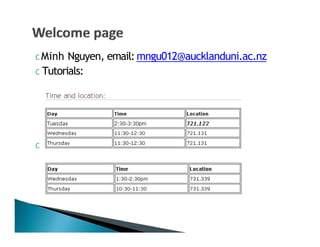
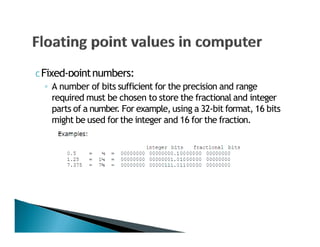
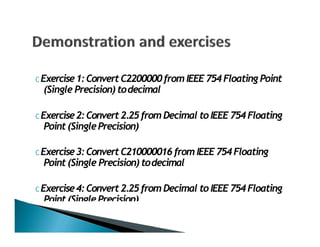
This document discusses floating point numbers and how they are represented in computers using binary rather than decimal. It notes that floating point numbers are approximations and certain calculations may result in numbers like 0.999999999 instead of the expected 1. This is due to the limitations of binary representation. It then explains how floating point numbers use a significand and exponent to represent a wide range of values with limited precision. Finally, it provides some examples of converting between decimal and IEEE 754 single-precision floating point format.