Embed presentation
Downloaded 148 times

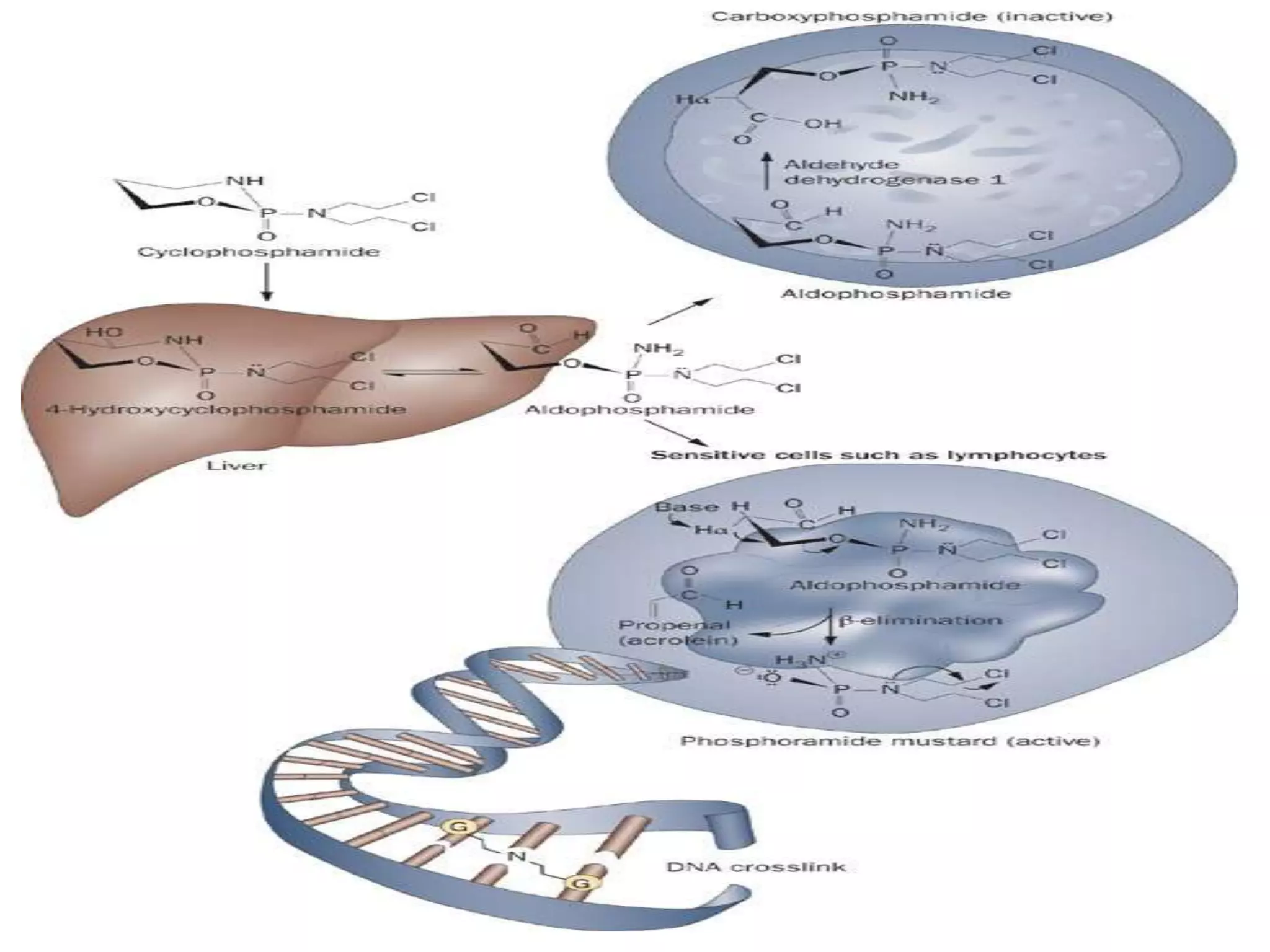
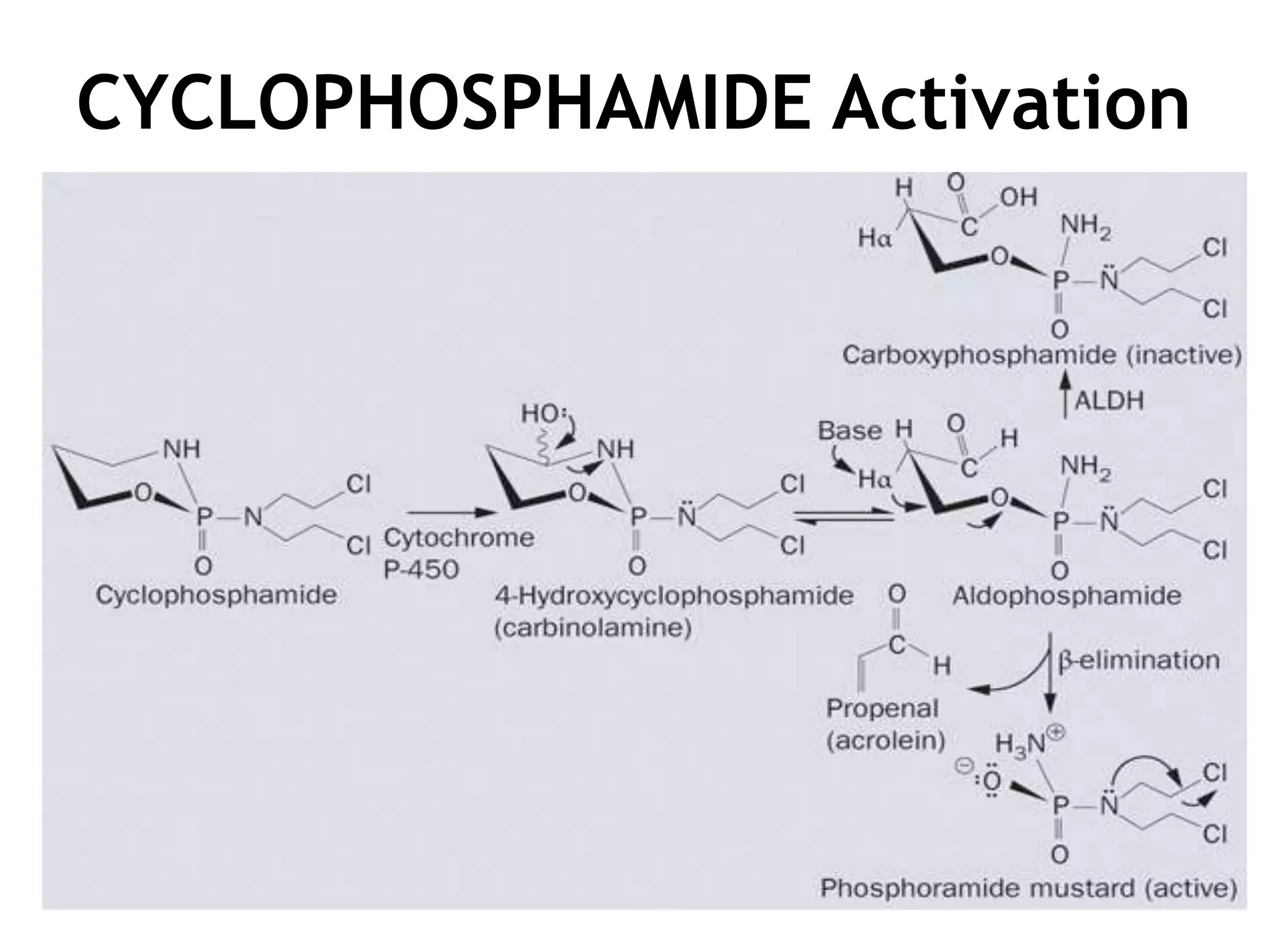
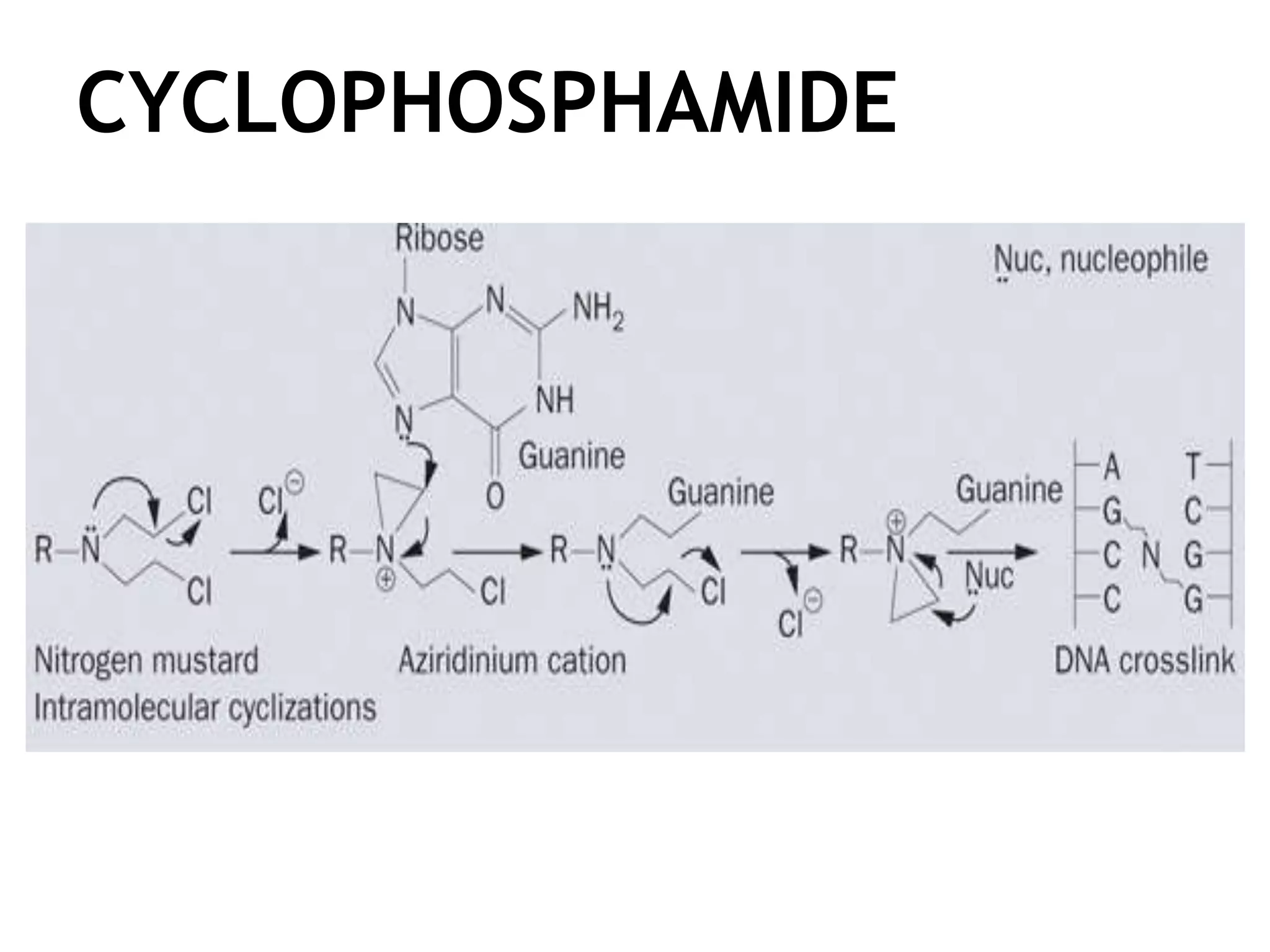
Cyclophosphamide is an alkylating agent used to treat white blood cell cancers and lymphoma. It works by being metabolized into phosphoramide mustard, which adds alkyl groups to DNA, forming crosslinks between and within DNA strands. This leads to DNA damage and ultimately cell death. The expression of genes coding for enzymes involved in cyclophosphamide metabolism, such as cytochrome P450 and ALDH, can affect how sensitive cancer cells are to the drug.






