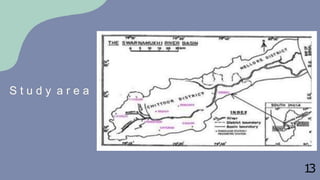
The document presents a dam breach analysis project conducted by a group of students. It discusses analyzing the Kalyani dam located in Andhra Pradesh, India to estimate outputs from a potential dam breach including discharge, flooding routes downstream, and inundation maps. The objectives are to determine outflow hydrographs, estimate breach parameters, route peak discharges, and map inundation levels. Methodologies include breach modeling and flood routing simulations using HEC-RAS software. Input data on dam design, river contours, and rainfall are also described.