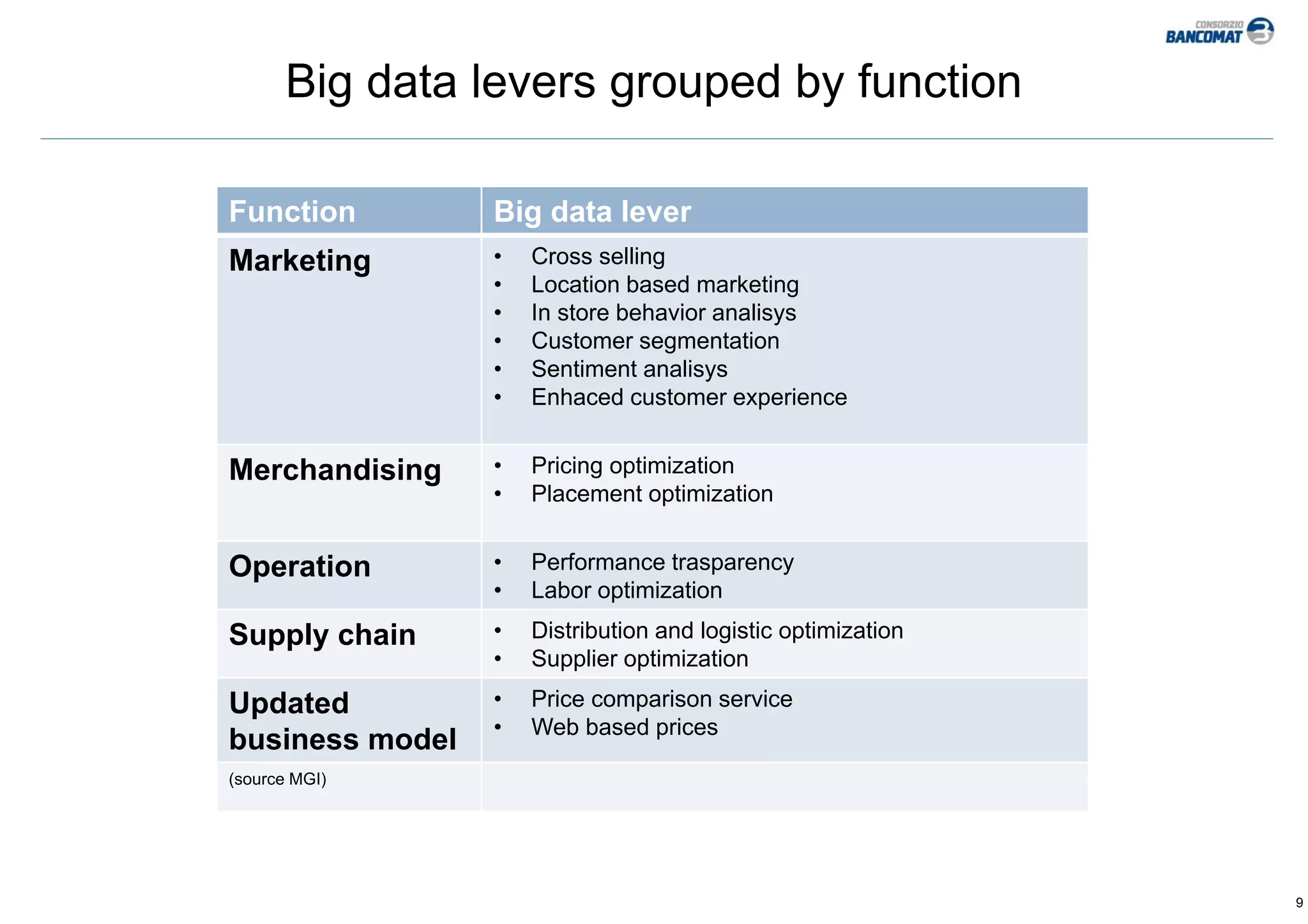
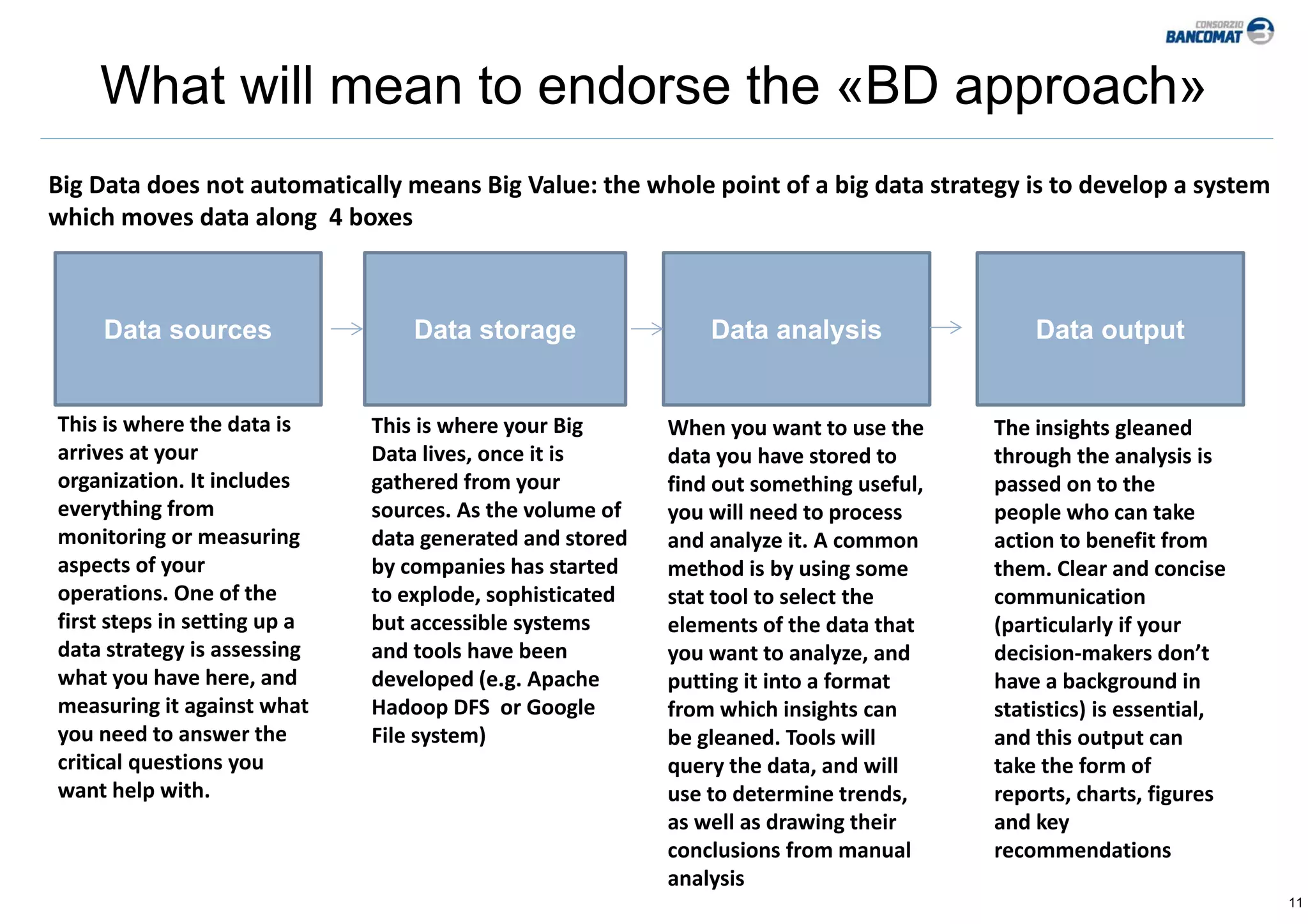
The document discusses big data and its potential applications for payment cards. It summarizes the European Commission's concerns about Europe falling behind the US and China in embracing big data. The Commission is calling for initiatives to develop enabling technologies, share public data, and ensure legal frameworks support innovation. The document defines big data and outlines typical benefits like improved marketing, pricing, and supply chain optimization. It also discusses how payment card schemes could be sources and users of big data to enhance fraud prevention, customer segmentation, merchant support, and new product development.