Embed presentation
Downloaded 22 times


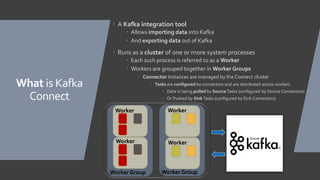




The document introduces Kafka Connect, a tool for integrating data into and out of Kafka, designed to facilitate the management of data across various technologies. It outlines the architecture of Kafka Connect, emphasizing its fault tolerance and scalability, particularly in situations where direct integration is impractical. Additionally, it details the implementation of custom connectors and the setting up of necessary infrastructure to utilize Kafka Connect effectively.






