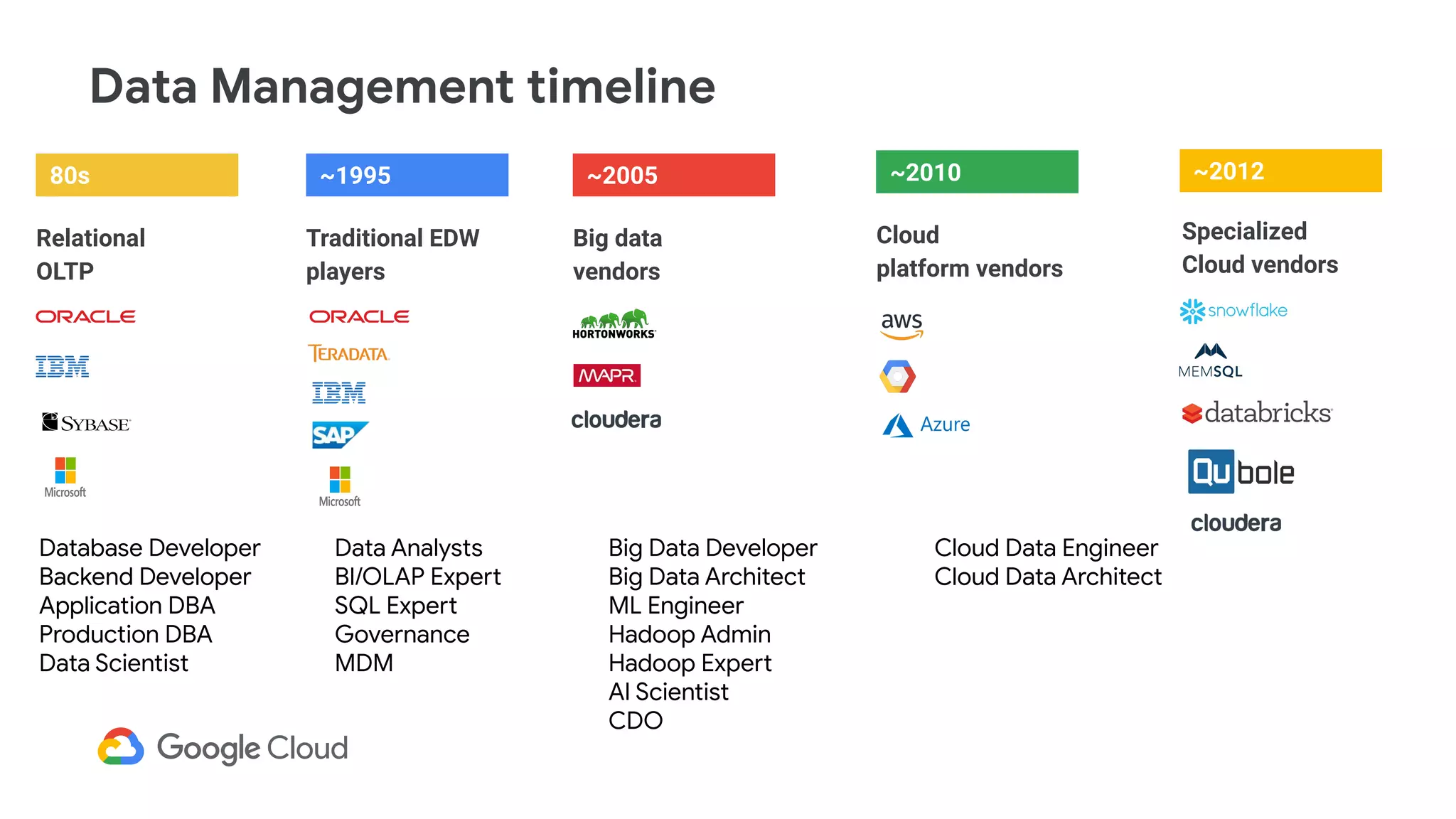
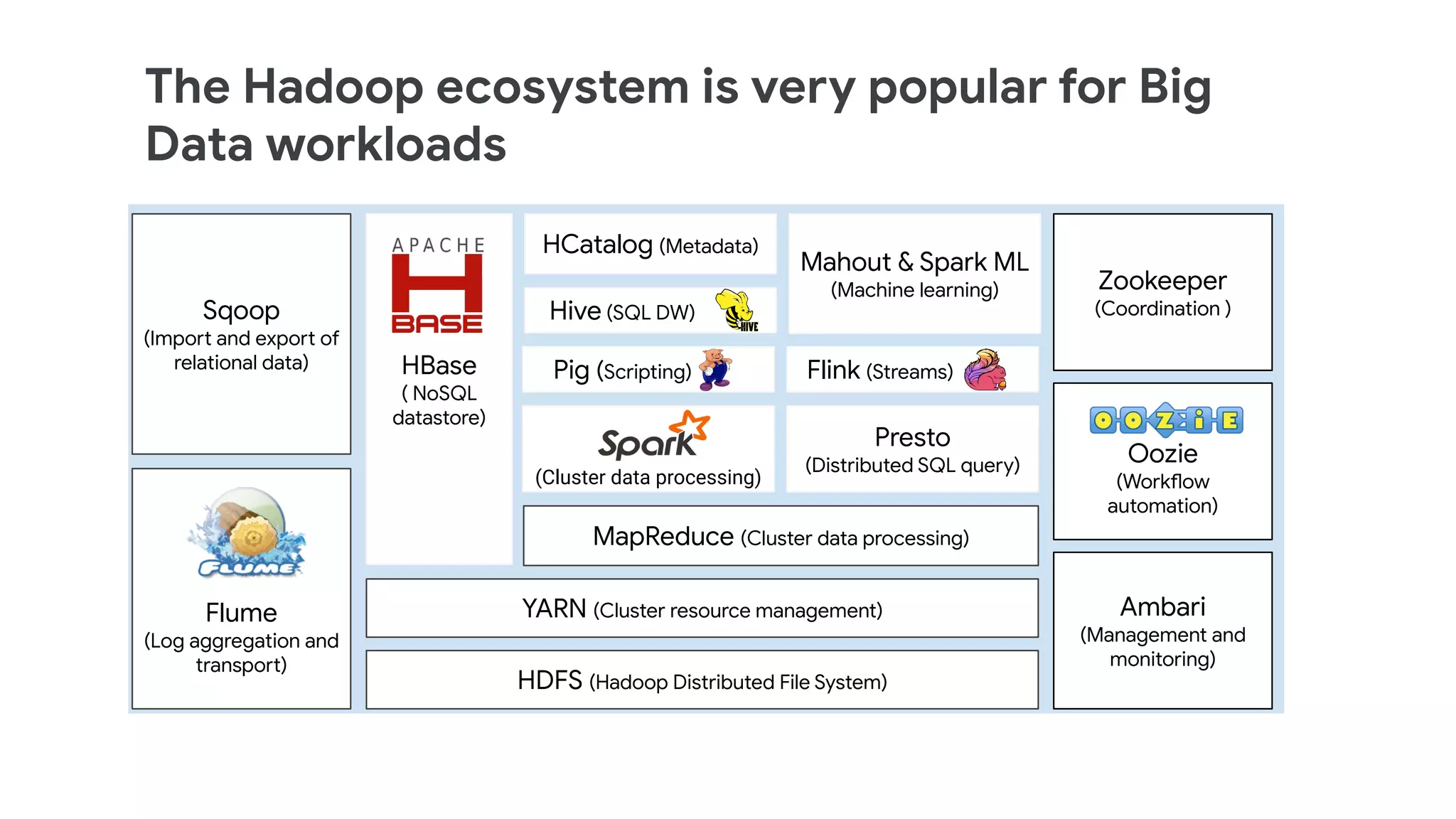
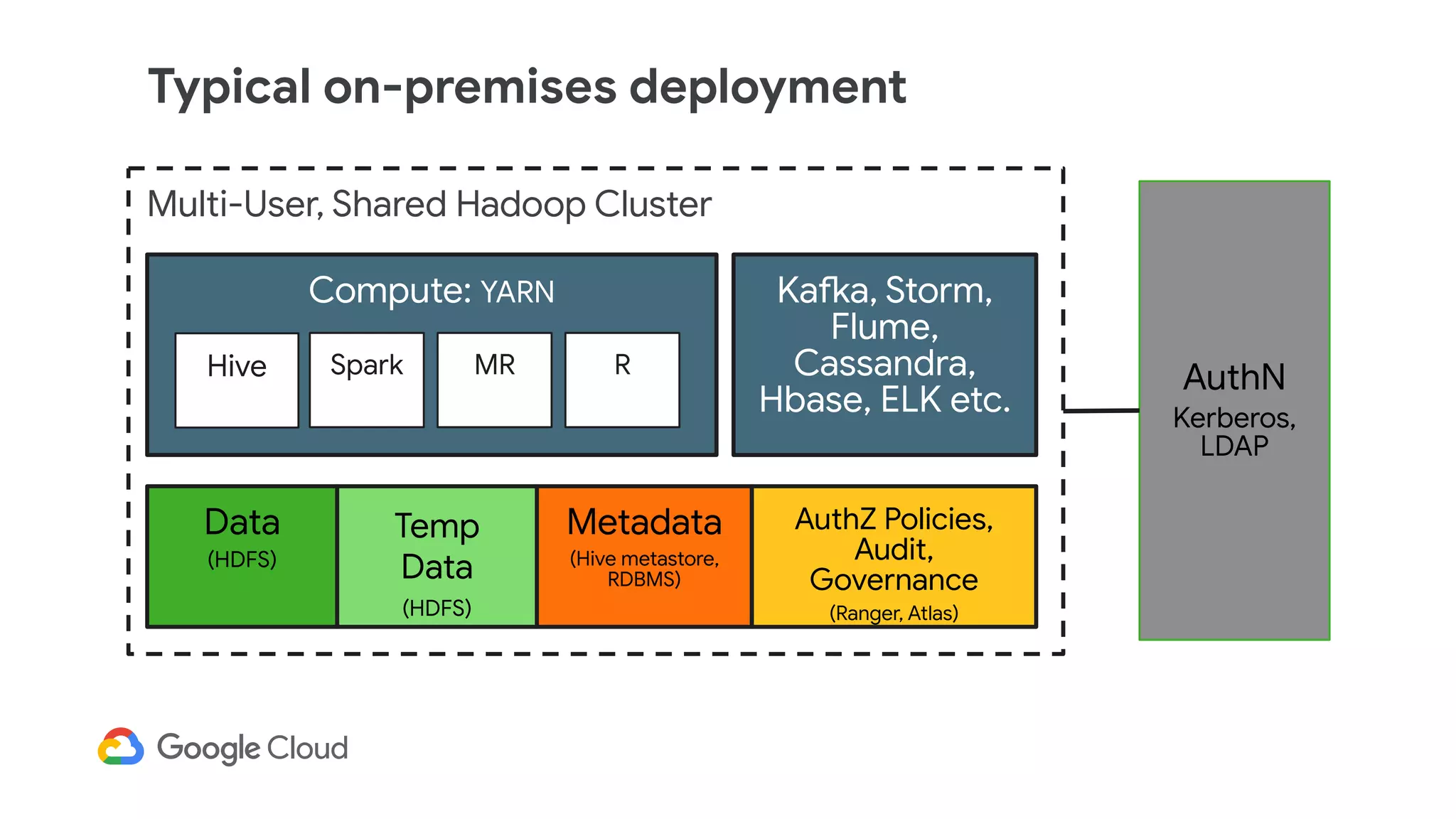
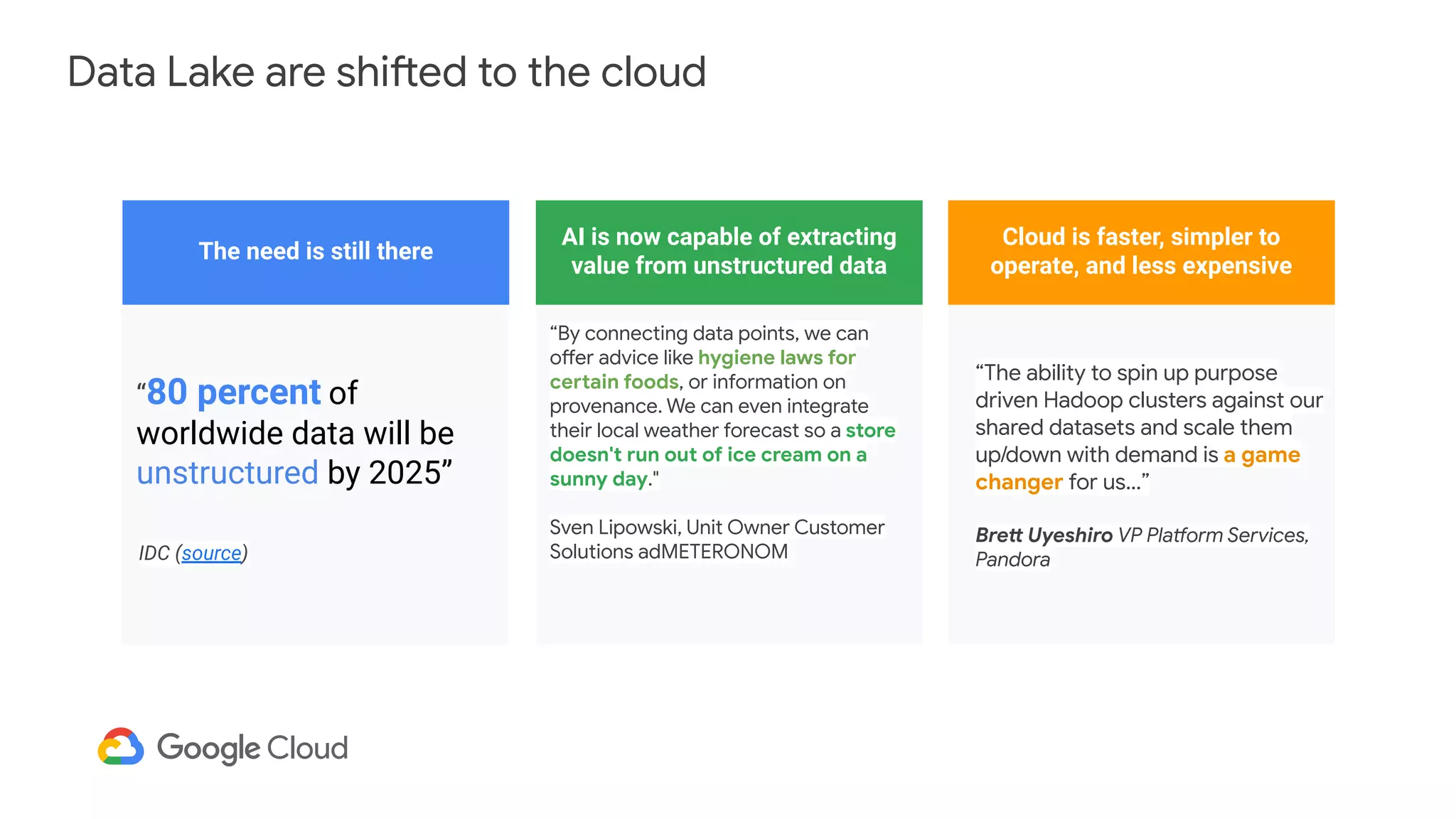
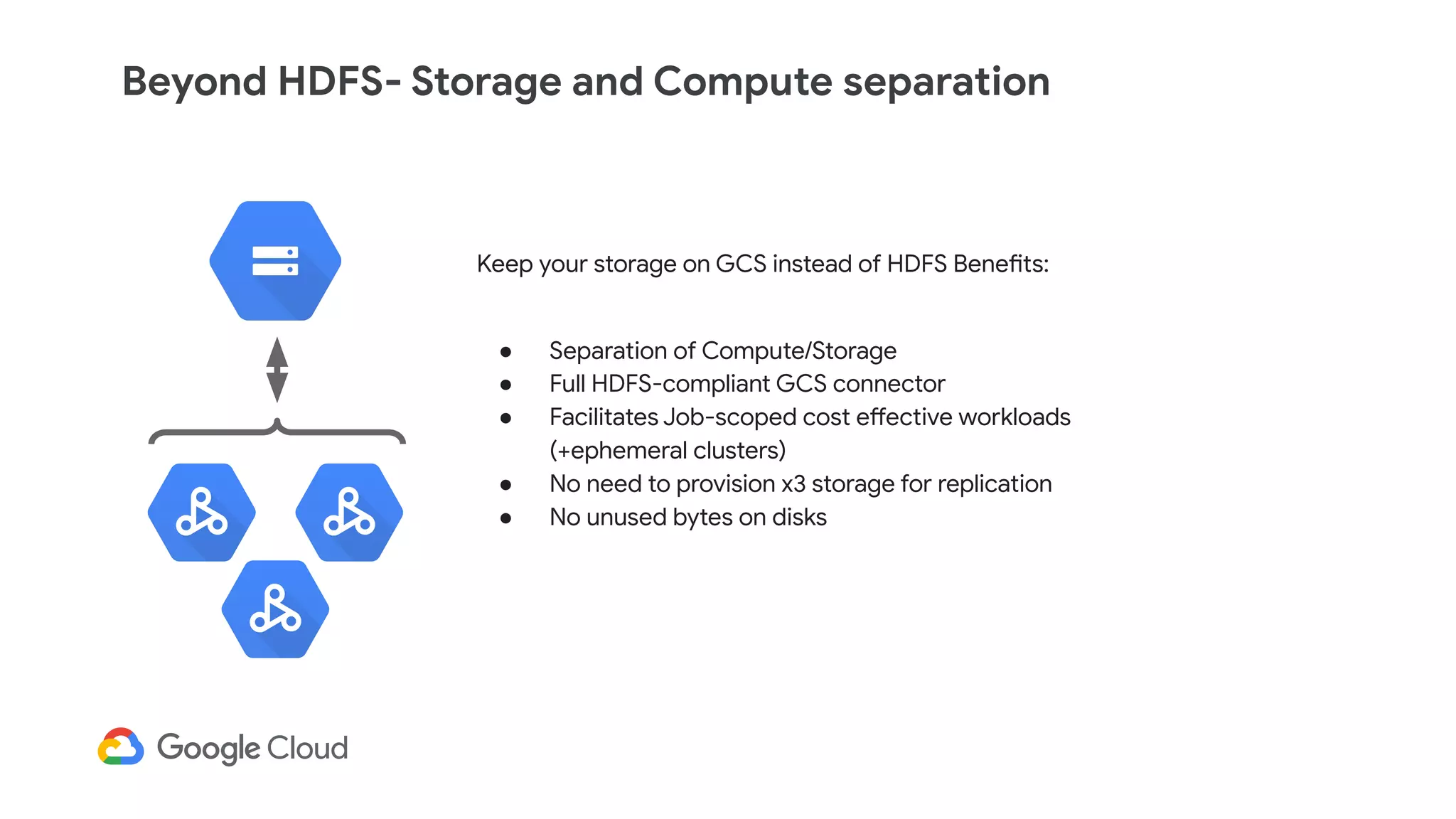
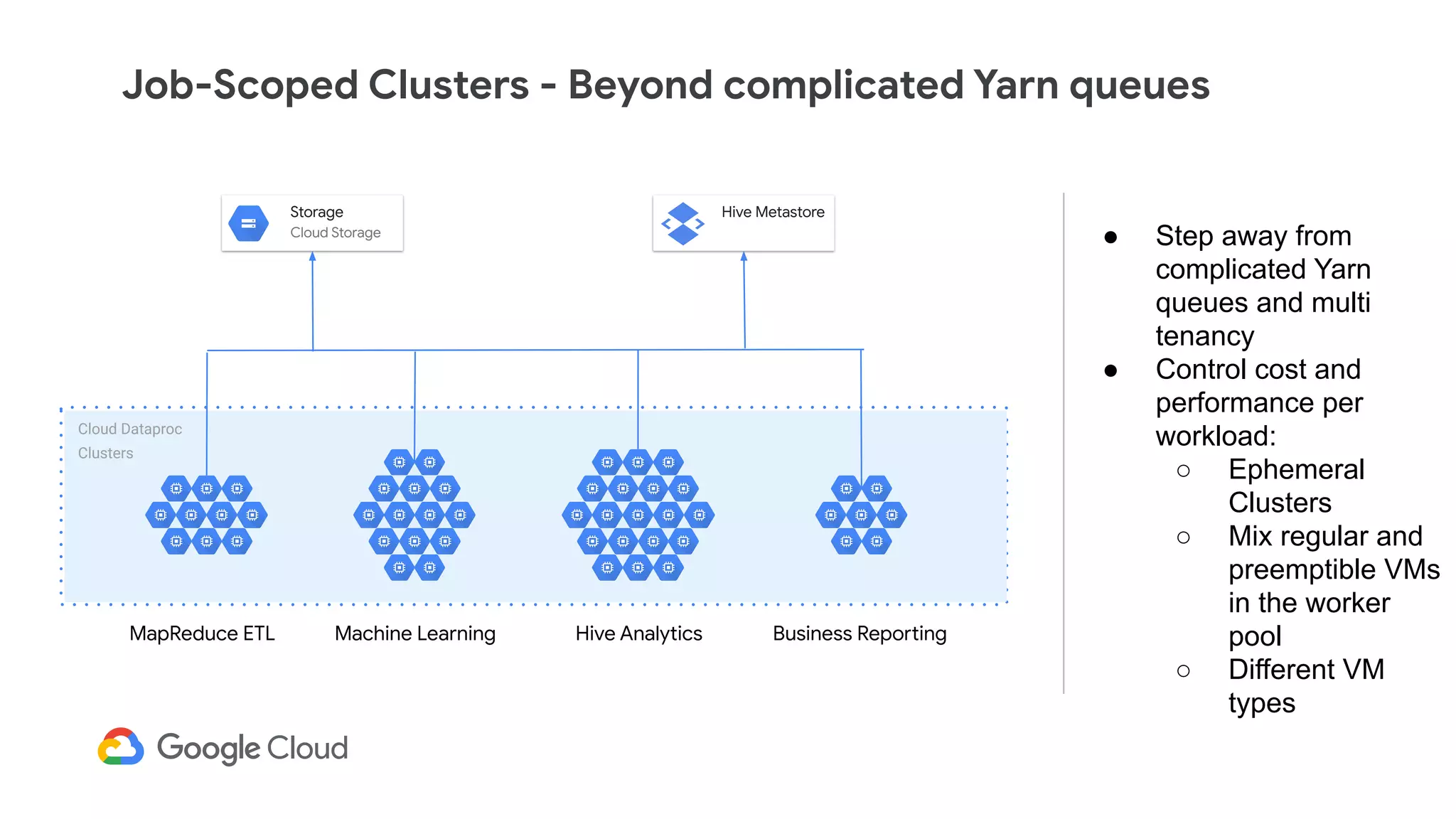
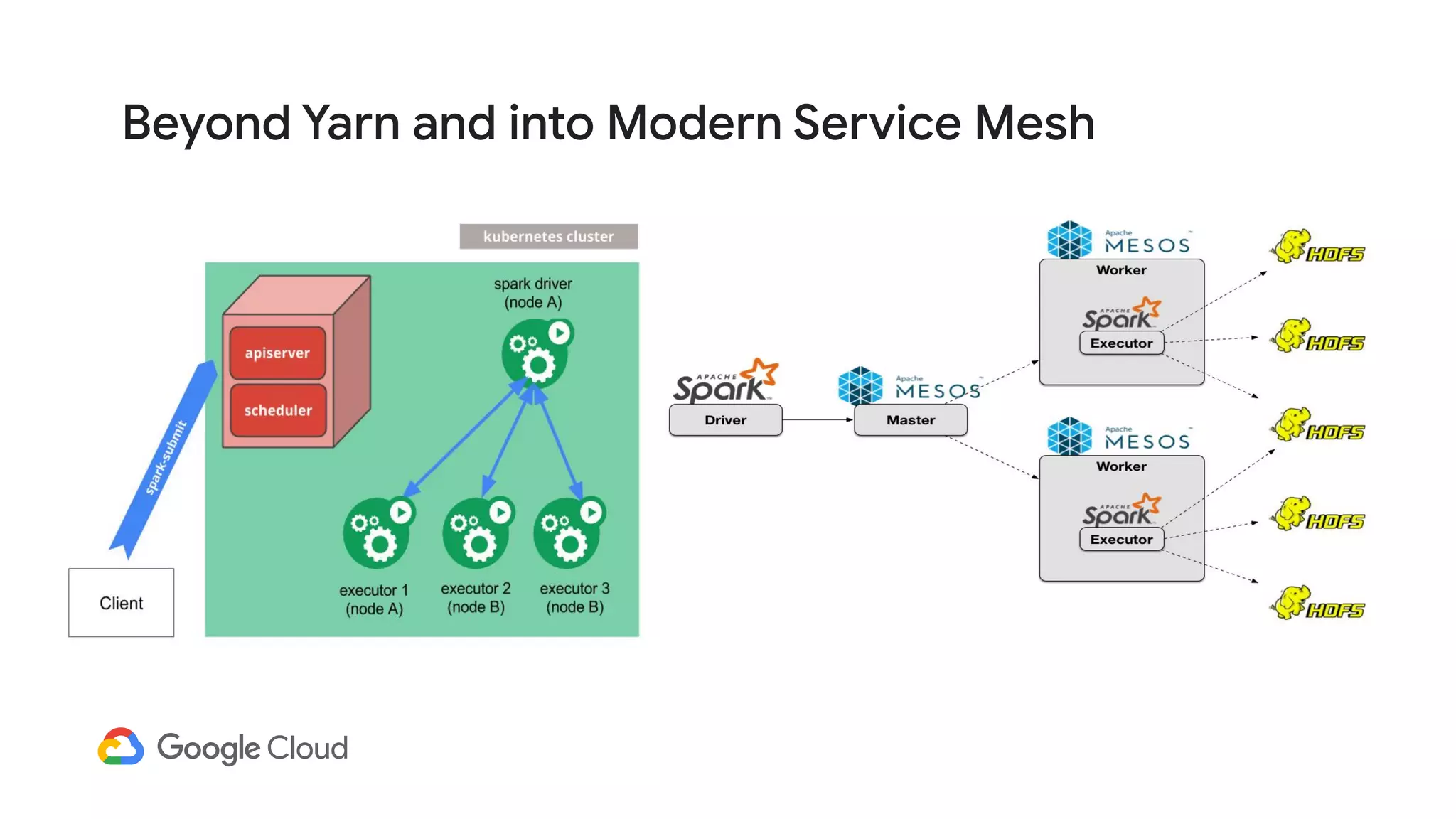
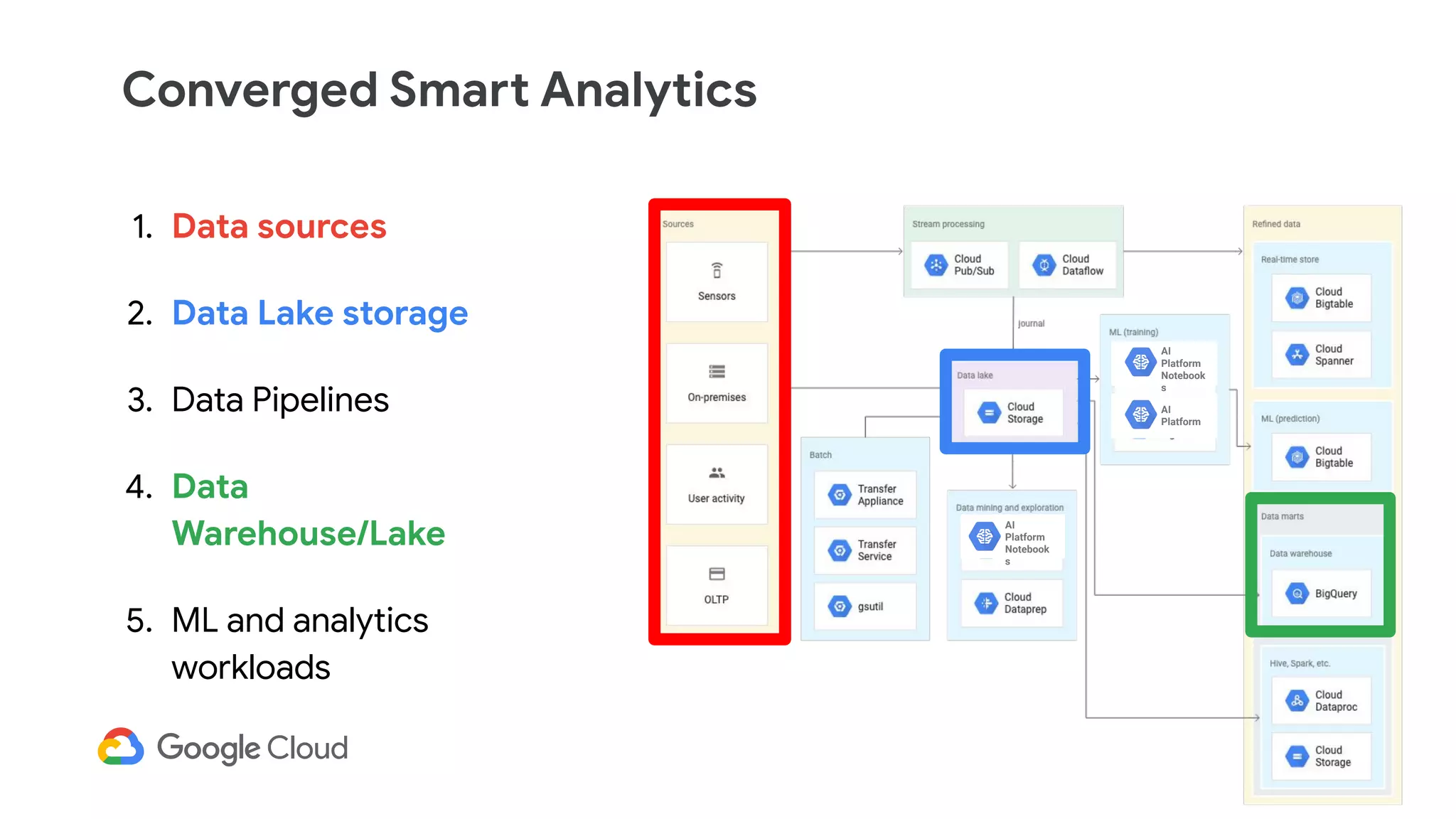
The document discusses the evolution of data management from traditional RDBMS to modern data lakes in the public cloud, highlighting the inefficiencies and challenges of on-premises data lakes. It emphasizes the benefits of shifting to cloud-based solutions, including improved resource management, cost-effectiveness, and enhanced agility for processing unstructured data. Key patterns for utilizing cloud storage and compute separation are outlined, promoting a more simplified and scalable approach to data analytics.