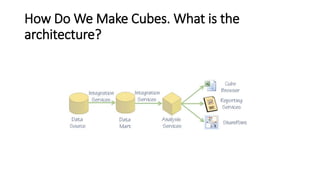
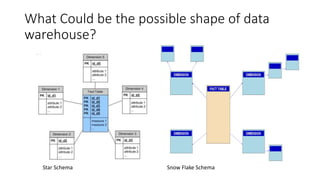
A data cube is a method used for interpreting data efficiently, especially with multiple dimensions for business analysis. It offers advantages over traditional data warehouses, such as improved speed through pre-aggregation, enabling multi-dimensional analysis, and allowing for better data security. The document outlines the structure of data warehouses, including fact and dimension tables, and different approaches for creating dimensional models.