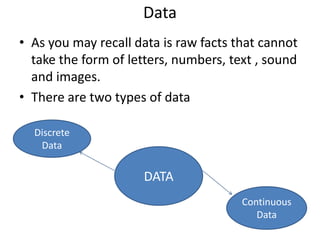
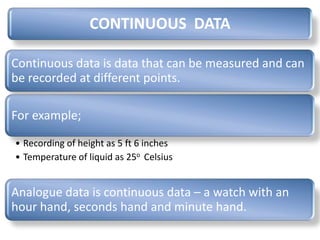
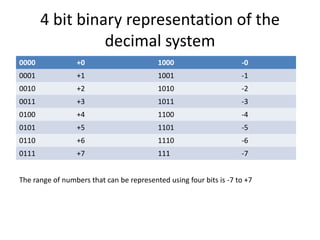
This document discusses data storage and representation in computers. It covers different types of data like discrete and continuous data. It also discusses number systems like the decimal and binary systems. The decimal system uses base 10 with digits 0-9, while the binary system uses base 2 with digits 0 and 1. The document explains how to perform binary addition and subtraction. It also discusses representing signed numbers in binary using methods like sign-magnitude, one's complement, and two's complement representations. Finally, it provides an example of a 4-bit binary representation of decimal numbers between -7 and +7.