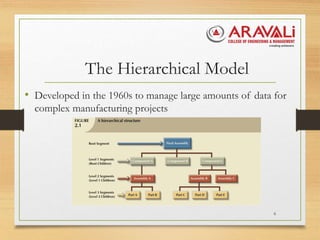
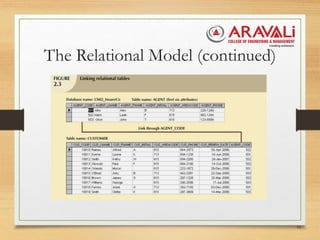
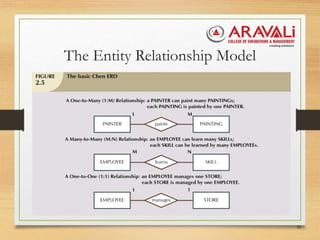
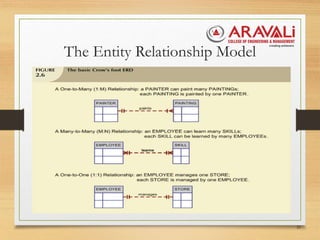
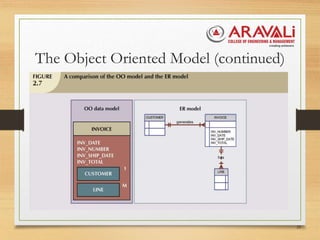
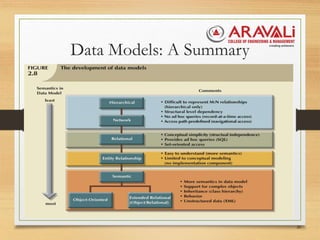
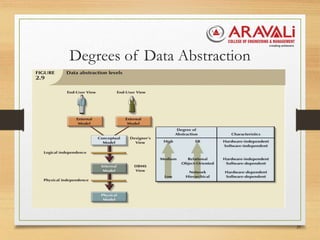
The document outlines the significance and evolution of data models in computer science, detailing their basic building blocks such as entities, attributes, and relationships. It discusses various types of data models, including hierarchical, network, relational, entity-relationship, and object-oriented models, highlighting their characteristics and functionalities. Additionally, it explains the levels of abstraction in data modeling as defined by standards from the American National Standards Institute.