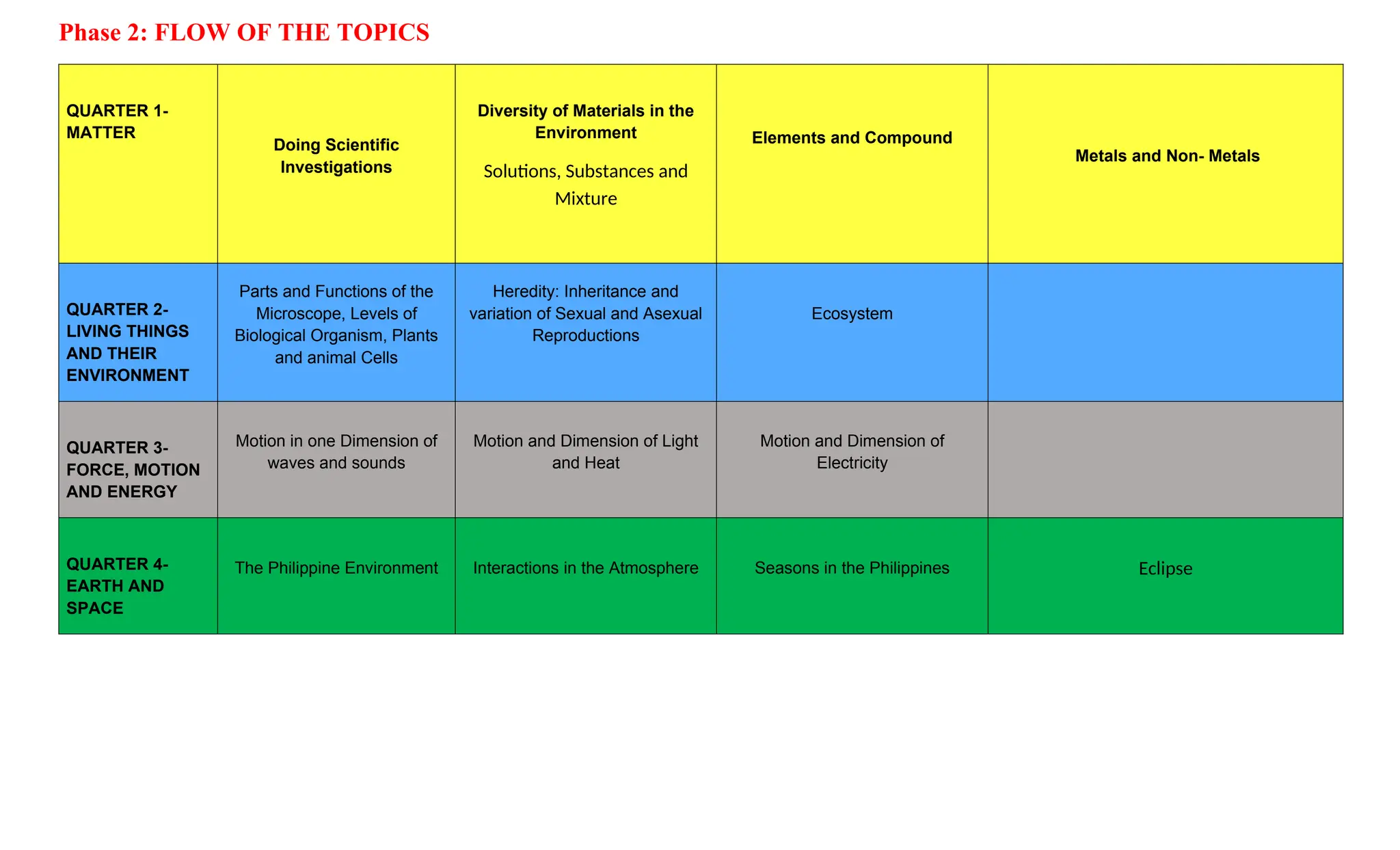
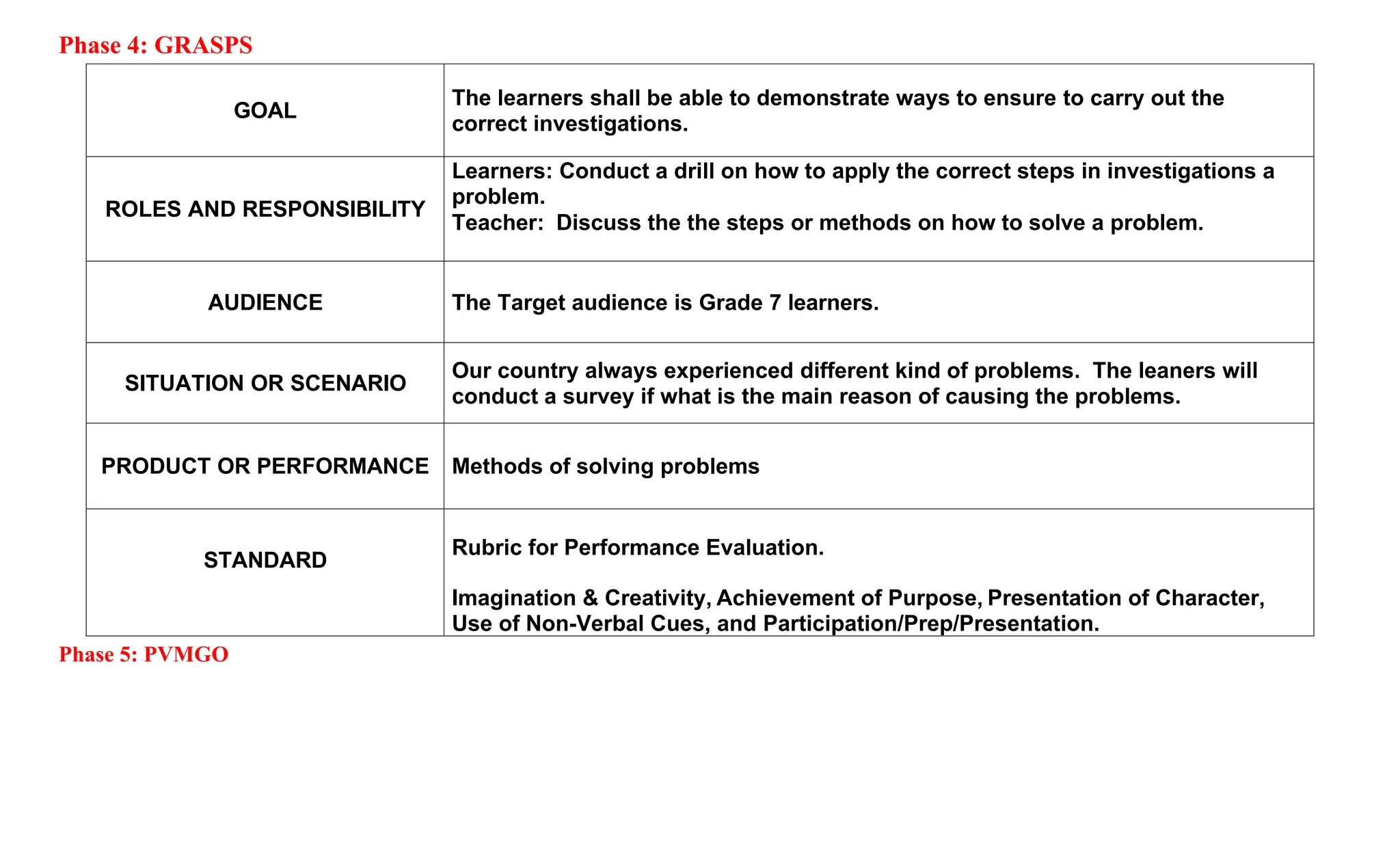
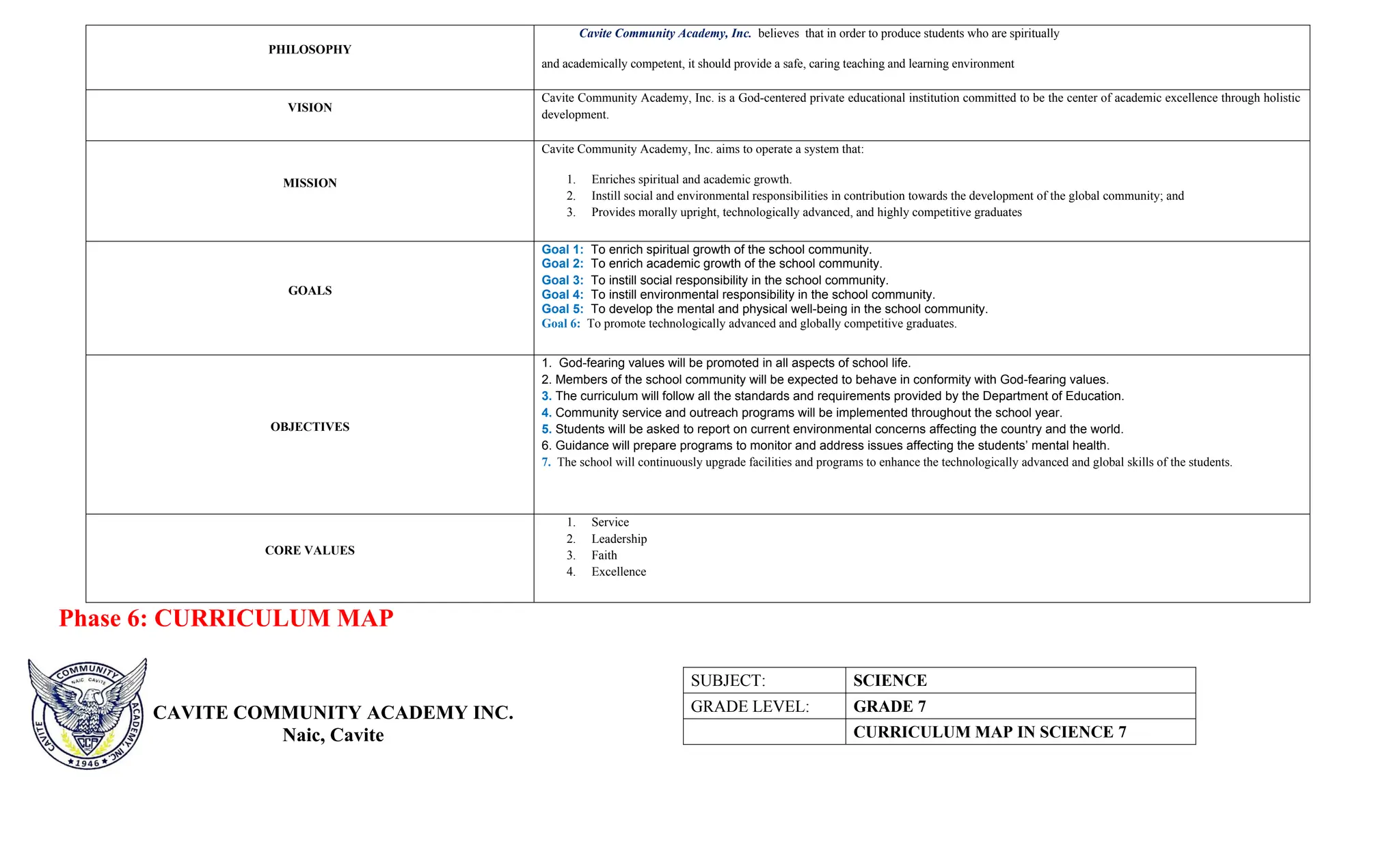
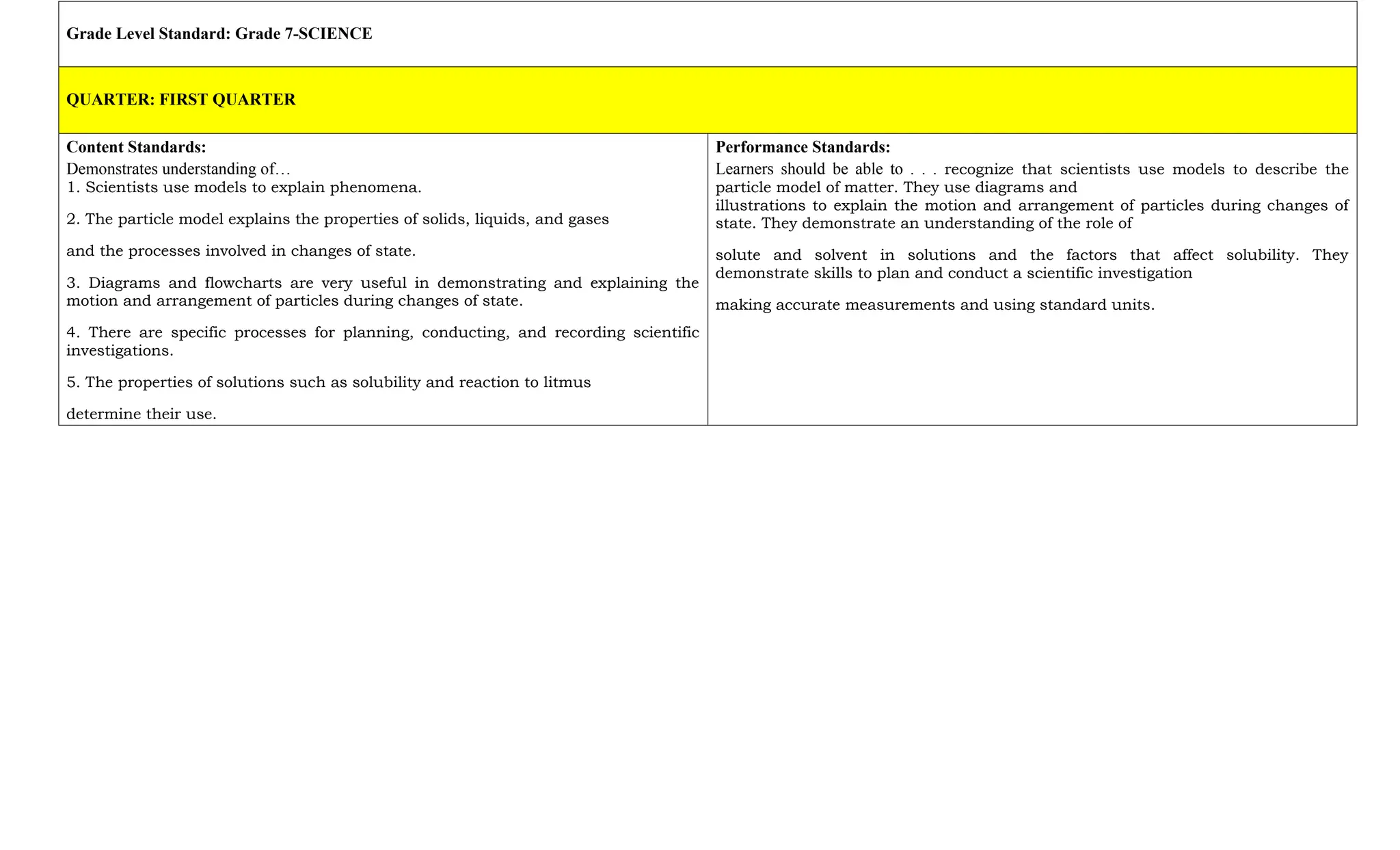
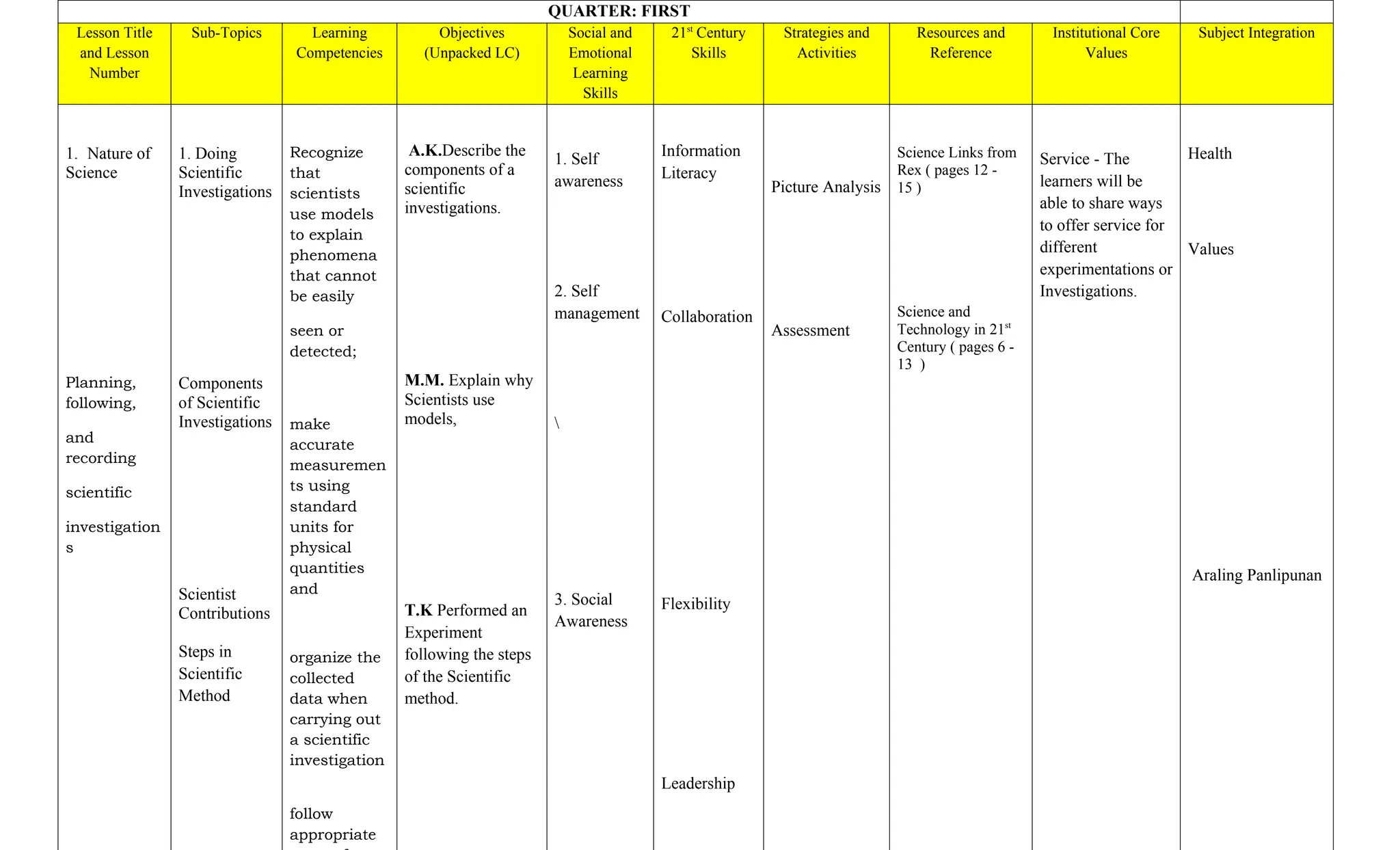
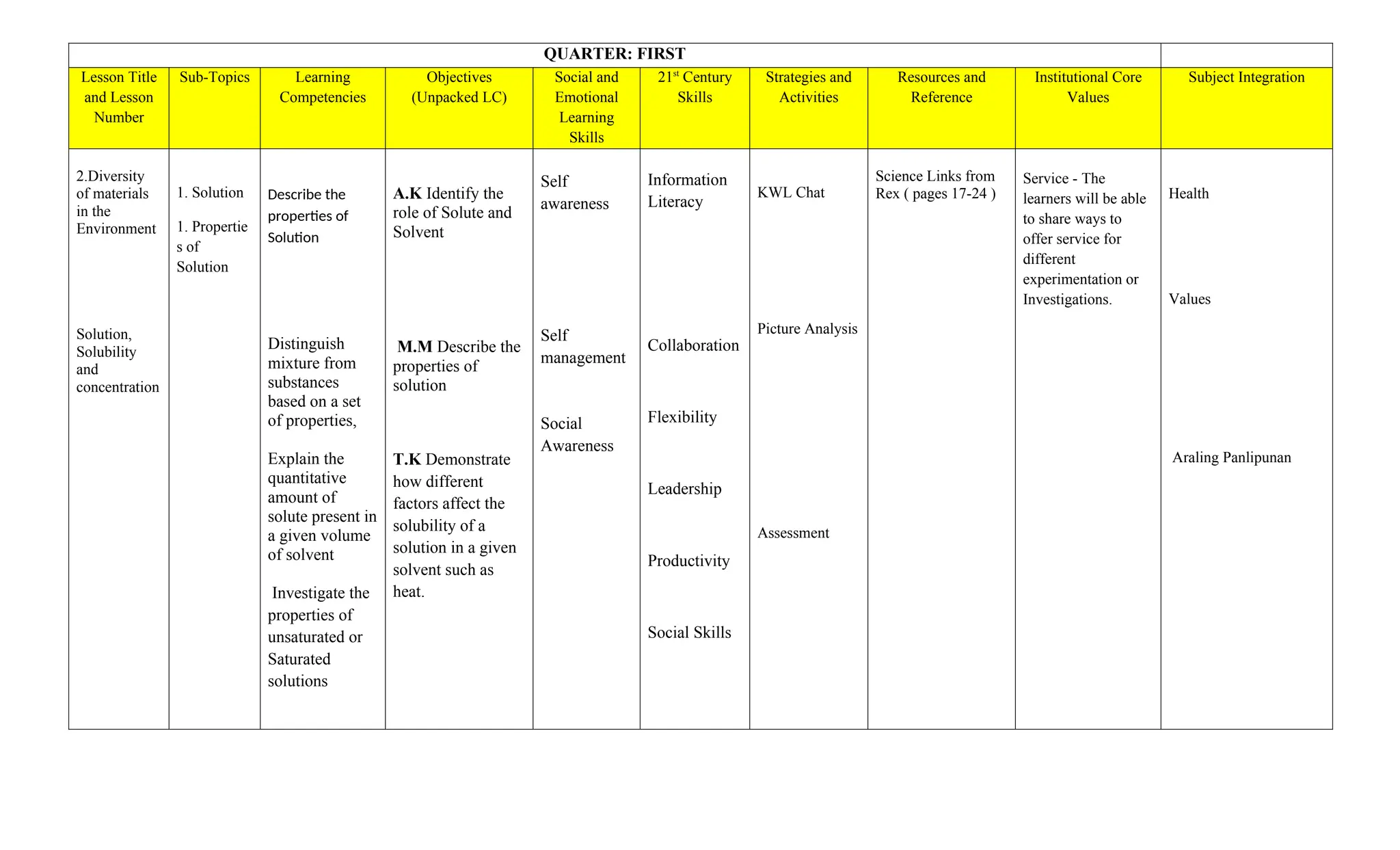
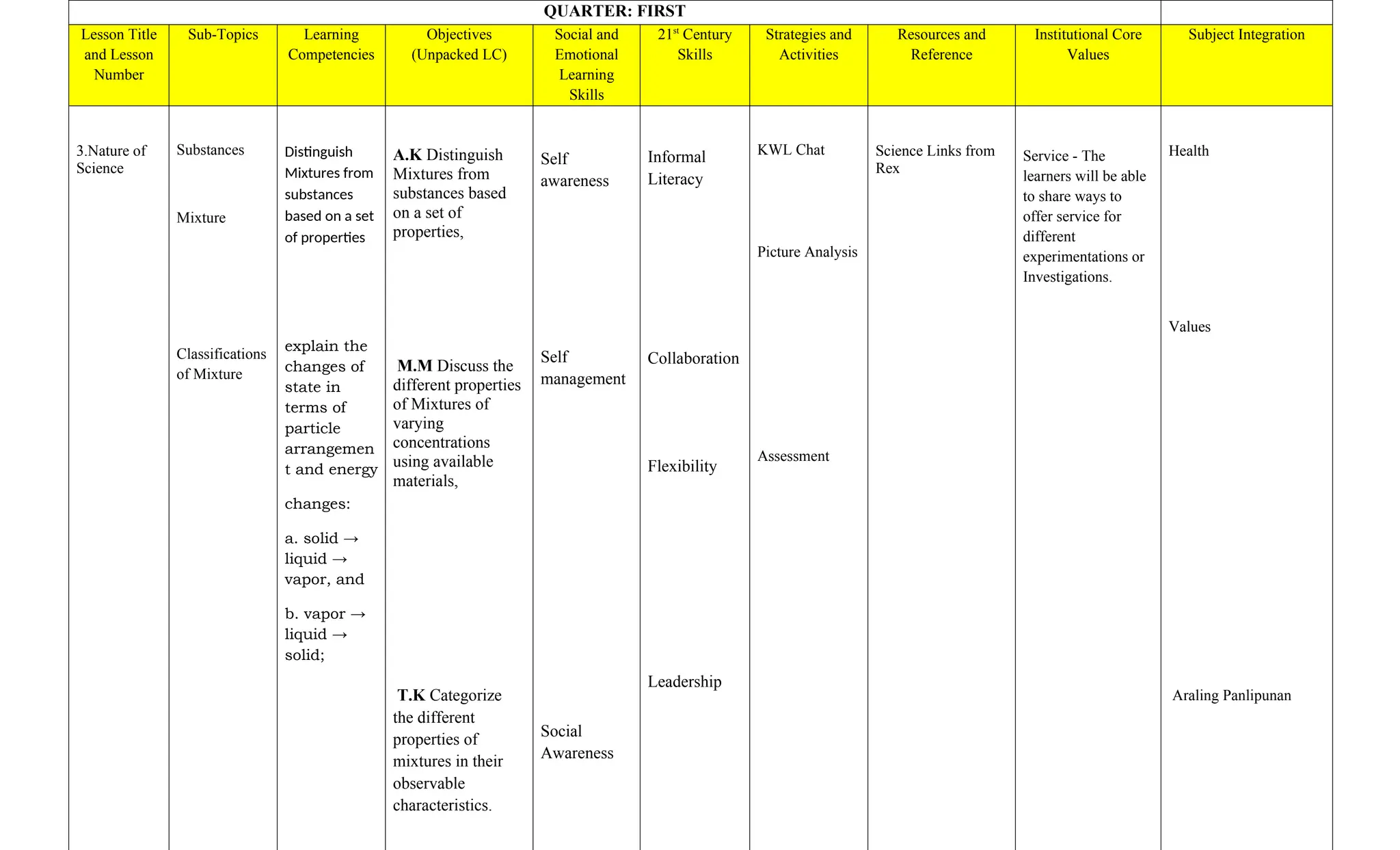
The document is a curriculum map for Grade 7 Science at Cavite Community Academy, emphasizing holistic development and academic excellence. It outlines various topics for the academic year, including scientific investigations, the particle theory of matter, living organisms, energy, and environmental issues, along with specific performance tasks for each quarter. The academy aims to cultivate spiritual, academic, social, and environmental responsibility among students while preparing them for modern technological challenges.