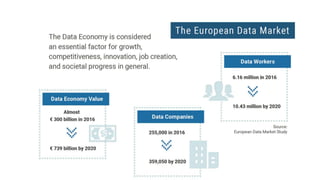
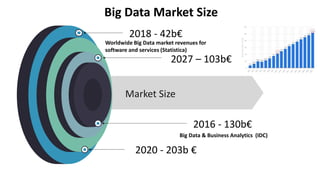
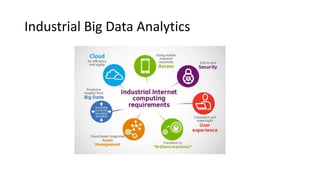
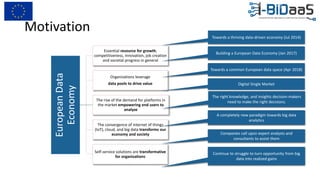
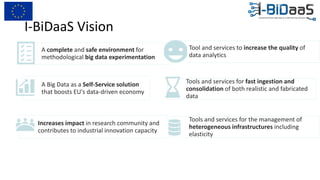
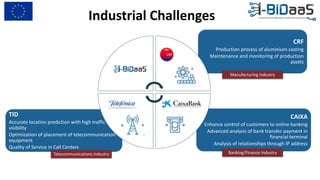
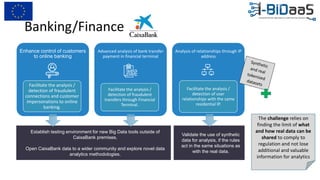
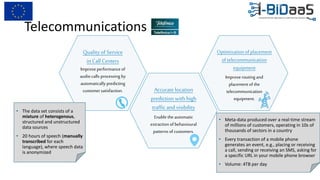
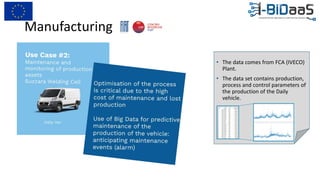
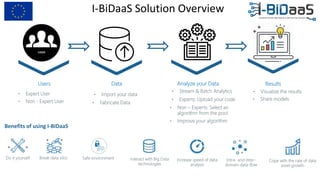
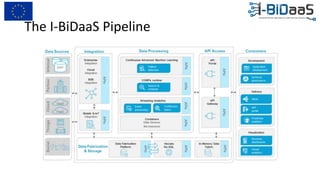
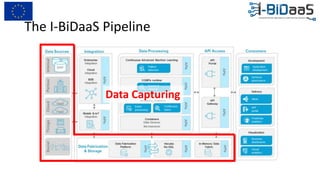
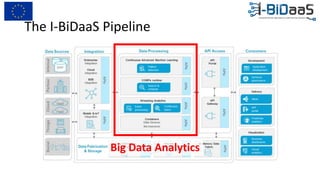
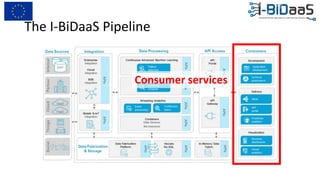
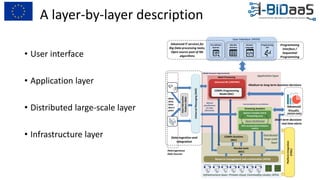
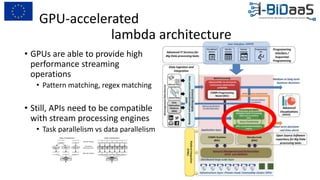
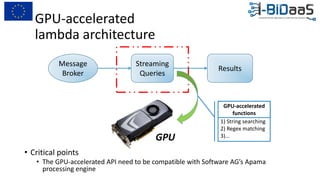
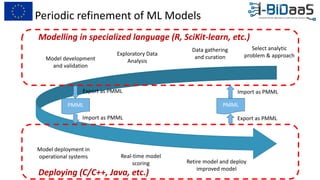
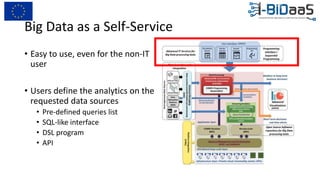
The document discusses the importance of data sharing between private companies and research facilities in the big data era, highlighting the vast volumes and varieties of data generated daily. It outlines challenges such as privacy concerns and intellectual property risks, while proposing the FAIR principles to enhance data transparency and reusability. The i-bidaas project aims to create self-service big data analytics solutions to empower organizations and improve data-driven decision-making across various industries.