The document discusses concepts related to lenses including:
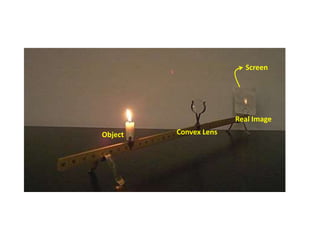
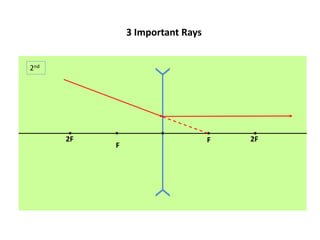
1) Convex and concave lenses form real or virtual images depending on whether the light rays converge or diverge after passing through the lens.
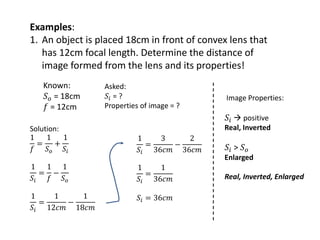
2) Important lens formula relates the focal length, object distance, and image distance.
3) Properties of images formed by convex and concave lenses such as magnification, orientation, and size are determined using the lens formula and relationships between object and image distances.