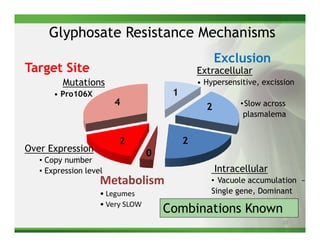
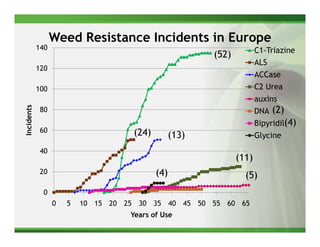
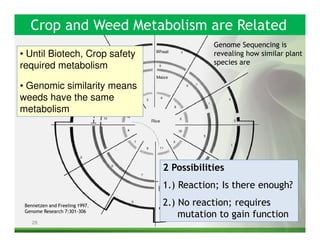
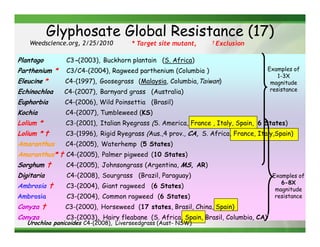
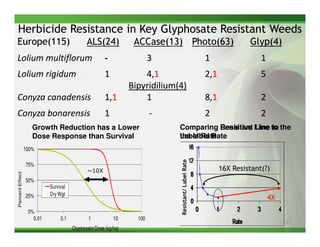
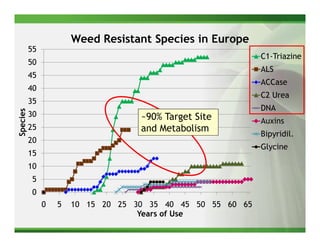
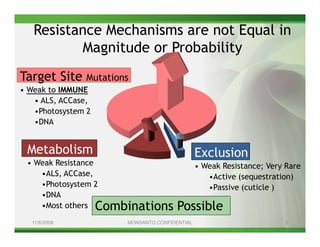
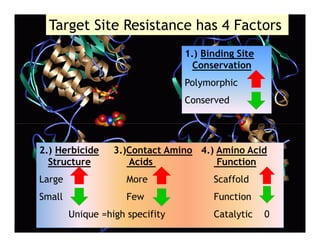
1) Glyphosate resistance has emerged in over 20 weed species worldwide through various mechanisms including target site mutations and increased metabolism.
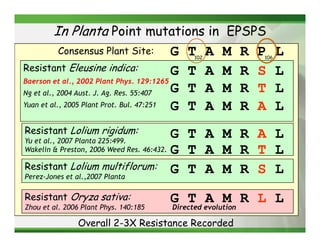
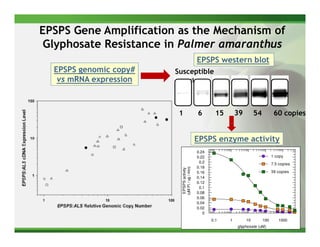
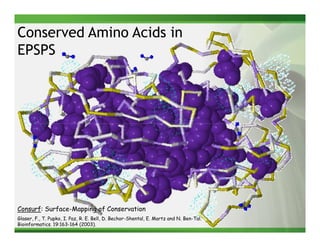
2) Target site mutations in the EPSPS gene have been identified in several glyphosate resistant weed species resulting in 2-3X levels of resistance.
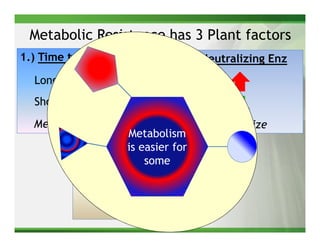
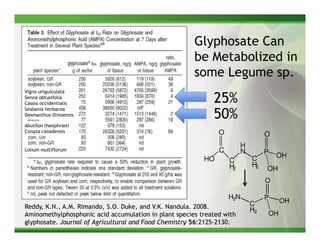
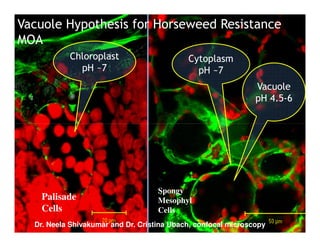
3) Metabolic resistance allows some weed species to break down glyphosate faster through enhanced neutralizing enzyme activity, resulting in weaker resistance.

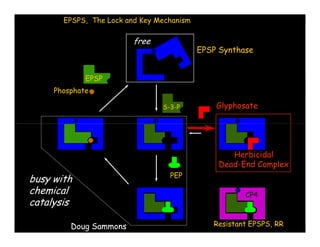
![Glyphosate mimics the Tetrahedral
Intermediate of the reaction.
Schönbrunn et al. 2001, PNAS 98:1376
[EPSPS:Tetrahedral Intermediate] [ EPSPS:S3P:Glyphosate ]
9 complex](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dsammons-100623070918-phpapp02/85/D-Sammons-9-320.jpg)