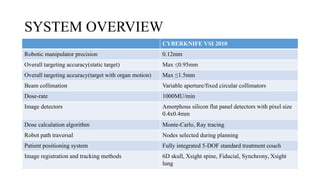
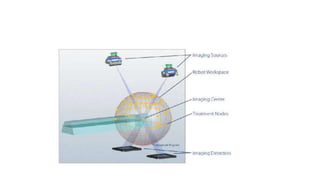
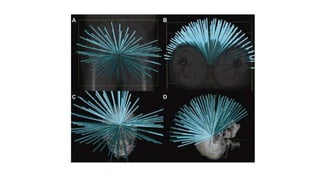
The document provides an overview of the CyberKnife system, a Robotic Radiosurgery platform developed by Accuray Inc. The system utilizes advanced imaging and treatment planning technologies to deliver precise radiation therapy, accommodating complex tumor geometries and patient motion. Key components include a robotic manipulator, adaptive imaging algorithms, and various treatment planning techniques to optimize radiation delivery with minimal patient movement.