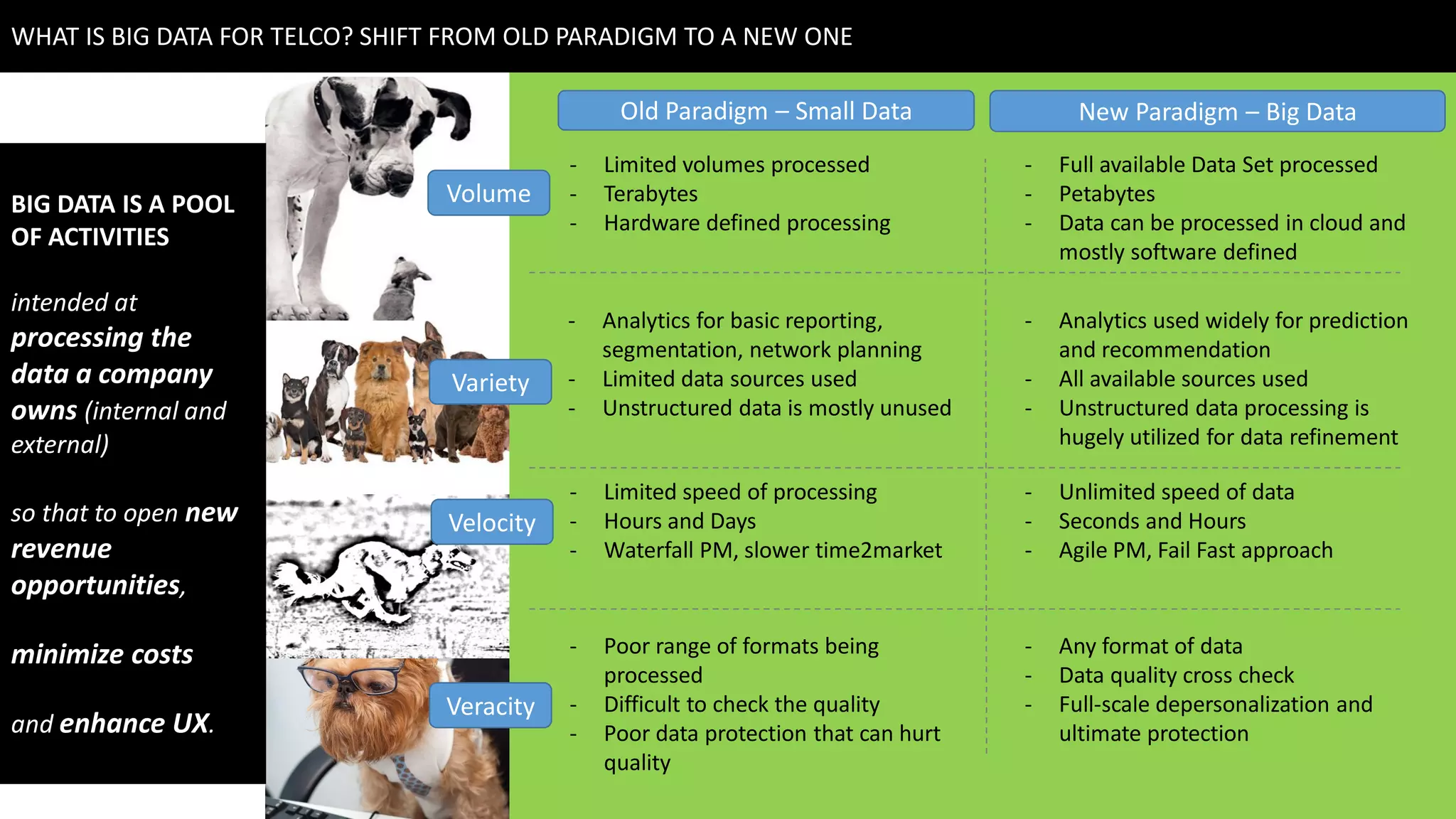
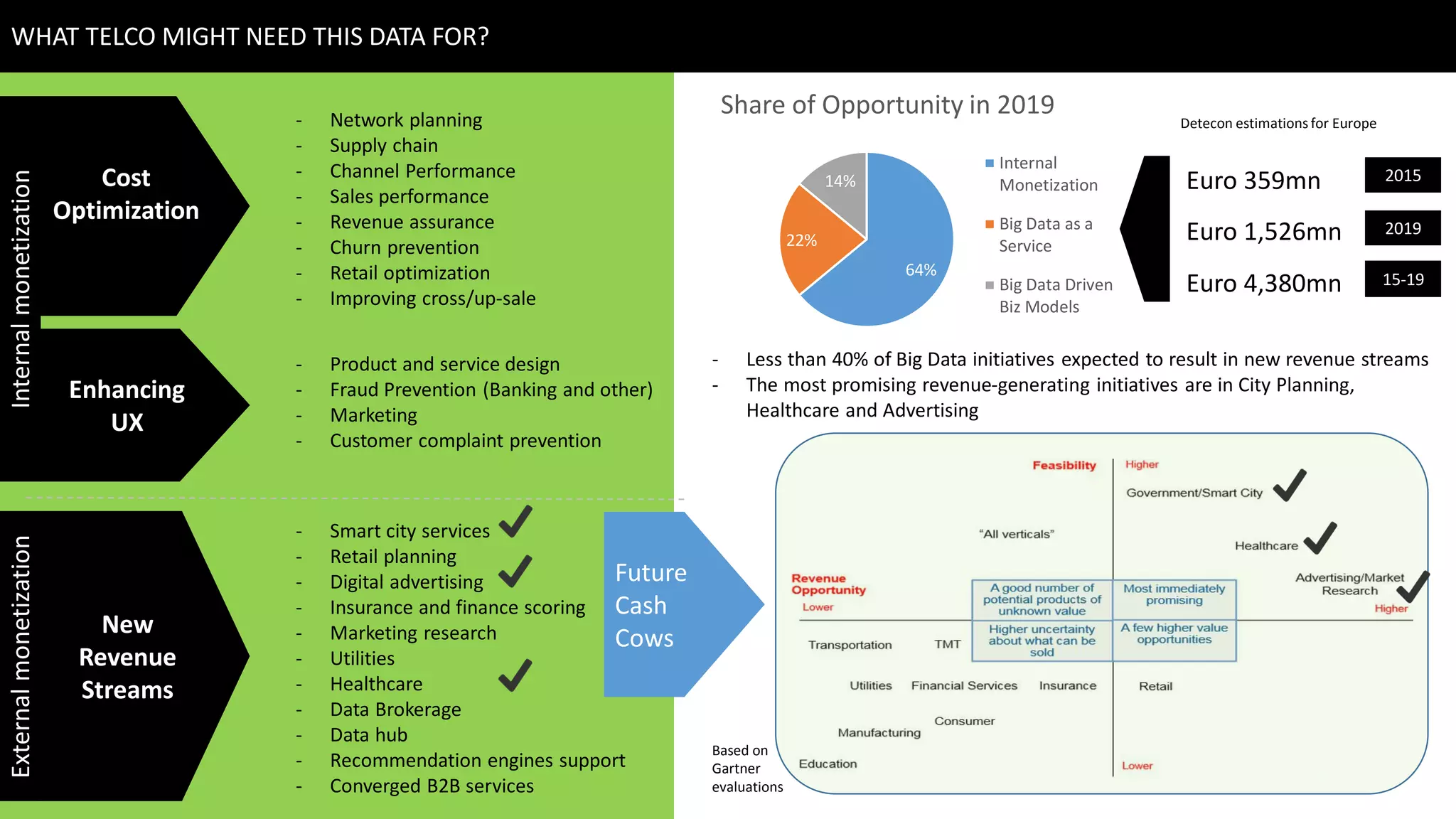
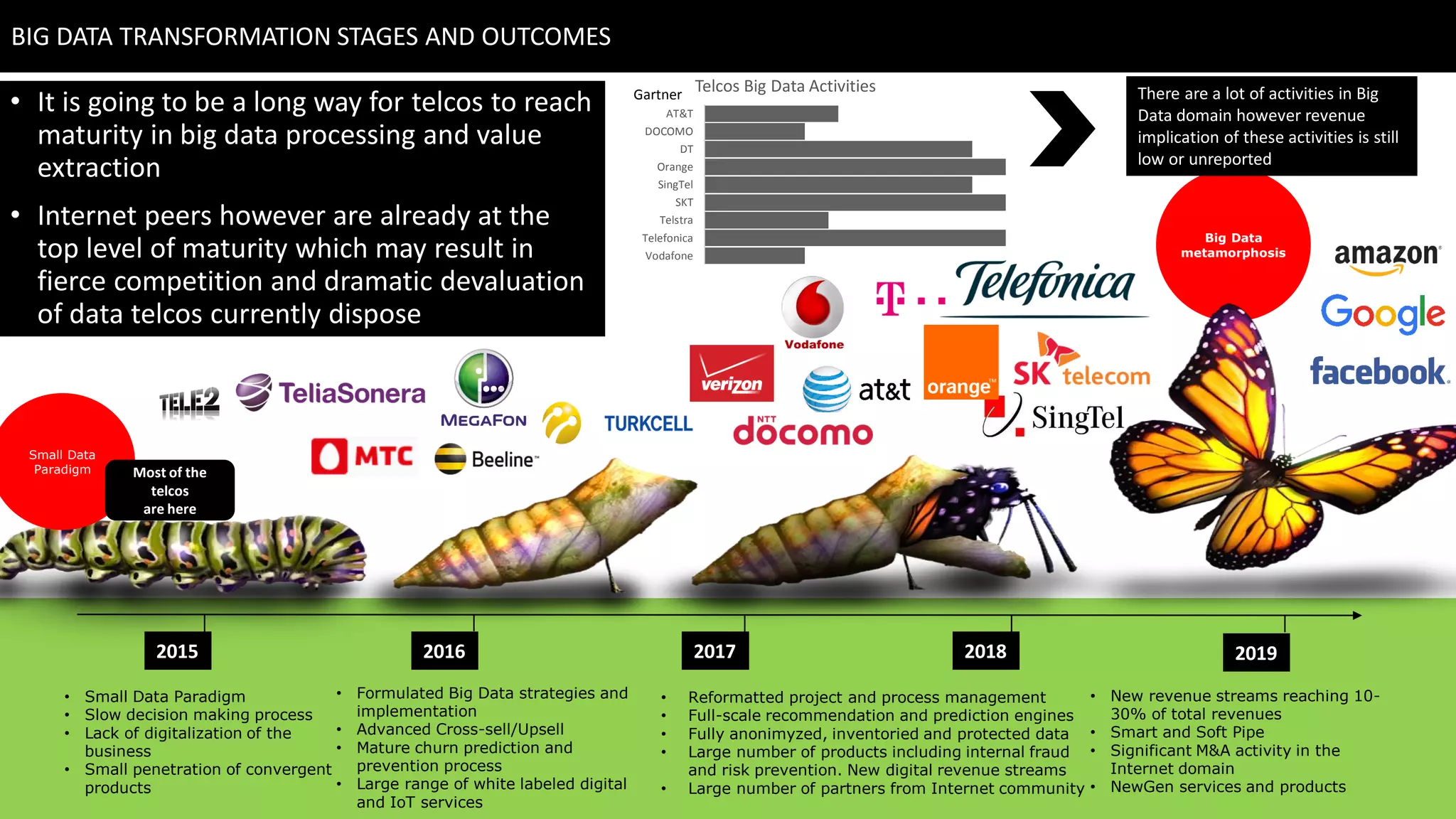
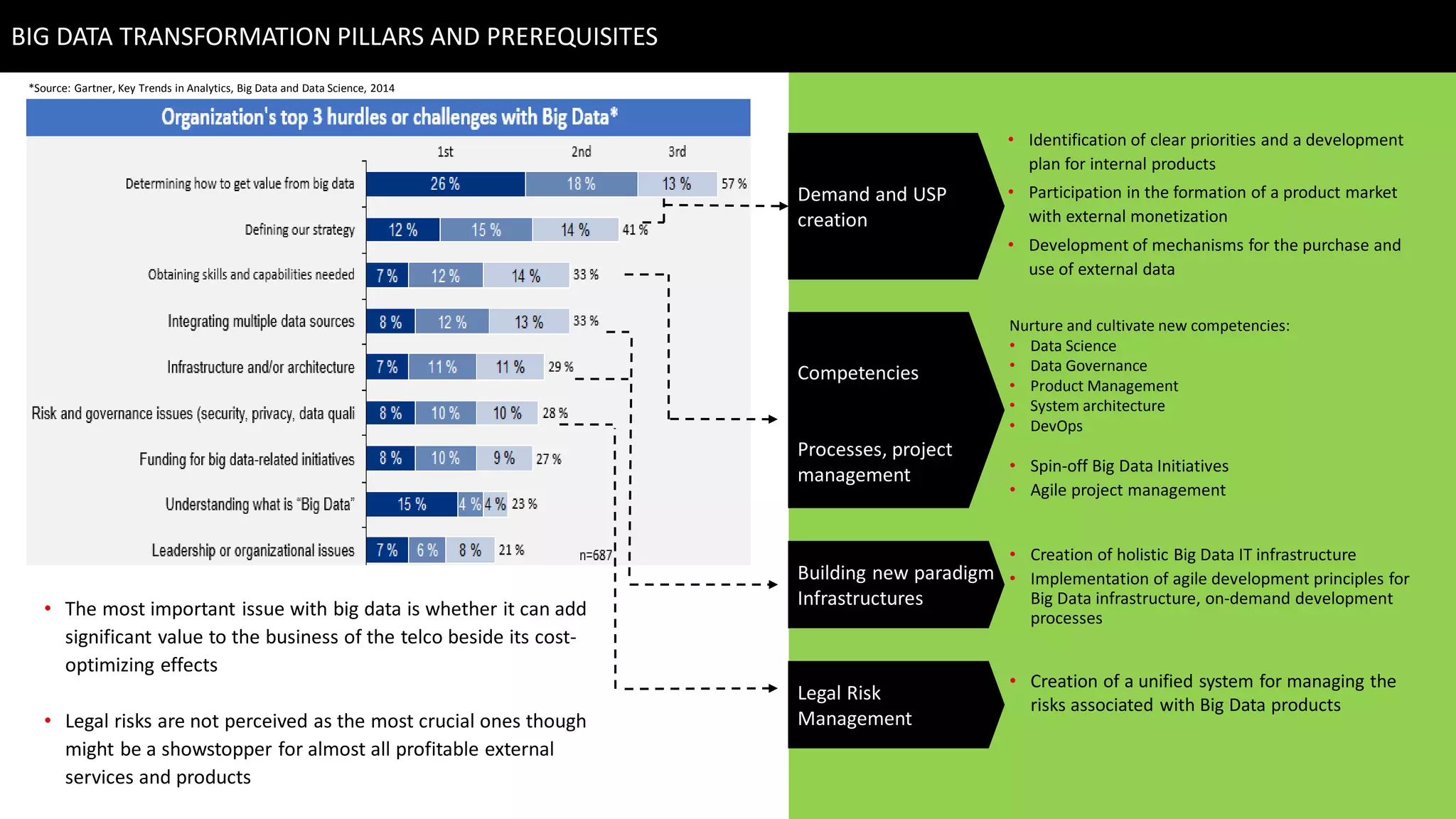
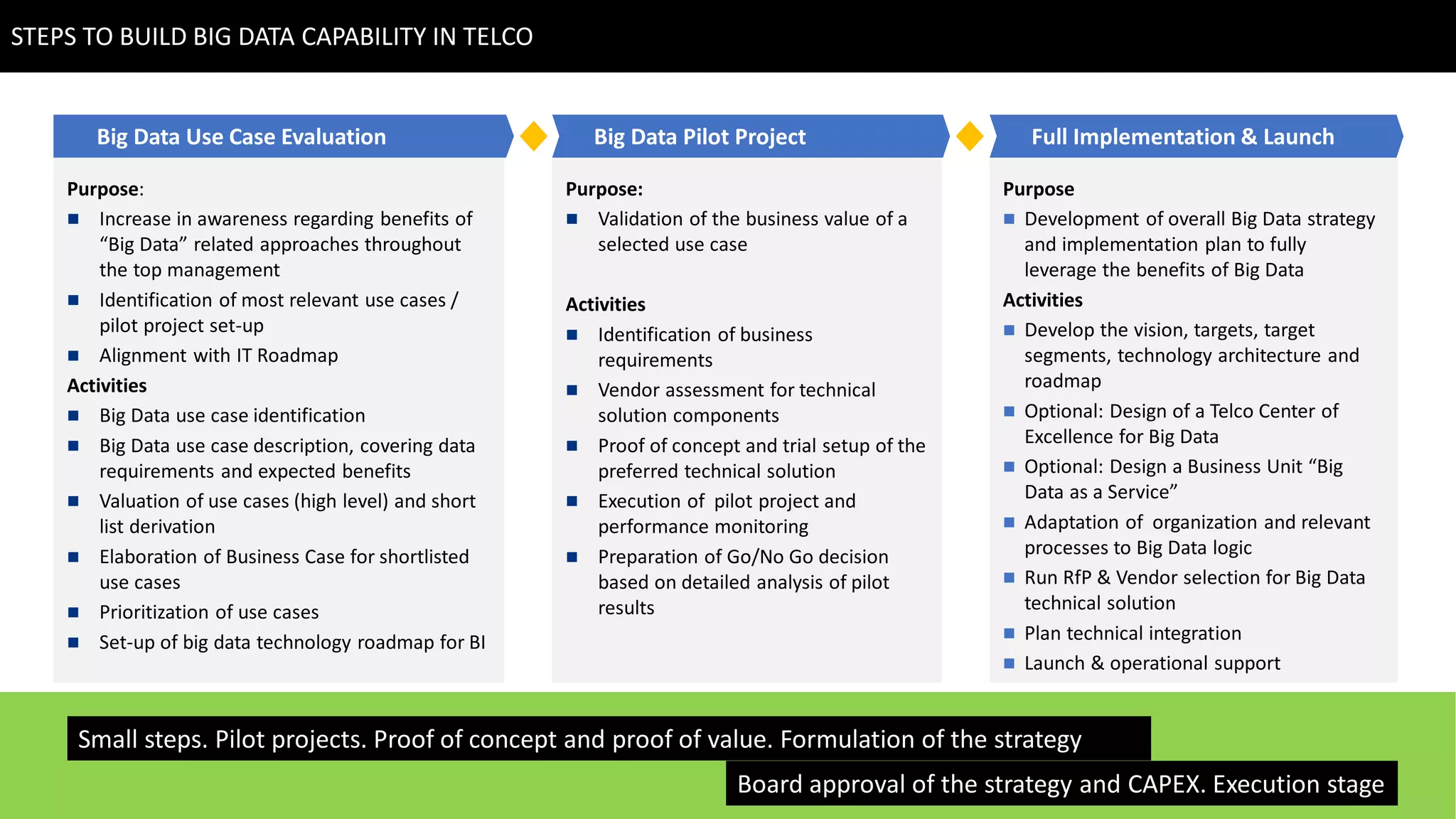
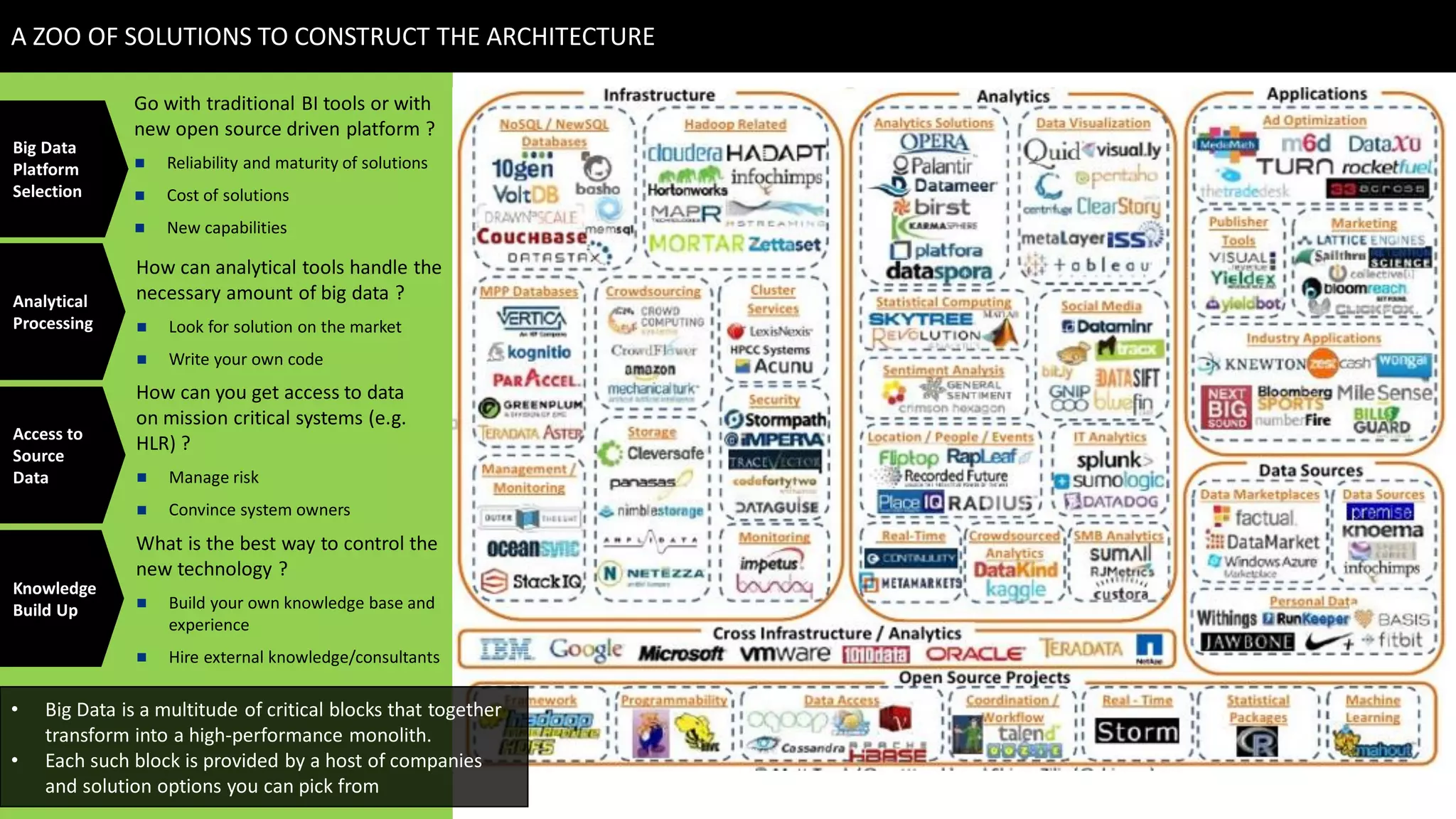
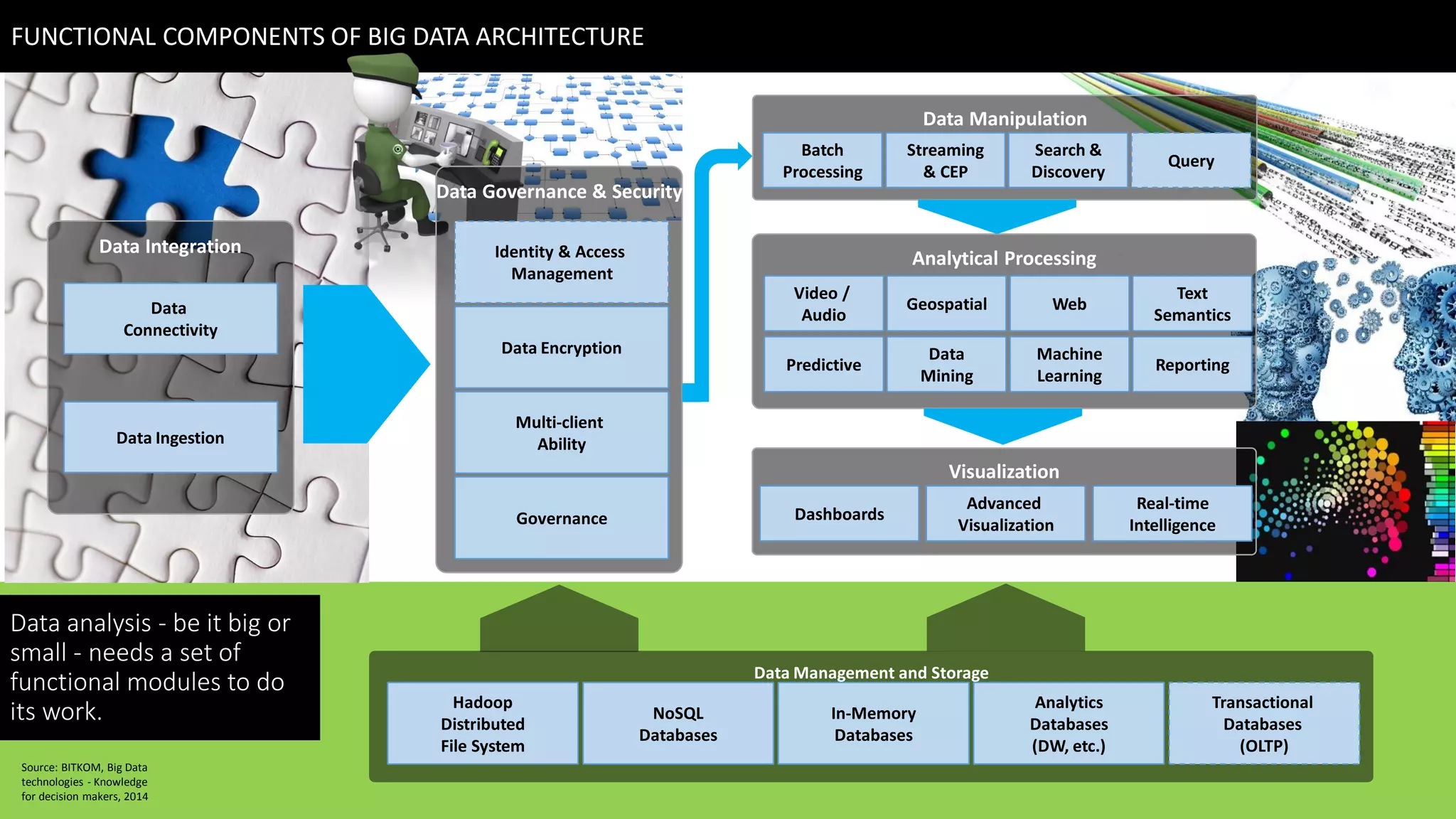
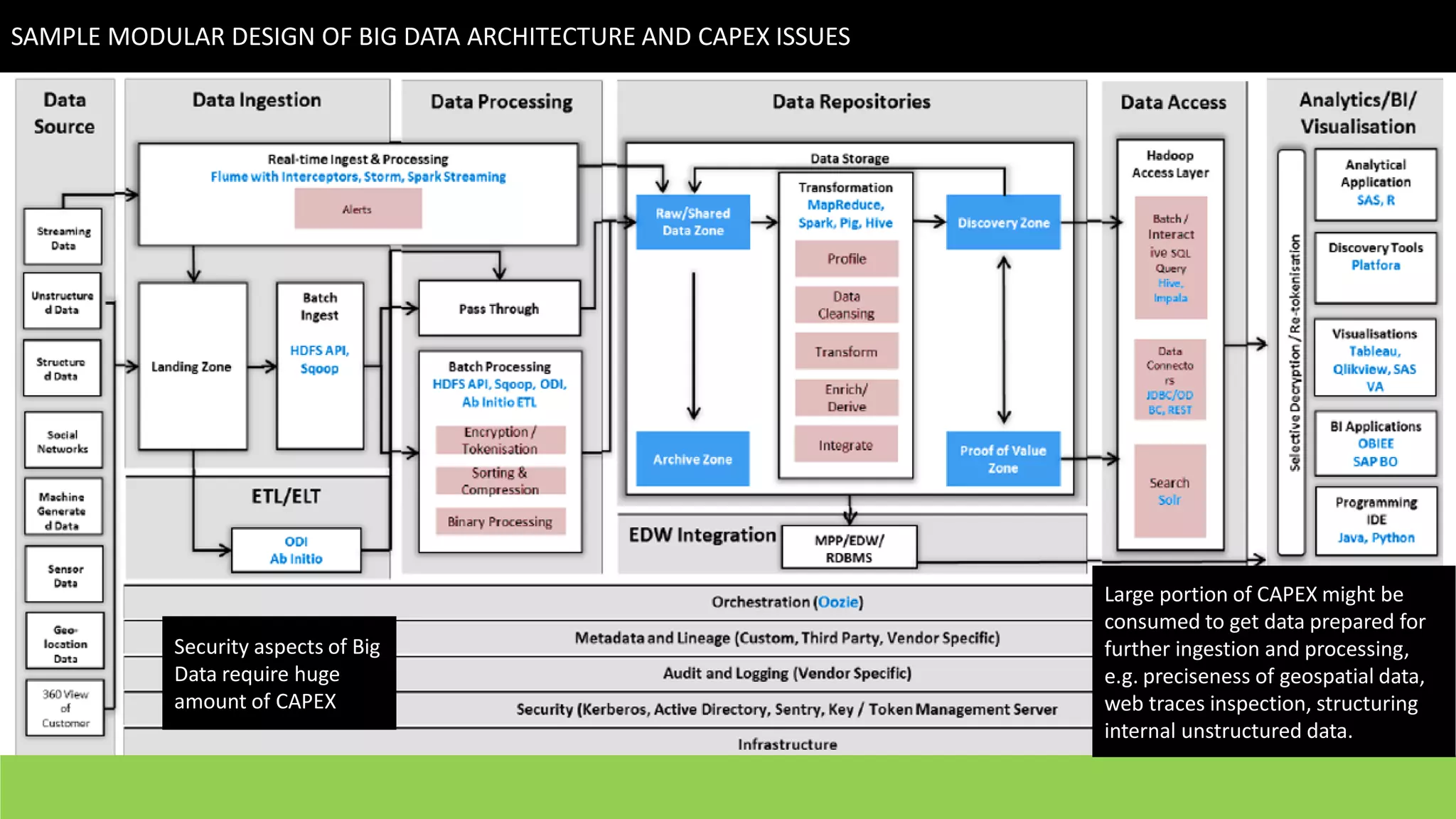
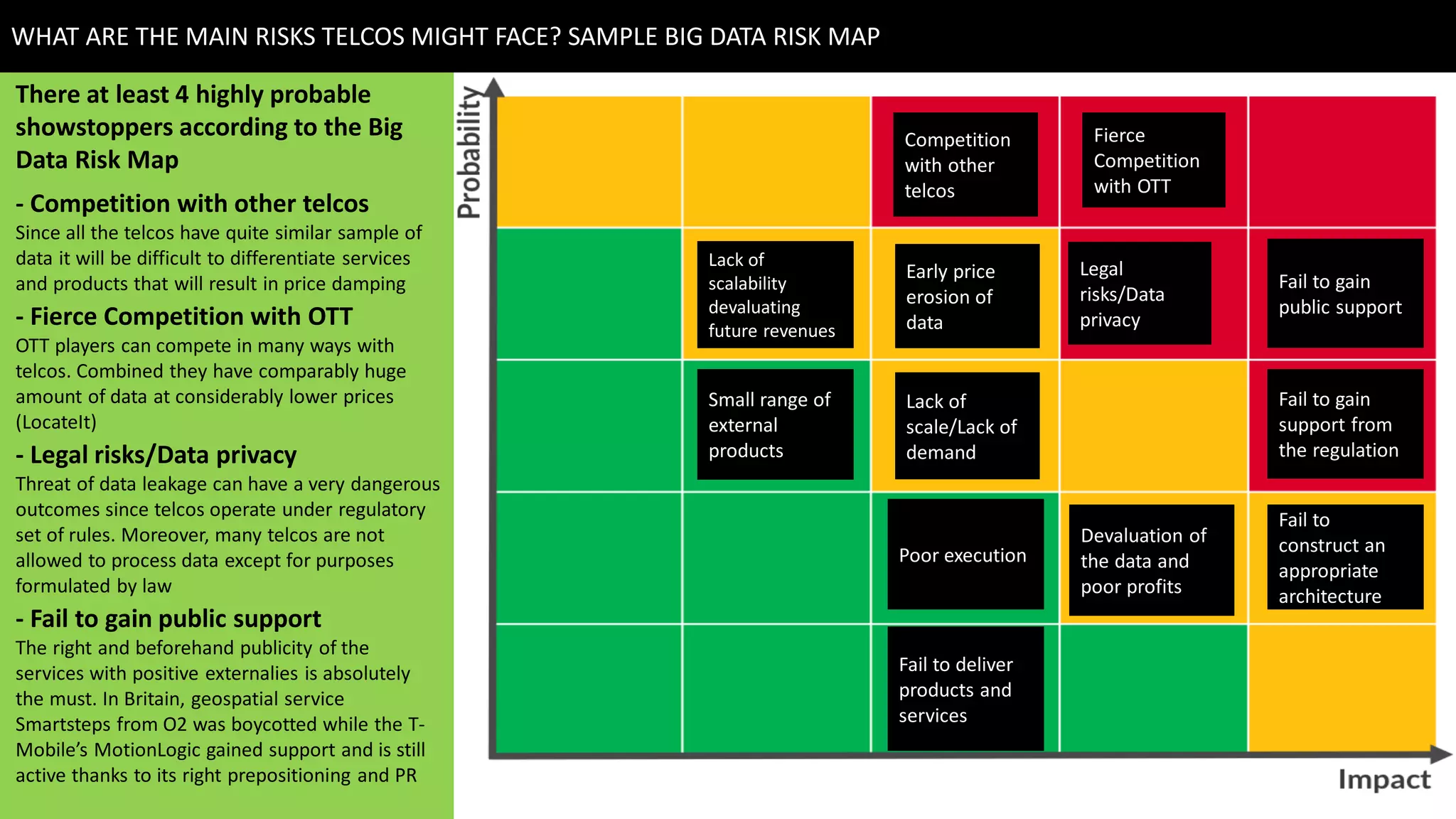
This document discusses strategies for telcos to leverage big data. It begins by outlining the shift from traditional "small data" paradigms to new "big data" approaches characterized by processing vast amounts of data from both internal and external sources. It then provides examples of the types of internal and external data available to telcos and how this data could be used. The document also outlines some of the main challenges telcos may face in developing big data capabilities, such as competition from internet companies and ensuring privacy and regulatory compliance. It concludes by emphasizing the importance of a gradual, pilot-based approach to building big data strategies.