Curved Mirrors.pdf 111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111
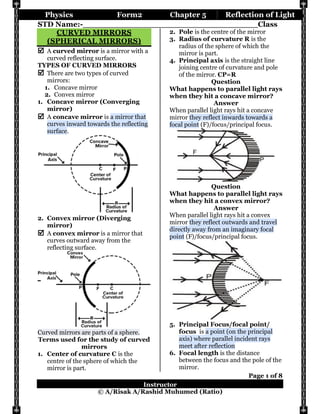
- 1. Physics Form2 Chapter 5 Reflection of Light STD Name:-__________________________________Class Page 1 of 8 Instructor © A/Risak A/Rashid Muhumed (Ratio) CURVED MIRRORS (SPHERICAL MIRRORS) A curved mirror is a mirror with a curved reflecting surface. TYPES OF CURVED MIRRORS There are two types of curved mirrors: 1. Concave mirror 2. Convex mirror 1. Concave mirror (Converging mirror) A concave mirror is a mirror that curves inward towards the reflecting surface. 2. Convex mirror (Diverging mirror) A convex mirror is a mirror that curves outward away from the reflecting surface. Curved mirrors are parts of a sphere. Terms used for the study of curved mirrors 1. Center of curvature C is the centre of the sphere of which the mirror is part. 2. Pole is the centre of the mirror 3. Radius of curvature R is the radius of the sphere of which the mirror is part. 4. Principal axis is the straight line joining centre of curvature and pole of the mirror. CP=R Question What happens to parallel light rays when they hit a concave mirror? Answer When parallel light rays hit a concave mirror they reflect inwards towards a focal point (F)/focus/principal focus. Question What happens to parallel light rays when they hit a convex mirror? Answer When parallel light rays hit a convex mirror they reflect outwards and travel directly away from an imaginary focal point (F)/focus/principal focus. 5. Principal Focus/focal point/ focus is a point (on the principal axis) where parallel incident rays meet after reflection 6. Focal length is the distance between the focus and the pole of the mirror.
- 2. Physics Form2 Chapter 5 Reflection of Light STD Name:-__________________________________Class Page 2 of 8 Instructor © A/Risak A/Rashid Muhumed (Ratio) IMAGES FORMED BY CURVED MIRRORS. 1. Image formed by concave mirror The position, size and the nature of the image formed by the concave mirror depends on the position of the object. 2. Image formed by convex mirror The position, size and the nature of the image formed by the convex mirror do not depend on the position of the object. The image formed by convex mirror is always virtual, upright, diminished and it is formed behind the mirror Drawing Ray Diagram for Curved Mirrors When we are drawing the image formed by curved mirror only two rays form the object are needed, but the following rules must be taken. 1. Rules for Concave mirrors 2. Rules for Convex mirrors 1. The ray of light parallel to the principal axis will be reflected through F. 1. A ray parallel to the principal axis is reflected as if it came from F. 2. The ray of light through F will be reflected parallel to the principal axis. 2. A ray towards F is reflected parallel to the principal axis. 3. The ray of light through C will be reflected back through C. 3. A ray towards C is reflected back along its own path. 4. A ray striking the pole is reflected so that the incident ray and the reflected ray make the same angle with the principle axis. 4. A ray striking the pole is reflected so that the incident ray and the reflected ray make the same angle with the principle axis.
- 3. Physics Form2 Chapter 5 Reflection of Light STD Name:-__________________________________Class Page 3 of 8 Instructor © A/Risak A/Rashid Muhumed (Ratio) DRAWING IMAGES FORMED BY CURVED MIRRORS 1. Images formed by concave mirror Position of the object Nature & size of image 1. When the object is placed at infinity. The image has the following characteristics Nature of image 1. Real 2. Inverted 3. Forms at the focus (At F) Size of image 4. Highly diminished (point sized) 2. When the object is placed beyond the centre of curvature of the mirror. The image formed has the following properties/characteristics Nature of image 1. Real 2. Inverted 3. Between the focus F center of curvature C (B/w F & C) size of image 4. Diminished/reduced 3. When the object is placed exactly at the centre of curvature C. The image formed has the following properties/characteristics Nature of image 1. Real 2. Inverted 3. Forms at the center of curvature C Size of image 4. Same size as the object 4. When the object is placed between the focus and centre of curvature. The image formed has the following properties/characteristics Nature of image 1. Real 2. Inverted 3. Beyond/behind C Size of image 4. Magnified/enlarged
- 4. Physics Form2 Chapter 5 Reflection of Light STD Name:-__________________________________Class Page 4 of 8 Instructor © A/Risak A/Rashid Muhumed (Ratio) 5. When the object is placed exactly at F. The image formed has the following properties/characteristics Nature of image v 1. Real 2. Inverted 3. At infinity Size of image 4. Highly enlarged(magnified) The table below summarizes the characteristics of the images formed by concave mirrors. Object position Image position Nature of image Image size At infinity F Real & inverted Diminished Beyond C b/w C and F Real & inverted Diminished At C At C Real & inverted Same size b/w C and F Beyond C Real & inverted Magnified At F At infinity Real & inverted Magnified b/w F and P Behind mirror Virtual & upright Magnified 2. Images formed by convex mirror
- 5. Physics Form2 Chapter 5 Reflection of Light STD Name:-__________________________________Class Page 5 of 8 Instructor © A/Risak A/Rashid Muhumed (Ratio) Nature of image The image formed by convex mirror has the following properties/characteristics: 1. Virtual 2. Upright 3. Behind the mirror 4. Diminished Mirror Formula/Mirror Equation f distance between F and Pole v distance of image from Pole u distance of object from Pole R distance between centre of curvature and pole. Where Magnification Magnification is the ratio of image distance and object distance. 𝐌𝐚𝐠𝐧𝐢𝐟𝐢𝐜𝐚𝐭𝐢𝐨𝐧 = 𝐝𝐢𝐬𝐭𝐚𝐧𝐜𝐞 𝐨𝐟𝐢𝐦𝐚𝐠𝐞 𝐕 𝐝𝐢𝐬𝐭𝐚𝐧𝐜𝐞 𝐨𝐟𝐨𝐛𝐣𝐞𝐜𝐭 𝐔 𝐌 = 𝐕 𝐔 − − − − − − − (𝟏) Magnification is the ratio of the height of the image to height of the object. 𝐌𝐚𝐠𝐧𝐢𝐟𝐢𝐜𝐚𝐭𝐢𝐨𝐧 = 𝐡𝐞𝐢𝐠𝐡𝐭 𝐨𝐟 𝐢𝐦𝐚𝐠𝐞 𝐡𝐞𝐢𝐠𝐡 𝐭𝐨 𝐟𝐨𝐛𝐣𝐞𝐜𝐭 𝐦 = 𝐡𝐢 𝐡𝐨 − − − − − − − − − (𝟐) From 1 and 2 equation 𝐌 = 𝐕 𝐔 = 𝐡𝐢 𝐡𝐨 𝐍𝐎𝐓𝐄 The +/- Sign Conventions f is + if the mirror is a concave mirror. f is - if the mirror is a convex mirror. di is + if the image is a real image and located on the object's side of the mirror. di is - if the image is a virtual image and located behind the mirror. Worked Examples: 1. Find the distance of the image from a concave mirror of focal length 15cm if the object is 20 cm from the mirror? Find the magnification and describe the nature of the image? Answer f = 15 cm u = 20cm v =? 𝟏 𝐟 = 𝟏 𝐮 + 𝟏 𝐯 𝐯 = 𝐟𝐮 𝐮 − 𝐟 = (𝟐𝟎𝐜𝐦)(𝟏𝟓𝐜𝐦) 𝟐𝟎𝐜𝐦 − 𝟏𝟓𝐜𝐦 = 𝟑𝟎𝟎𝐜𝐦𝟐 𝟔𝐜𝐦 = 𝟔𝟎𝐜𝐦 m = v/u = (60cm)/20cm = 3 So the image is 60cm in front of the mirror and it is real and magnified. 2. Find the distance of the image from a convex mirror of focal length 10 cm if the object is 15 cm from the mirror? Calculate the magnification and describe the nature of the image?
- 6. Physics Form2 Chapter 5 Reflection of Light STD Name:-__________________________________Class Page 6 of 8 Instructor © A/Risak A/Rashid Muhumed (Ratio) Answer f = - 10 cm u = 15cm v =? 𝟏 𝐟 = 𝟏 𝐮 + 𝟏 𝐯 𝐯 = 𝐟𝐮 𝐮 − 𝐟 = (−𝟏𝟎 𝐜𝐦)(𝟏𝟓𝐜𝐦) 𝟏𝟓𝐜𝐦 − (−𝟏𝟎𝐜𝐦) = 𝟏𝟓𝟎𝐜𝐦𝟐 𝟐𝟓𝐜𝐦 = − 𝟔𝐜𝐦 m = v/u = -6cm/15cm = - 0.4 v = - 6cm (the minus sign indicates that the image is virtual) The image is 6cm behind the mirror and it is virtual and diminished. 3. Find the distance of the image from a concave mirror of focal length 10 cm if the object is 5 cm from the mirror? Calculate the magnification and describe the nature of the image? Answer f = 10 cm u = 5cm v =? 𝟏 𝐟 = 𝟏 𝐮 + 𝟏 𝐯 𝐯 = 𝐟𝐮 𝐮 − 𝐟 = (𝟏𝟎𝐜𝐦)(𝟓𝐜𝐦) 𝟓𝐜𝐦 − 𝟏𝟎𝐜𝐦 = 𝟓𝟎𝐜𝐦𝟐 − 𝟓𝐜𝐦 = −𝟏𝟎𝐜𝐦 The image is 5 cm behind the mirror. It is virtual because v is negative and magnified. 4. When an object is placed 20cm from a concave mirror, a real image magnified three times is formed. a) Find the focal length of the mirror? b) Where the object must be placed to give a virtual image magnified three times? a) 𝐦 = 𝐯 𝐮 therefore v = mu = (3) (20cm) = 60cm. 𝐟 = 𝐮𝐯 (𝐯 + 𝐮) = 𝟏𝟐𝟎𝟎𝐜𝐦𝟐 𝟖𝟎𝐜𝐦 = 𝟏𝟓𝐜𝐦 b) m = - 3 Therefore v = - 3u 𝟏 𝐟 = 𝟏 𝐮 + 𝟏 𝐯 𝟏 𝟏𝟓𝐜𝐦 = ( 𝟏 𝐮 ) + ( 𝟏 − 𝟑𝐮 ) then 3u = 30cm and u=10cm. Exercise: 1. A concave mirror of focal length 15cm has an object placed 25cm from it. Find the position (image distance) and the nature of the image? 2. A concave mirror of focal length 15 has an object placed 10cm from it. calculate a) The distance between the image and the mirror? b) The magnification of the image? c) The height of the image if the object is 4cm high? d) Describe the nature of the image? 3. An object 5cm high is placed 30cm in front of a concave mirror. The image is 60cm in front of the mirror. Find a) The focal length of the mirror? b) The magnification? c) The size of the image? APPLICATIONS/USES OF CURVED MIRRORS Concave mirrors are used:- 1. Head lamps of the car 2. Torches (to produce parallel beam of light) 3. Astronomical telescope 4. Tv dishes (To collect Tv signals) 5. Dentists to examine the teeth 6. Projectors Convex mirrors are used:- 1. Rear view mirrors in a car 2. To provide a wide view ====END===
- 7. Physics Form2 Chapter 5 Reflection of Light STD Name:-__________________________________Class Page 7 of 8 Instructor © A/Risak A/Rashid Muhumed (Ratio) Section Review Questions 1. What are the two types of curved mirrors? A. Concave and convex B. Convex and flat C. Concave and plane D. Flat and spherical 2. Which type of mirror curves inward towards the reflecting surface? A. Convex B. Plane C. Concave D. Spherical 3. When parallel light rays hit a concave mirror, they reflect towards: A. The center of curvature B. The pole C. A focal point D. Away from the mirror 4. The point where parallel incident rays meet after reflection in a concave mirror is called: A. Vertex B. Focus C. Center of curvature D. Pole 5. What type of image is formed by a convex mirror? A. Real and inverted B. Virtual and inverted C. Real and upright D. Virtual and upright 6. Which mirror type always forms an image that is virtual, upright, and diminished? A. Concave B. Plane C. Convex D. Spherical 7. What is the distance between the focus and the pole of a mirror called? A. Radius of curvature B. Focal length C. Magnification D. Image distance 8. The mirror formula relates the focal length, object distance, and: A. Magnification B. Image distance C. Radius of curvature D. Height of the mirror 9. What is the formula for magnification using image distance and object distance? A. M = V/U B. M = H/V C. M = F/U D. M = R/U 10.When an object is placed between the focus and the center of curvature of a concave mirror, the image formed is: A. Virtual and magnified B. Real and magnified C. Real and inverted D. Virtual and diminished 11.Which mirror type is commonly used in rear-view mirrors in cars? A. Concave B. Convex C. Plane D. Spherical 12.The position, size, and nature of the image formed by a convex mirror: A. Depend on the position of the object B. Do not depend on the position of the object C. Are always real and inverted D. Are always virtual and upright 13.In a concave mirror, when an object is placed at the center of curvature, the image formed is: A. Virtual and magnified B. Real and magnified C. Real and inverted D. Virtual and diminished 14.What type of mirror is used in headlamps of cars? A. Convex B. Plane C. Concave D. Spherical 15.Which mirror type is used in telescopes to collect light? A. Convex
- 8. Physics Form2 Chapter 5 Reflection of Light STD Name:-__________________________________Class Page 8 of 8 Instructor © A/Risak A/Rashid Muhumed (Ratio) B. Plane C. Concave D. Spherical 16.When an object is placed at infinity from a concave mirror, the image formed is: A. Virtual and enlarged B. Real and enlarged C. Real and inverted D. Virtual and diminished 17.What is the nature of the image formed by a convex mirror? A. Real and inverted B. Virtual and upright C. Virtual and inverted D. Real and upright 18.The mirror formula is applicable to: A. Concave mirrors only B. Convex mirrors only C. Both concave and convex mirrors D. Plane mirrors only 19.What is the nature of the image formed by a concave mirror when the object is placed beyond the center of curvature? A. Virtual and inverted B. Real and inverted C. Real and upright D. Virtual and upright 20.The principal focus of a concave mirror is located: A. Between the pole and the center of curvature B. At the center of curvature C. Beyond the center of curvature D. At the pole 21.Which mirror type forms an image that is always virtual, upright, and diminished? A. Concave B. Convex C. Plane D. Spherical 22.What happens to parallel light rays when they hit a convex mirror? A. They converge at a focal point B. They diverge and spread out C. They reflect back parallel to the principal axis D. They reflect towards the center of curvature 23.Which mirror type is commonly used in projectors? A. Concave B. Convex C. Plane D. Spherical 24.The distance between the focus and the pole of a mirror is called: A. Focal length B. Radius of curvature C. Image distance D. Magnification 25.What happens to light rays when they hit a concave mirror through the center of curvature? A. They reflect parallel to the principal axis B. They converge at a focal point C. They reflect back along their own path D. They spread out and diverge "Mastering Curved Mirrors: MCQs Directly from Your Notes Await!" These MCQs are directly drawn from your notes on curved mirrors. Read your notes thoroughly and tackle the questions with confidence. Your understanding of the material will be reflected in your answers. Good luck!" Warm regards, [A/Risak A/Rashid Mohumed] ====END=== Best regards, YOUR SUCCESS IS OUR GOAL.