, entanglement, and quantum algorithms like Shor's and Grover's algorithms. It discusses the potential advantages of quantum computers over classical computers, particularly in fields like cryptography and optimization, while highlighting their transformative impact on industries such as pharmaceuticals and material science. The document also addresses concerns regarding security and the implications of quantum computing on data privacy.