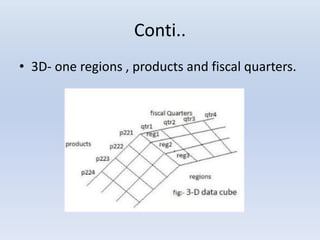
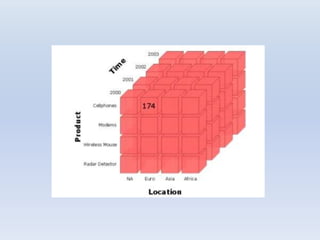
- Multidimensional data modeling (MDDM) was developed for data warehousing and marts. It allows for interactive analysis of large amounts of data to aid decision making.
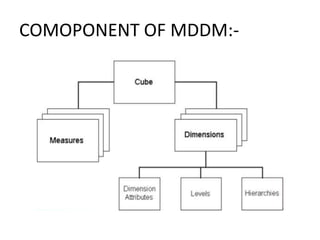
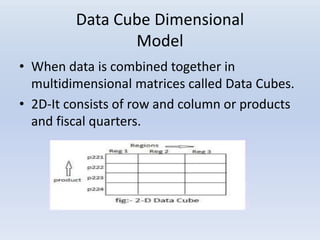
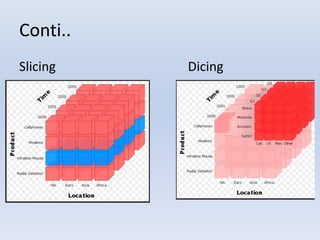
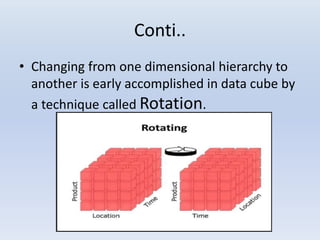
- Dimensions and measures make up data cubes, with dimensions being categories like time and location, and measures being numeric facts. Slicing, dicing, and rotating allow analyzing the data from different angles.
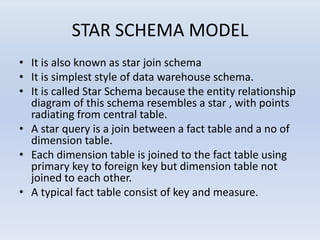
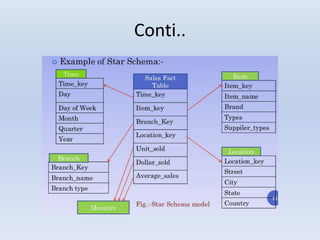
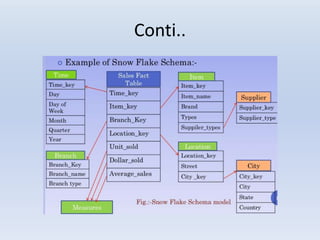
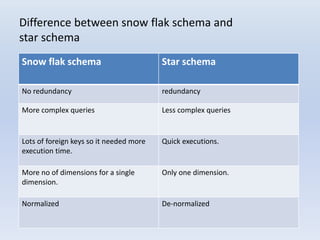
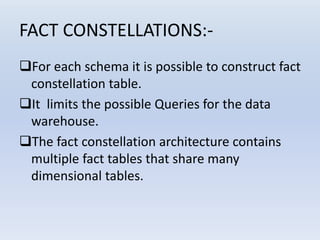
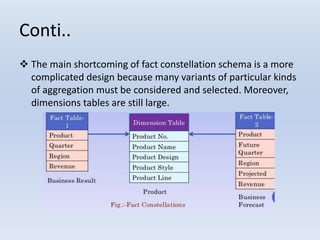
- Star schemas and snowflake schemas are common MDDM structures. Star schemas have a central fact table linked to dimension tables, while snowflake schemas further normalize the dimension tables. Fact constellations link multiple fact tables through shared dimensions.