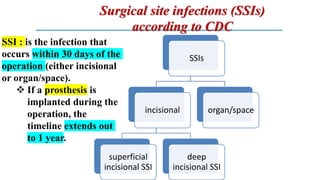
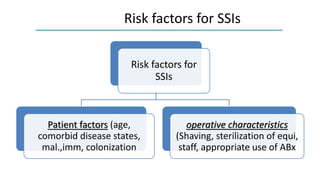
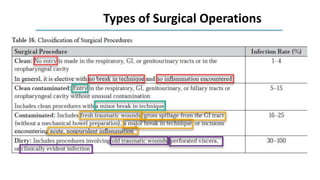
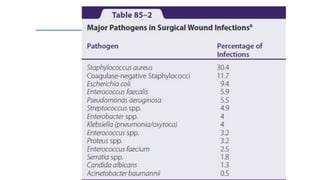
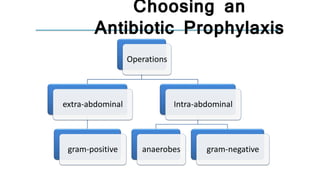
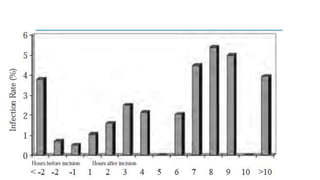
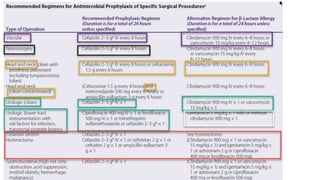
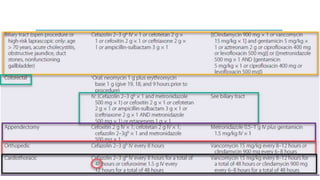
The document discusses antimicrobial prophylaxis in various types of surgeries to prevent surgical site infections (SSIs), which have significant morbidity and mortality rates. It outlines the importance of appropriate antibiotic choice, dosing, timing, and duration for different surgical procedures, emphasizing the differences between prophylaxis and treatment. Additionally, it suggests alternative methods to reduce SSIs, such as glucose control and decolonization strategies.