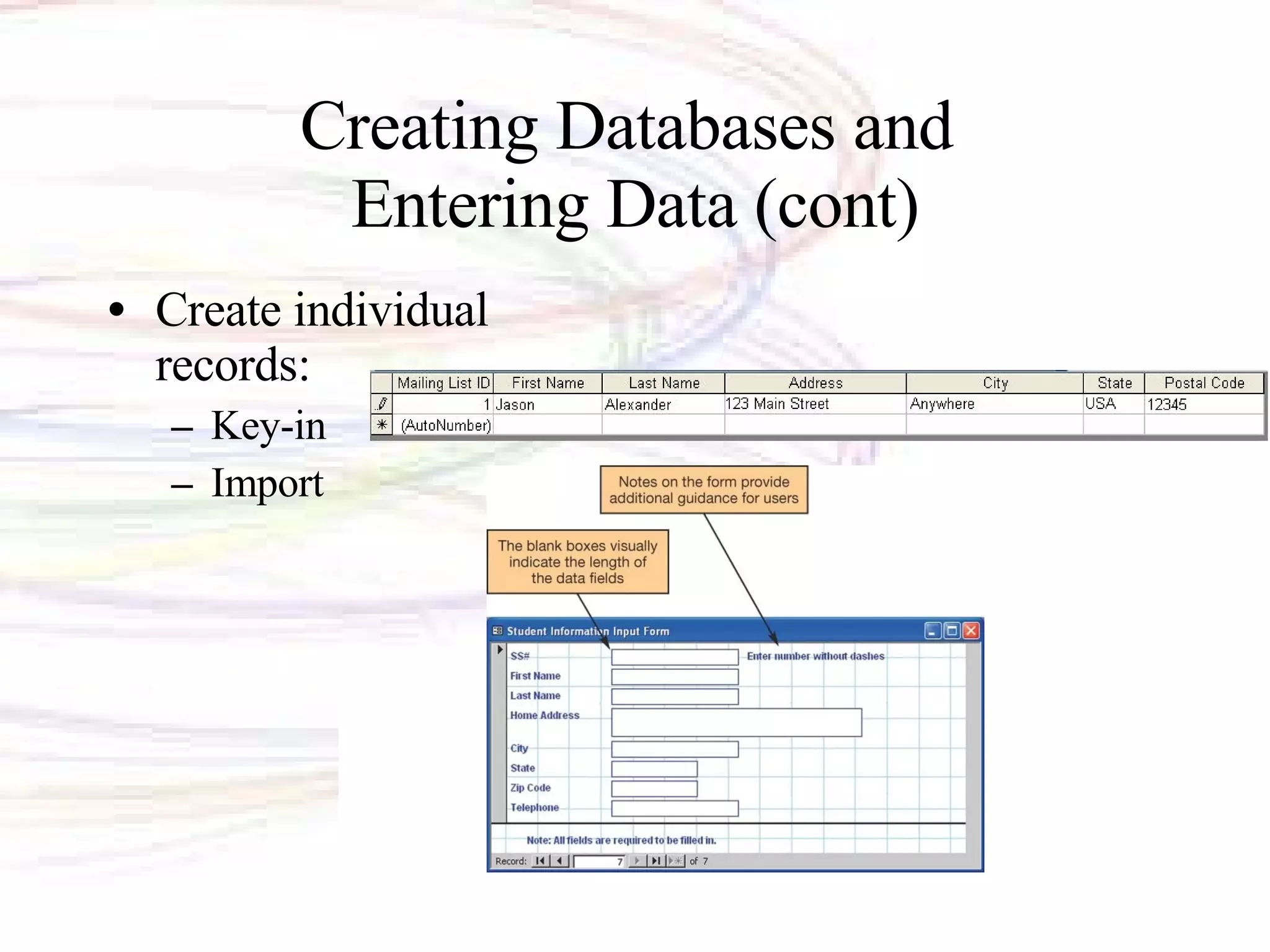
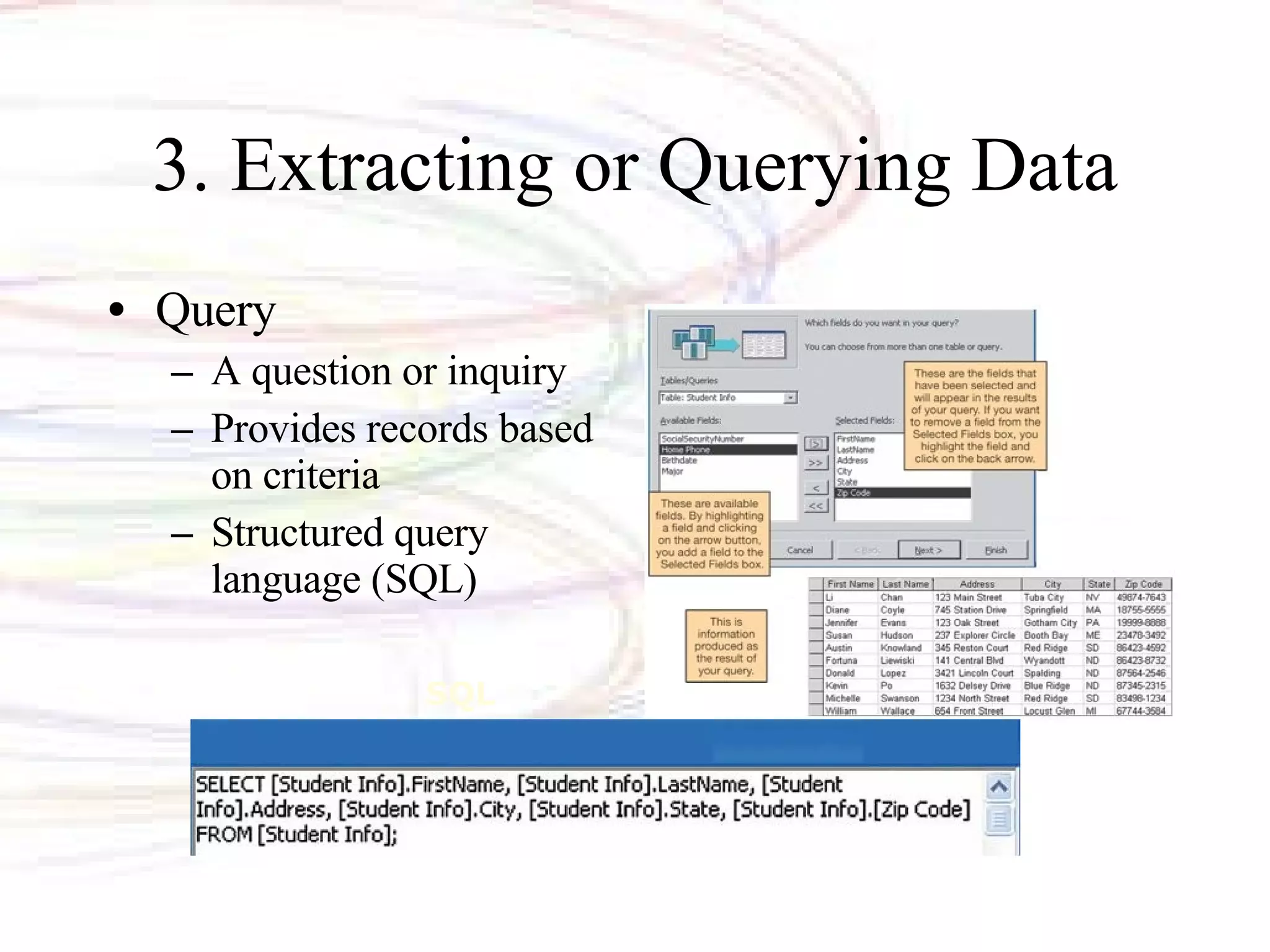
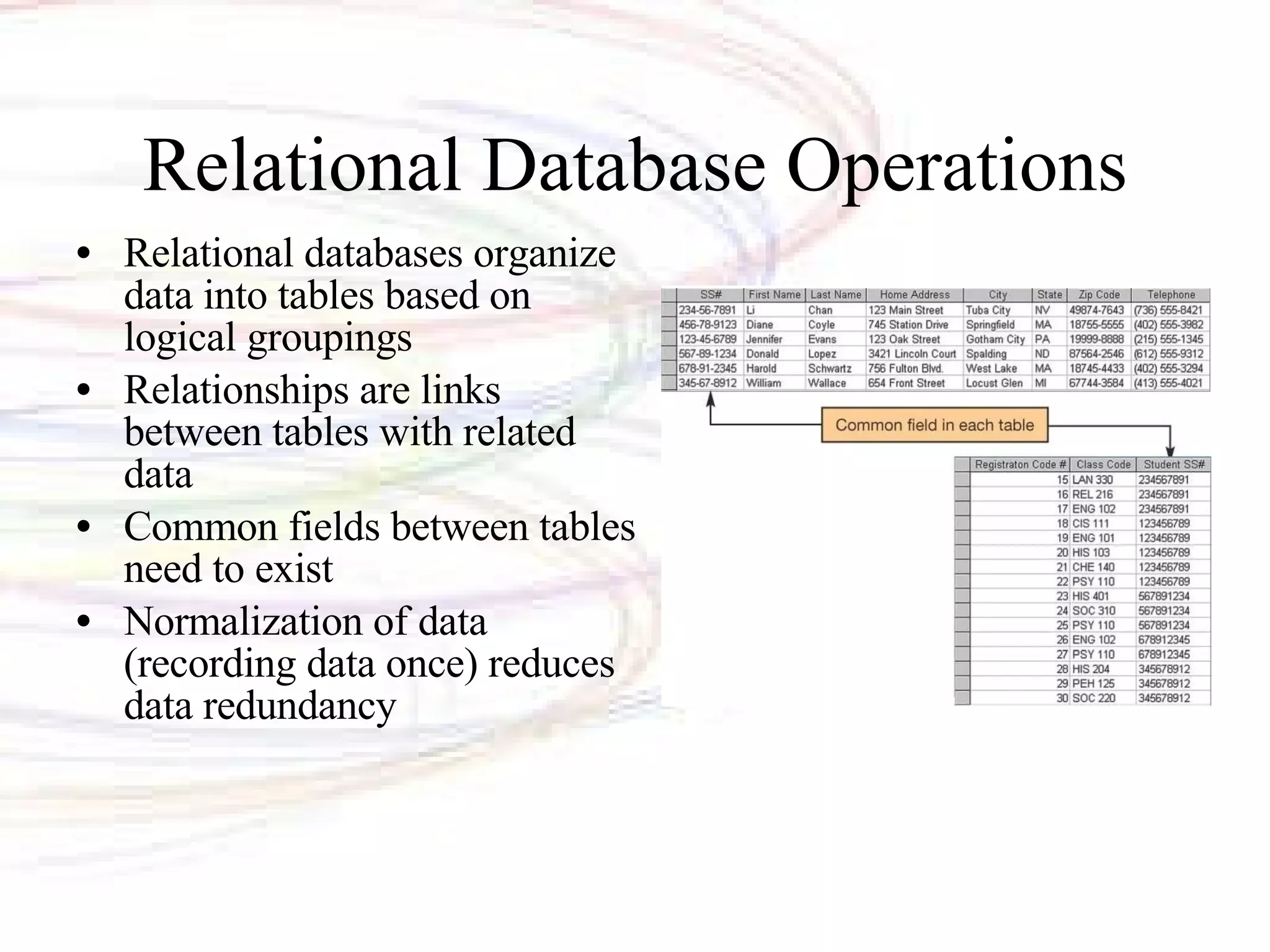
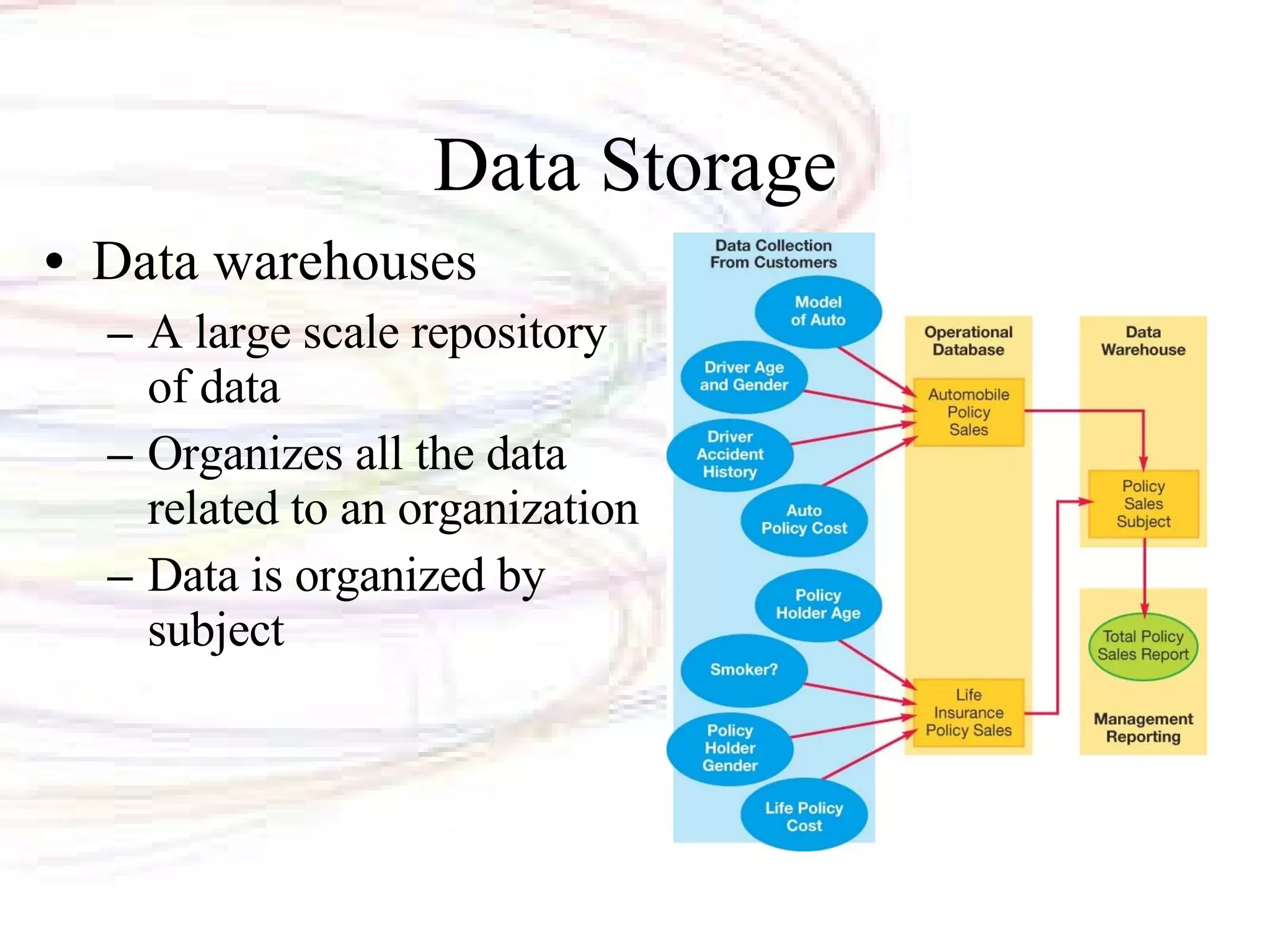
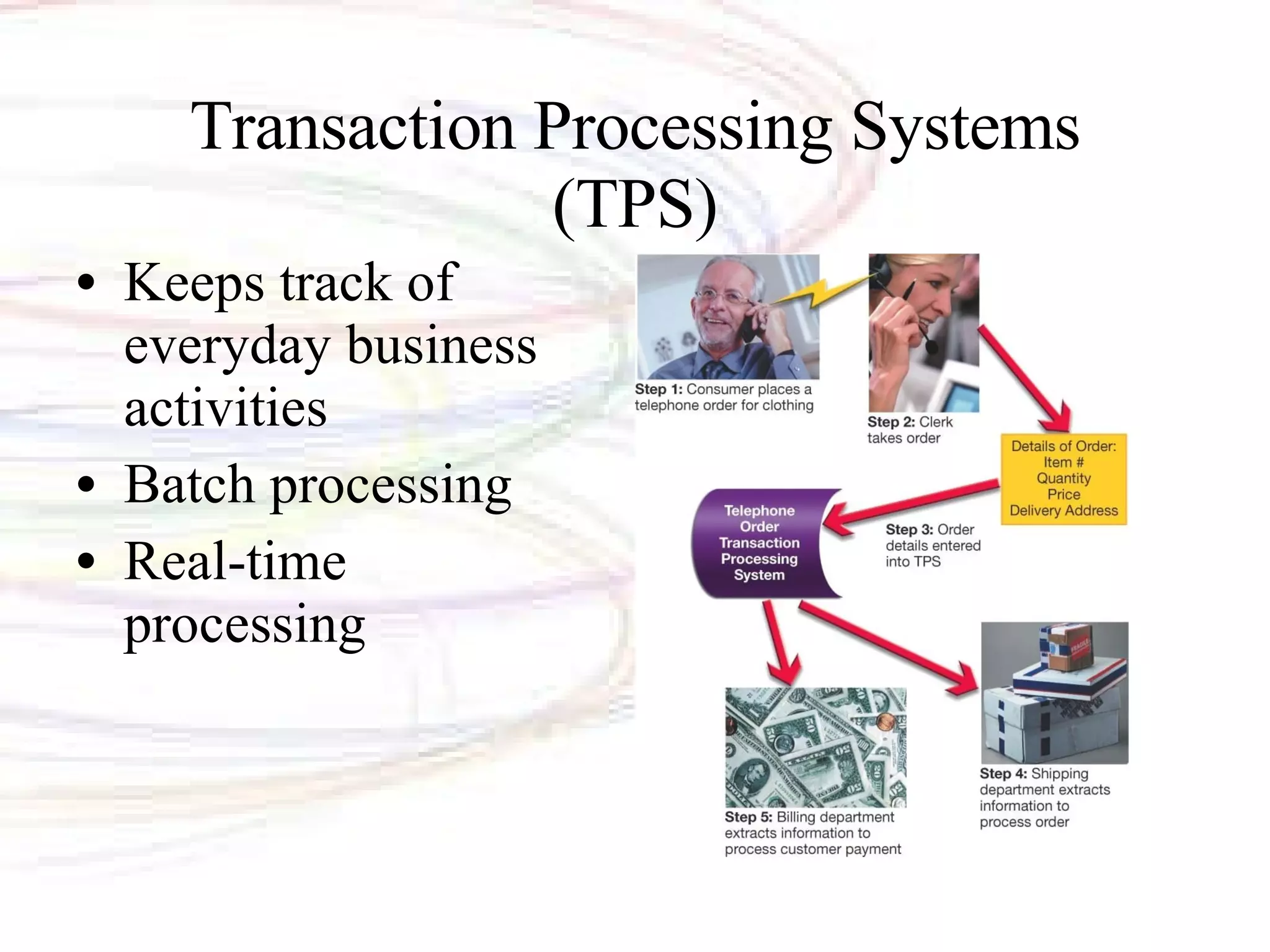
The document discusses databases and information systems. It describes how databases organize and store data, as well as the advantages of using databases. It then defines key database terminology like fields, records, tables, and primary keys. It also outlines the main types of databases and database management systems. Database management systems have four main operations - creating databases and entering data, viewing and sorting data, extracting data, and outputting data. The document finally discusses information systems and how they are used to gather, process, store, and provide output of information to assist with business operations and decision making.