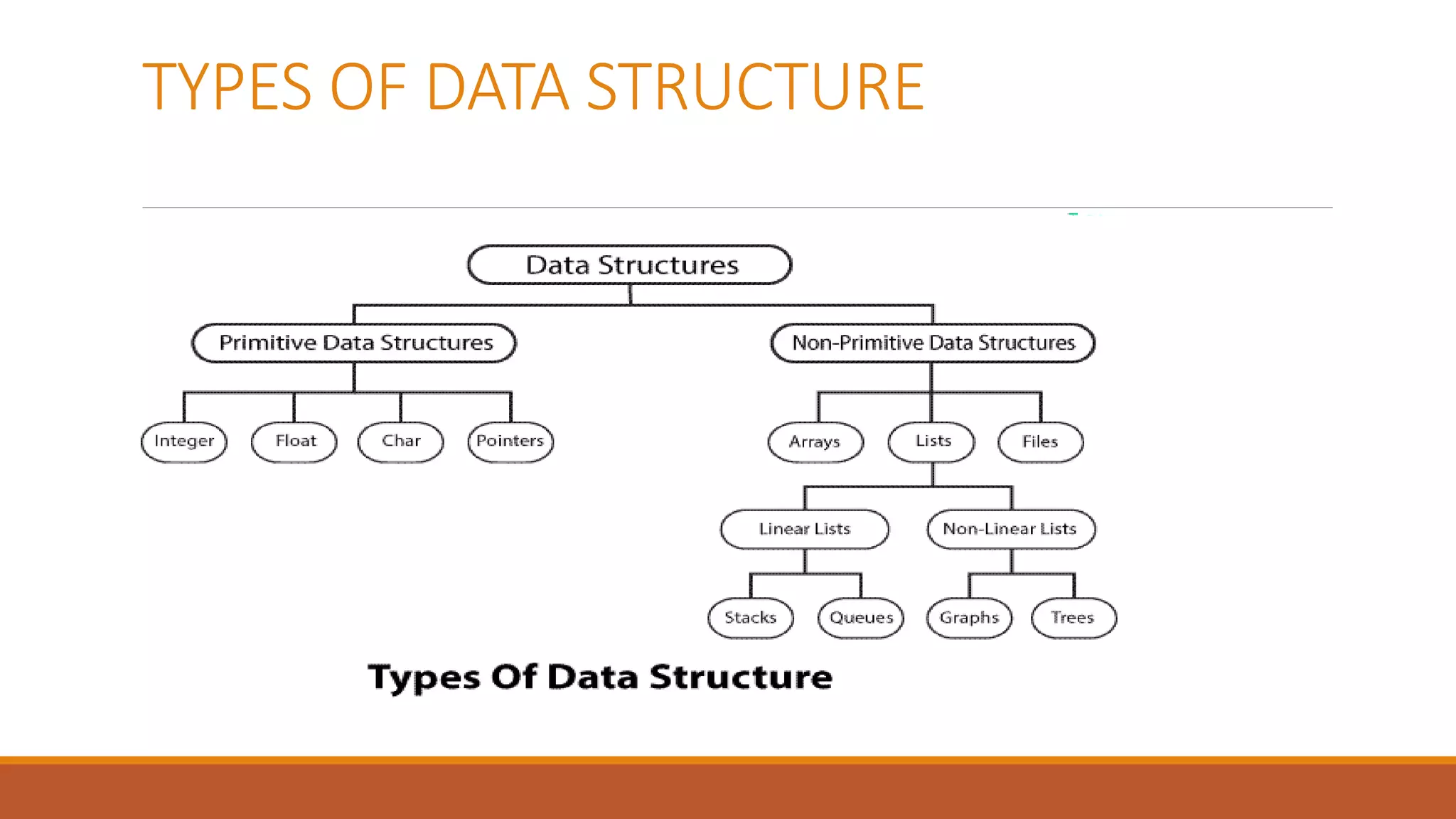
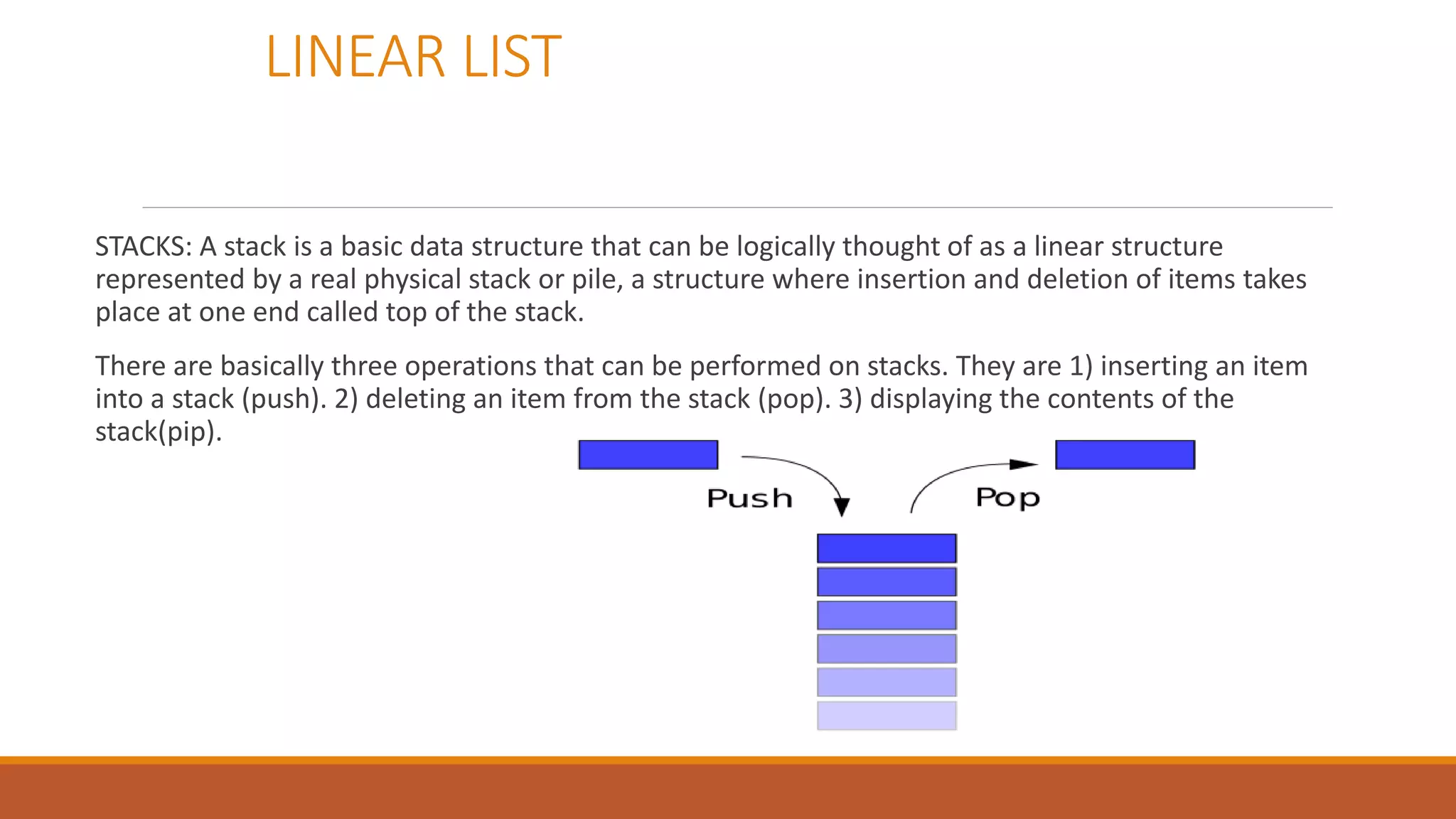
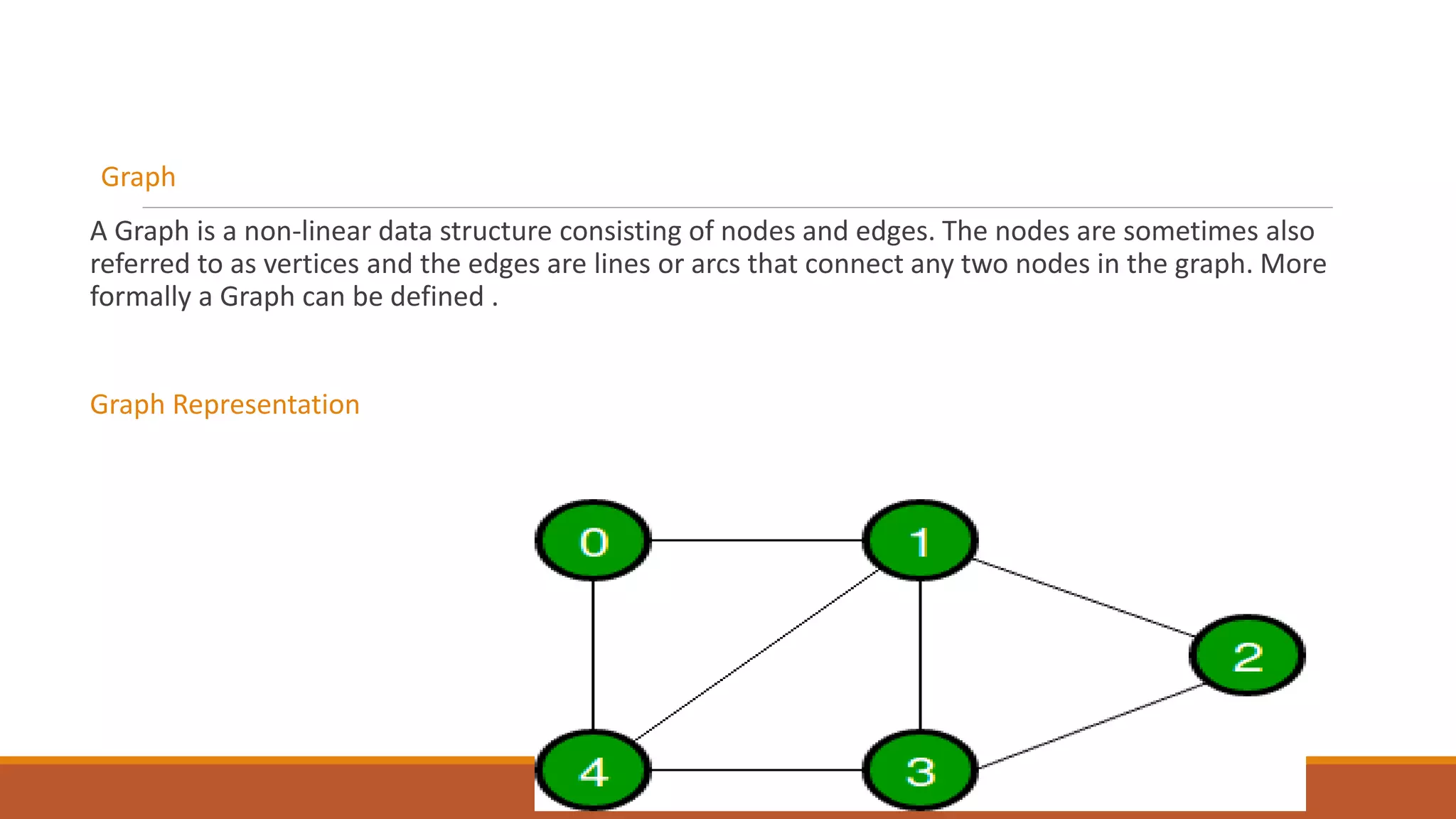
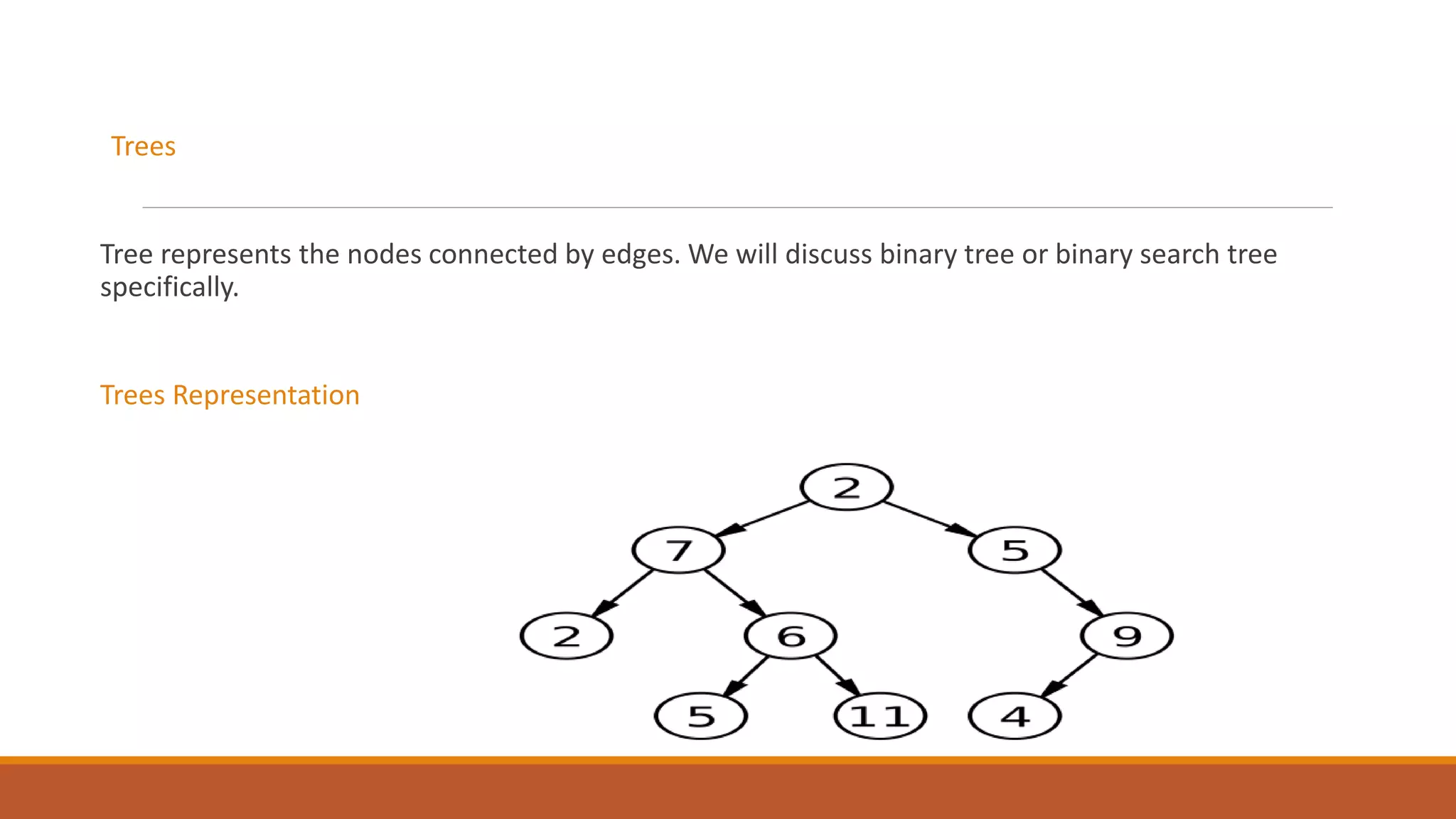
This document provides an overview of data structures. It defines data structures as a way to organize and store data to allow for effective operations. The document outlines common data structure operations like traversing, searching, insertion, and deletion. It also categorizes data structures as primitive, non-primitive, linear, and non-linear. Linear structures discussed include stacks and queues. Non-linear structures covered are trees and graphs. Details are provided on representing graphs and trees.