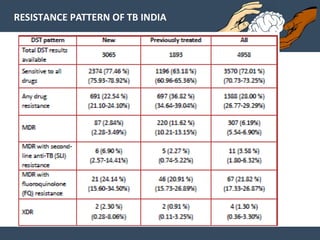
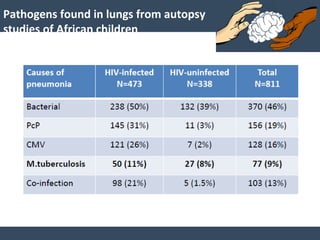
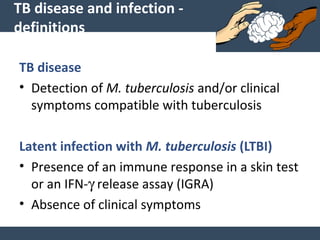
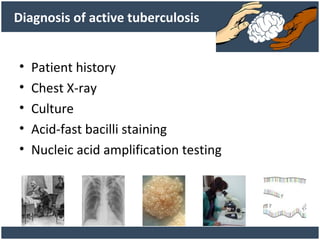
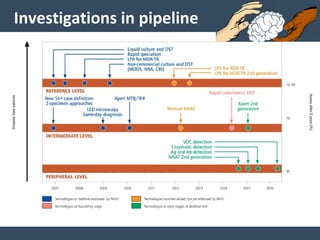
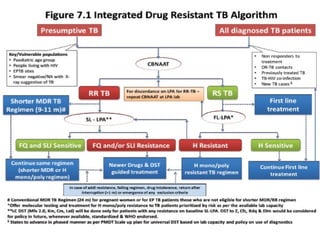
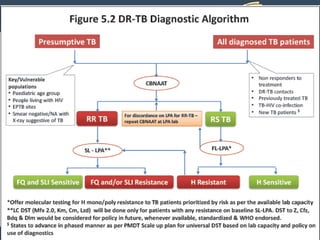
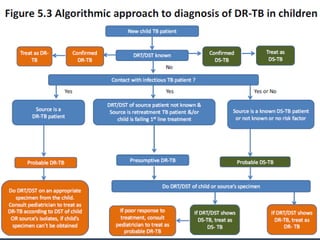
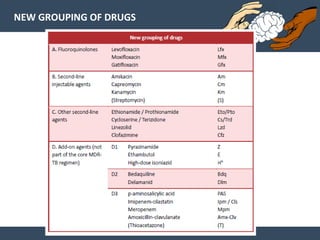
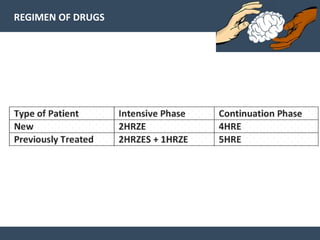
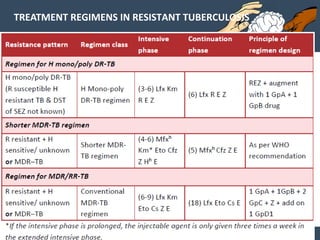
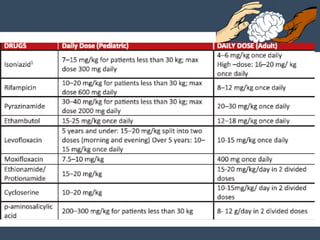
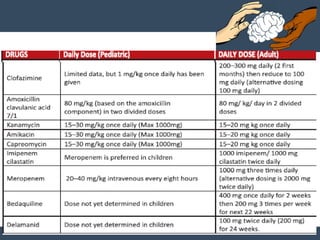
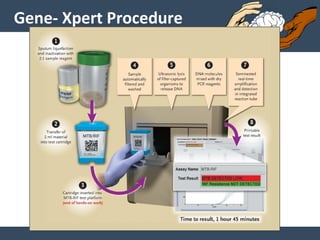
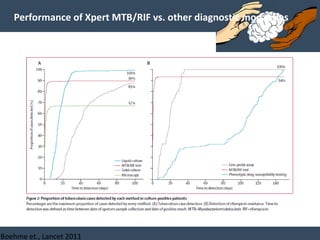
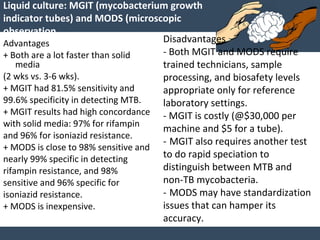
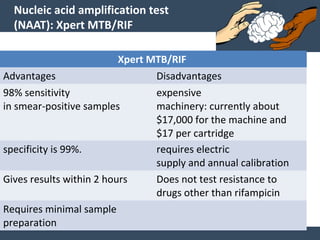
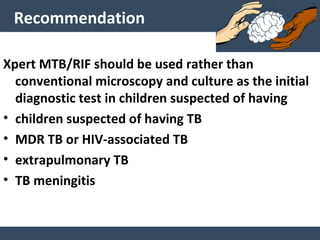
Dr. Amit Vatkar, a pediatric neurologist in Mumbai, discusses recent updates in childhood tuberculosis, highlighting diagnosis methods and treatment regimens for drug-resistant strains. The document outlines definitions of TB disease and latent infection, as well as new diagnostic tools recommended by WHO, such as nucleic acid amplification tests. Key recommendations include the use of Xpert MTB/RIF for diagnosing various forms of TB in children.