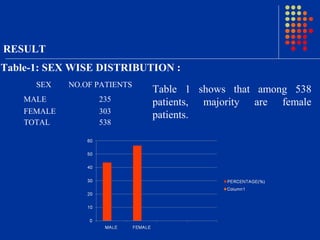
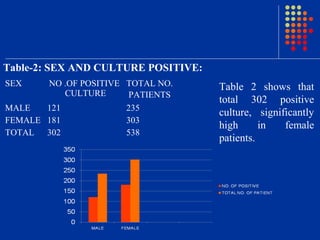
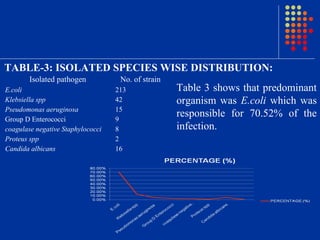
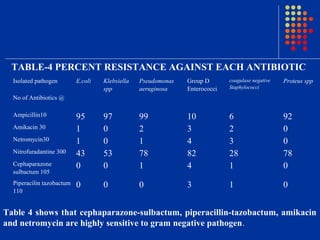
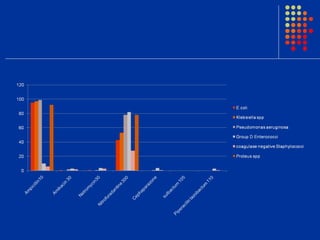
Escherichia coli was the predominant pathogen isolated (70.52%) from the urine cultures of 538 patients with urinary tract infections in Surat, India. Antibiotics like ampicillin showed high resistance rates of over 90% among isolated gram-negative pathogens. However, gram-negative pathogens demonstrated the highest sensitivity to amikacin, netromycin, piperacillin/tazobactum and cefoperazone/sulbactum with resistance rates below 5%. The study highlights the increasing antimicrobial resistance seen with commonly used antibiotics and identifies alternative antibiotic options for empirical therapy of urinary tract infections in the region.

![INTRODUCTION
Urinary tract infection (UTI) is common both in the community and
hospitalized patients.
The widespread use of antimicrobial agents often leads to the
emergence of resistant microorganisms to one or several of them. [1]
Urinary tract infection (UTI) is a broad term that encompasses both
asymptomatic microbial colonization of the urine and symptomatic
infection with microbial invasion and inflammation of urinary tract
structures .](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dpppp-140601020918-phpapp01/85/D-p-ppp-2-320.jpg)