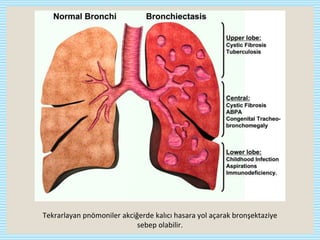
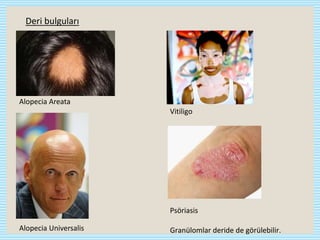
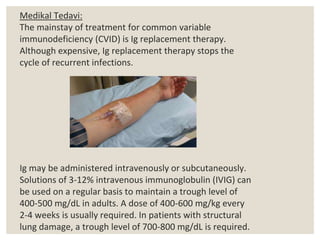
CVID is the most common symptomatic primary immunodeficiency in adults. It is characterized by hypogammaglobulinemia, defective antibody responses, and recurrent infections. It may also be accompanied by autoimmune diseases, granulomatous diseases, and malignancies. Diagnosis involves recurrent infections, low immunoglobulin levels, poor response to vaccines, and exclusion of secondary causes. Treatment consists of lifelong Ig replacement therapy via IV or SC routes to prevent infections, along with treatment of specific infections, complications, and immunosuppressants for autoimmune manifestations. Prognosis depends on severity and organ involvement.